In today’s digital landscape, understanding the types of attack is crucial for safeguarding your online presence. Cyber threats are evolving rapidly, and knowing what you’re up against can make all the difference in protecting your data and privacy. Have you ever wondered how hackers exploit vulnerabilities?
This article dives into various types of attacks that target individuals and organizations alike. From phishing scams to ransomware, each method has its own tactics and impacts. By familiarizing yourself with these threats, you’ll be better equipped to defend against them. Get ready to explore real-world examples that illustrate how these attacks operate and what you can do to stay safe in an increasingly hostile environment.
Overview of Types of Attack
Understanding the various types of attacks is essential for safeguarding your digital assets. Cyber threats continue to evolve, with hackers employing different methods to exploit vulnerabilities. Here are some common types:
- Phishing Attacks: These involve deceptive emails that appear legitimate, tricking you into providing sensitive information like passwords or credit card numbers.
- Ransomware: This malicious software encrypts your files and demands payment for their release. It’s crucial to have backups to mitigate this risk.
- DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service): Attackers overwhelm a website with traffic, causing it to crash. This can disrupt services and harm reputations.
- SQL Injection: Hackers manipulate backend databases through insecure web applications. Proper validation can help prevent these attacks.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM): In this scenario, attackers intercept communications between two parties. Using encrypted connections helps secure data from interception.
Recognizing these attack types empowers you to implement effective defense strategies against cyber threats. By staying informed and vigilant, you enhance your online safety significantly.
Common Types of Attack
Understanding various types of attacks helps you recognize and mitigate risks. Here are some common categories:
Physical Attacks
Physical attacks involve direct interaction with hardware or facilities. They can disrupt operations significantly. Examples include:
- Theft of devices: Laptops or servers stolen from offices can lead to data breaches.
- Vandalism: Damage to physical resources can cripple business operations.
- Unauthorized access: Intruders gaining entry into secure areas may compromise sensitive information.
Taking security measures, like surveillance cameras and access controls, minimizes the risk of these attacks.
Cyber Attacks
Cyber attacks target digital assets through various methods. They exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks. Common examples include:
- Phishing scams: Fraudulent emails trick users into revealing personal information.
- Ransomware: Malicious software locks files until a ransom is paid.
- DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service): Overloading servers with traffic causes downtime for websites.
Staying updated on security protocols can help defend against these threats effectively.
Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering relies on manipulating individuals to gain confidential information. This approach targets human psychology rather than technical flaws. Notable examples are:
- Pretexting: An attacker pretends to be someone trustworthy to extract sensitive data.
- Baiting: Offering free items convinces victims to download malware unknowingly.
- Tailgating: Following authorized personnel into secure areas allows unauthorized access.
Training employees on recognizing social engineering tactics enhances overall security awareness.
Analyzing Attack Vectors
Understanding attack vectors is crucial for strengthening security measures. These vectors represent the paths that cybercriminals use to exploit system vulnerabilities. By analyzing these vectors, you can better defend against potential threats.
Network Attacks
Network attacks target your organization’s infrastructure, aiming to disrupt services or steal data. Common examples include:
- DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service): Attackers flood a network with excessive traffic, crippling services.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM): Cybercriminals intercept communication between two parties to steal sensitive information.
- Packet Sniffing: Hackers capture data packets traveling over a network, gaining access to unencrypted data.
Recognizing these tactics helps you implement stronger defenses and reduce risks.
Application Attacks
Application attacks focus on exploiting software vulnerabilities. They often lead to unauthorized access or data breaches. Key types include:
- SQL Injection: Attackers inject malicious SQL queries into input fields, manipulating databases and accessing sensitive information.
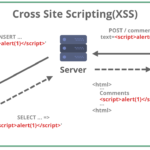
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Cybercriminals insert scripts into web applications, targeting users’ browsers and stealing their cookies or session tokens.
- Remote Code Execution (RCE): Exploiting flaws in applications allows attackers to execute arbitrary code on your server.
By understanding these application attack methods, you enhance your ability to protect valuable assets effectively.
Preventive Measures
Effective preventive measures significantly reduce the risk of cyber attacks. Implementing these strategies enhances your security posture and protects your digital assets.
Security Protocols
Establishing strong Security Protocols is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information. Examples include:
- Firewalls: These act as barriers between trusted and untrusted networks, preventing unauthorized access.
- Encryption: Use encryption technologies to protect data in transit and at rest, making it unreadable without proper authorization.
- Regular Updates: Keep software updated to patch vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit.
Incorporating multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an additional layer of protection by requiring more than one form of verification before granting access.
Employee Training
Investing in Employee Training ensures that your team recognizes potential threats. Key areas to focus on include:
- Phishing Awareness: Train employees to identify suspicious emails and links, reducing the likelihood of successful phishing attempts.
- Social Engineering Tactics: Educate staff on common tactics used by attackers, like pretexting or baiting.
- Incident Response Procedures: Provide clear guidelines on how employees should respond if they suspect a breach or encounter a suspicious activity.
Engaging employees through regular training sessions reinforces their understanding of security practices, fostering a culture of vigilance within your organization.