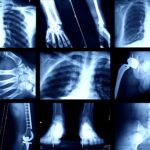
Imagine stepping into a world where invisible rays unlock secrets about your health. X-rays uses extend far beyond just diagnosing broken bones; they play a crucial role in modern medicine and various industries. From detecting cavities in dental care to ensuring safety in airport security, X-rays are everywhere, making them an essential tool you might not fully appreciate.
In this article, you’ll discover the diverse applications of X-rays that impact daily life. Whether you’re curious about how they aid in cancer treatment or their function in manufacturing quality control, understanding these uses can enhance your knowledge of this powerful technology. Ready to explore the fascinating ways X-rays shape our world? Let’s dive into their remarkable capabilities and uncover how they continue to transform healthcare and beyond.
Overview Of X-Rays
X-rays play a crucial role in various fields, not just in medical diagnostics. They provide valuable insights that enhance safety and efficiency.
In healthcare, X-rays help detect issues such as fractures, infections, and tumors. For instance, dental X-rays identify cavities or impacted teeth early on.
In airport security, X-rays scan luggage to reveal hidden items like weapons or explosives. This process enhances passenger safety significantly.
In cancer treatment, radiation therapy uses targeted X-rays to destroy malignant cells while sparing healthy tissue. The precision of this technique improves patient outcomes.
In manufacturing quality control, X-rays inspect materials for defects without causing damage. Inspectors ensure the integrity of welds and structures by identifying flaws that may compromise safety.
X-ray technology continues to advance, expanding its applications across industries and improving overall effectiveness in numerous processes.
Medical Applications Of X-Rays
X-rays play a crucial role in modern medicine, providing insights that lead to effective diagnosis and treatment. Their applications range from identifying injuries to guiding therapeutic procedures.
Diagnostic Imaging
X-rays are essential for diagnostic imaging, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize internal structures. Common examples include chest X-rays, which diagnose pneumonia or heart failure. Dental X-rays reveal cavities and assess the health of teeth and surrounding bone. Moreover, CT scans use multiple X-ray images to create detailed cross-sectional views of organs, aiding in detecting tumors or internal bleeding.
- Chest X-rays: Identify lung infections.
- Dental X-rays: Detect tooth decay.
- CT scans: Provide comprehensive organ assessment.
Therapeutic Uses
In addition to diagnostics, X-rays have significant therapeutic uses. Radiation therapy employs targeted X-ray beams to treat cancer effectively. This method destroys malignant cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue. Interventional radiology utilizes fluoroscopy—an advanced form of real-time imaging—to guide catheters during procedures like angioplasty or biopsies.
- Radiation therapy: Treats various cancers.
- Fluoroscopy: Aids minimally invasive surgeries.
- Barium swallow studies: Examine esophageal issues through live imaging.
Each application underscores the versatility of X-ray technology in enhancing patient care across the medical field.
Industrial Applications Of X-Rays
X-rays play a vital role in various industrial applications, significantly enhancing safety and efficiency in multiple sectors. Their ability to penetrate materials makes them invaluable for inspecting, analyzing, and ensuring the quality of products.
Nondestructive Testing
Nondestructive testing (NDT) utilizes X-rays to examine structures without causing damage. This method allows you to identify flaws like cracks or voids within components such as:
- Welds: X-rays reveal internal defects that could compromise structural integrity.
- Pipelines: Inspection helps detect corrosion or other issues before they lead to leaks.
- Aerospace parts: Ensures the reliability of critical components by identifying imperfections.
This approach not only saves time but also reduces costs associated with repairs and replacements.
Material Analysis
X-ray technology is essential for material analysis, providing insights into composition and properties. You can analyze various materials using techniques like X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Here are some examples:
- Metals: Determine alloy compositions for quality control.
- Minerals: Analyze mineral content in geological samples.
- Plastics: Assess fillers or additives used in manufacturing processes.
These analyses support industries ranging from mining to electronics, helping ensure product standards are met.
Research Applications Of X-Rays
X-rays play a critical role in various research fields, providing insights that enhance understanding and innovation. Their applications extend beyond diagnostics into structural biology and material science.
Structural Biology
In structural biology, X-rays help determine the three-dimensional structures of biological macromolecules like proteins and DNA. For example, X-ray crystallography enables researchers to analyze how these molecules interact with each other. This method has led to significant discoveries, such as understanding enzyme mechanisms or drug interactions.
Material Science
In material science, X-rays assist in examining the properties and structures of materials at a microscopic level. For instance, X-ray diffraction provides information about crystal structures, helping scientists identify defects or phase transitions in metals and ceramics. Additionally, techniques like X-ray fluorescence aid in determining elemental compositions of materials, which is crucial for quality control in manufacturing processes.