In today’s fast-paced tech landscape, understanding the different cloud service models is crucial for businesses and developers alike. One such model that’s gaining traction is Platform as a Service (PaaS). But what exactly does it entail? You might be surprised to learn how PaaS can streamline your development process by providing essential tools and services without the hassle of managing underlying infrastructure.
Key Features of PaaS
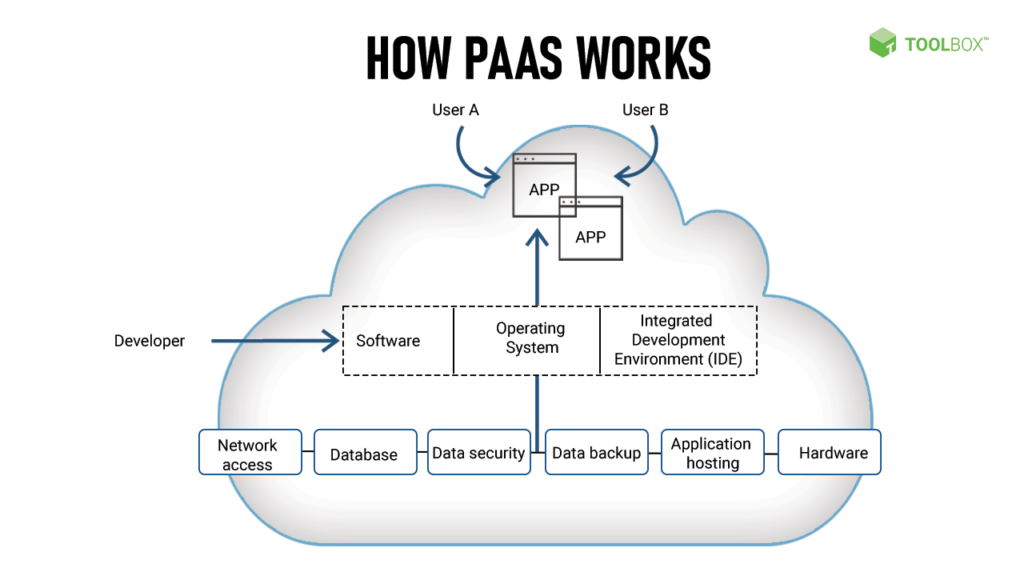
Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides various features that streamline application development and deployment. Understanding these features helps you leverage PaaS effectively.
Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability is a significant advantage of PaaS. You can easily adjust resources based on your application’s needs. For instance, during peak usage times, you might require additional computing power or storage. Flexibility in scaling allows for efficient resource management without the hassle of physical infrastructure changes.
Integrated Development Tools
PaaS offers integrated development tools that enhance productivity. These tools include built-in IDEs (Integrated Development Environments), version control systems, and API management solutions. By using these resources, you streamline your workflow, enabling faster application building and testing processes. This integration reduces setup time and allows more focus on coding rather than configuration.
Examples of PaaS Providers
PaaS providers offer a range of platforms that enhance application development and deployment. Here are some notable examples to consider:
Google App Engine
Google App Engine allows you to build and host applications on Google’s infrastructure. It supports multiple programming languages, enabling flexibility in development. This platform automatically scales your applications based on traffic demands. With features like integrated monitoring and built-in services, it streamlines the development process significantly.
Microsoft Azure App Services
Microsoft Azure App Services provides a robust environment for building web apps, mobile app backends, and APIs. You can easily integrate with various Microsoft services. This platform supports several programming languages, offering flexibility and scalability. Moreover, it includes tools for continuous integration and deployment, which enhances productivity for developers.
Heroku
Heroku is a popular choice among developers for its simplicity and ease of use. This platform enables quick deployment of applications across various languages with minimal configuration. With add-ons available for database management, caching, and monitoring, it caters well to diverse application needs. Additionally, its focus on developer experience makes it an attractive option.
IBM Cloud Foundry
IBM Cloud Foundry offers a cloud-native platform ideal for developing modern applications. This service supports multiple frameworks and languages while providing strong integration capabilities. Its emphasis on microservices architecture promotes agility in application deployment. Furthermore, IBM’s extensive catalog of services enhances the functionality available to developers using this platform.
Choosing the Right PaaS Solution
Selecting a suitable Platform as a Service (PaaS) solution requires careful consideration of various factors. Understanding these factors helps you align your development needs with the right platform.
Factors to Consider
When choosing a PaaS provider, consider the following:
- Supported Languages and Frameworks: Ensure the platform supports the programming languages and frameworks you plan to use.
- Scalability Options: Look for features that allow seamless scaling based on application demands.
- Integrated Tools: Check for built-in tools such as IDEs, databases, and CI/CD pipelines that can simplify your workflow.
- Cost Structure: Analyze pricing models to find one that fits your budget while meeting service requirements.
- Security Features: Evaluate security protocols and compliance standards offered by the provider.
Use Cases for PaaS
PaaS solutions cater to various scenarios, including:
- Web Application Development: Rapidly build and deploy web applications without managing infrastructure details.
- API Development: Create and manage APIs efficiently with integrated tools for testing and deployment.
- Microservices Architecture: Develop applications using microservices for enhanced flexibility and scalability.
- Mobile Application Backend: Provide backend services for mobile apps without worrying about server maintenance.
By considering these factors and use cases, you can select a PaaS solution that best aligns with your project needs.