Every great piece of writing starts with a solid foundation, and that’s where writing structures come into play. Whether you’re crafting an essay, a novel, or even a blog post, understanding the right structure can transform your ideas into compelling narratives. Have you ever wondered why some articles grab your attention while others fall flat?
Understanding Writing Structures
Writing structures form the backbone of effective communication. They guide readers through your content, ensuring clarity and engagement. Here are key examples of common writing structures:
1. The Five-Paragraph Essay
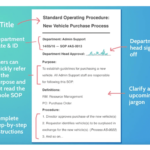
The five-paragraph essay is a classic structure often used in academic writing. It consists of:
- An introduction with a thesis statement
- Three body paragraphs, each presenting a supporting point
- A conclusion that summarizes the main ideas
This format helps maintain focus and coherence.
2. Narrative Structure
Narrative structure involves storytelling elements to engage readers emotionally. Key components include:
- Exposition: Setting the scene and introducing characters
- Rising Action: Building tension through conflict
- Climax: The turning point of the story
- Falling Action: Events leading towards resolution
- Resolution: Conclusion where conflicts resolve
This approach captivates audiences by creating an emotional connection.
3. Problem-Solution Format
Using a problem-solution format effectively addresses issues while proposing solutions. This structure includes:
- Identifying a specific problem
- Discussing its implications
- Presenting viable solutions
By clearly outlining these elements, you can persuade your readers to take action.
4. Chronological Order
Chronological order presents information in time sequence, making it easier for readers to follow events or processes. For instance:
- Introduction of the topic.
- Timeline of key events or steps.
- Final outcomes or conclusions drawn from those events.
This method works well for historical narratives or process descriptions.
5. Comparative Structure
A comparative structure highlights similarities and differences between two or more subjects, which might be useful in persuasive writing or analysis:
- Subject A characteristics
- Subject B characteristics
- Similarities between both subjects
- Differences noted
Such clarity helps readers understand complex topics better.
Understanding these writing structures equips you with tools to craft compelling content across various formats, enhancing readability and engagement throughout your work.
Types of Writing Structures
Writing structures play a crucial role in organizing content effectively. Here are some key types of writing structures you can use.
Narrative Structure
Narrative structure focuses on storytelling. It includes elements like characters, settings, and plots that engage readers emotionally. For example, you might start with an introduction to the main character’s dilemma, followed by rising action, climax, and resolution. This structure captivates audiences by creating a relatable experience.
Descriptive Structure
Descriptive structure emphasizes vivid details. It paints pictures with words to immerse readers in the scene or subject being discussed. You could describe a location using sensory details such as sights, sounds, and smells. For instance:
- Sight: The vibrant colors of the sunset.
- Sound: The soothing rustle of leaves.
- Smell: The fresh aroma of blooming flowers.
This technique enhances reader engagement through rich imagery.
Expository Structure
Expository structure informs or explains concepts clearly. It often uses facts and examples to convey information logically. You might organize your content into sections or subsections for clarity:
- Introduction to the topic
- Key points outlined
- Supporting evidence provided
This method is effective for academic papers and informative articles where clarity is paramount.
Persuasive Structure
Persuasive structure aims to convince readers of a particular viewpoint. It presents arguments supported by evidence and appeals to emotions or logic. Typically organized as follows:
- Introduction: State your position.
- Body paragraphs: Present arguments with supporting data.
- Conclusion: Summarize points and reinforce your stance.
Using this format helps persuade readers toward acceptance of your argument while maintaining logical flow throughout the piece.
Importance of Writing Structures
Writing structures play a critical role in effective communication. A clear structure allows you to convey your ideas logically, making it easier for readers to follow along. Without a defined structure, even the best content can become confusing and disengaging.
Different types of writing benefit from unique structures. For instance, the five-paragraph essay provides a straightforward format that keeps arguments focused and coherent. This structure is especially useful for academic writing where clarity is essential.
Narrative structures engage readers through storytelling elements like characters and plots. Using this approach invites emotional investment, encouraging readers to connect with your message on a deeper level.
The problem-solution format works well in persuasive writing by clearly outlining an issue before presenting solutions. This method helps establish authority while guiding readers toward actionable insights.
Additionally, chronological order presents information based on time sequence, which is ideal for historical or procedural content. This structure allows you to build context and enhance comprehension as events unfold logically.
Comparative structures highlight similarities and differences between subjects effectively. This approach assists in clarifying distinctions that might not be immediately obvious to the reader.
Understanding these various writing structures equips you with valuable tools for crafting engaging content across different formats.
Tips for Effective Writing Structures
Effective writing structures enhance clarity and engagement. Implementing the right structure can transform your writing significantly.
Organizing Ideas
Organizing ideas effectively ensures that your message resonates with readers. Start by outlining main points, which acts as a roadmap for your content. For example:
- Use bullet points to list key arguments or steps.
- Group related themes together to maintain coherence.
- Begin with an introduction, followed by supporting details, and conclude with a summary.
By structuring information logically, you help readers grasp complex concepts easily.
Using Transition Words
Using transition words connects ideas smoothly, guiding readers through your text. These words clarify relationships between sentences and paragraphs. Examples include:
- Additionally, to add more information.
- However, to present contrasting views.
- Consequently, to indicate results or outcomes.
Incorporating these transitions makes your writing flow better and enhances overall readability.