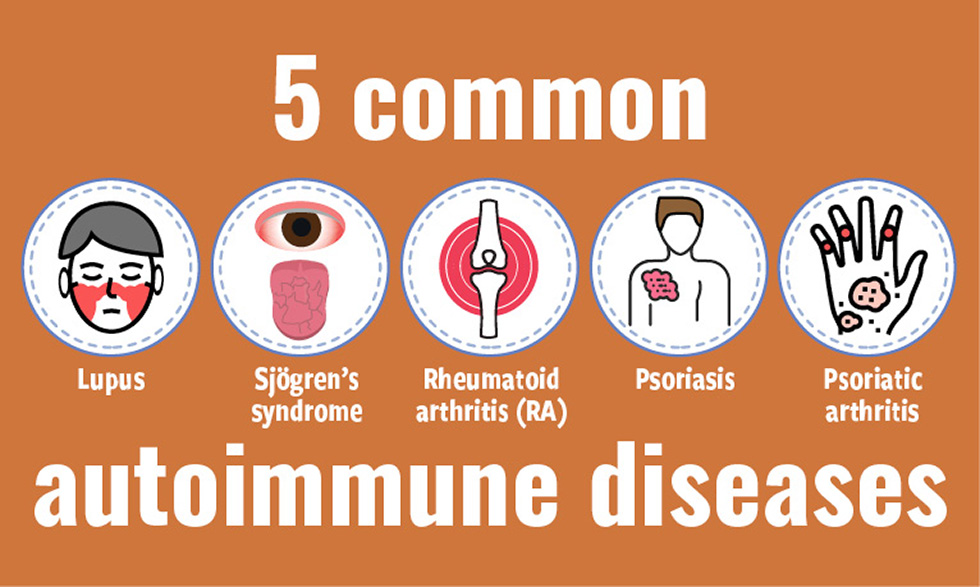
Autoimmune diseases can be puzzling and often misunderstood. Have you ever wondered why your body might mistakenly attack its own cells? Understanding which of the following examples describes an autoimmune disease is crucial for grasping how these conditions affect millions of people worldwide.
Understanding Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases occur when your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells. This confusion can lead to various health issues. Here are some common examples:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: In this condition, the immune system targets joints, causing inflammation and pain.
- Lupus: Lupus affects multiple organs, including the skin and kidneys, leading to a wide range of symptoms.
- Multiple Sclerosis: The immune system attacks nerve fibers in this disease, disrupting communication between the brain and body.
- Type 1 Diabetes: In this case, the immune response destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: This disorder results from an attack on the thyroid gland, often leading to hypothyroidism.
Recognizing these examples helps you understand how autoimmune diseases impact daily life. Each condition presents unique challenges that require targeted management strategies.
Types of Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases manifest when the immune system erroneously targets healthy cells. Understanding these conditions is vital for recognizing their effects on health.
Common Examples
Several autoimmune diseases are prevalent and impact many individuals. Here’s a list of common examples:
Each example presents unique challenges that require specific management strategies.
Rare Autoimmune Disorders
In addition to common conditions, several rare autoimmune disorders exist. These may not be widely known but can significantly impact those affected. Some include:
Recognizing these less common types helps broaden understanding of autoimmune diseases overall.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing symptoms is vital for identifying autoimmune diseases. Each condition presents unique signs that can vary in severity.
Recognizable Symptoms
Common symptoms of autoimmune diseases include:
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness despite rest.
- Joint pain: Discomfort or swelling in joints, often found in Rheumatoid Arthritis.
- Skin rashes: Red or scaly patches, frequently seen in Lupus.
- Fever: Low-grade fever that may occur intermittently.
- Muscle weakness: Reduced strength impacting daily activities, common in conditions like Myasthenia Gravis.
These symptoms can overlap with other illnesses, making it essential to consult a healthcare provider for accurate assessment.
Diagnostic Tools
Various diagnostic tools assist in confirming autoimmune diseases:
- Blood tests: These identify specific autoantibodies and inflammatory markers.
- Imaging studies: X-rays or MRIs help visualize joint damage or inflammation.
- Biopsy procedures: Tissue samples can reveal abnormalities linked to certain autoimmune disorders.
Utilizing these methods ensures a comprehensive evaluation, leading to appropriate treatment options tailored to individual needs.
Treatment Options
Autoimmune diseases require comprehensive management strategies to address symptoms and improve quality of life. Understanding treatment options helps you make informed decisions about your health.
Medications
Medications play a crucial role in managing autoimmune diseases. They can reduce inflammation, suppress the immune system, and alleviate symptoms. Common medication types include:
- NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) for pain relief.
- Corticosteroids to decrease inflammation rapidly.
- DMARDs (Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs) for long-term control of conditions like Rheumatoid Arthritis.
- Biologics, which target specific components of the immune system.
Each medication type serves distinct purposes depending on the condition and severity. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best option for your situation.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes significantly impact how well you manage an autoimmune disease. Adopting healthier habits can enhance overall well-being. Key lifestyle modifications include:
- Regular exercise, which boosts energy levels and reduces fatigue.
- Balanced diet, focusing on anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness or yoga, that help lower stress levels.
Incorporating these changes into your routine promotes better management of symptoms while improving physical and mental health.