Have you ever wondered how society influences your behavior without formal rules? Informal social control plays a crucial role in maintaining order and shaping our actions through unwritten norms and expectations. This subtle yet powerful mechanism operates within families, communities, and peer groups, guiding us on what’s acceptable or not.
Understanding Informal Social Control
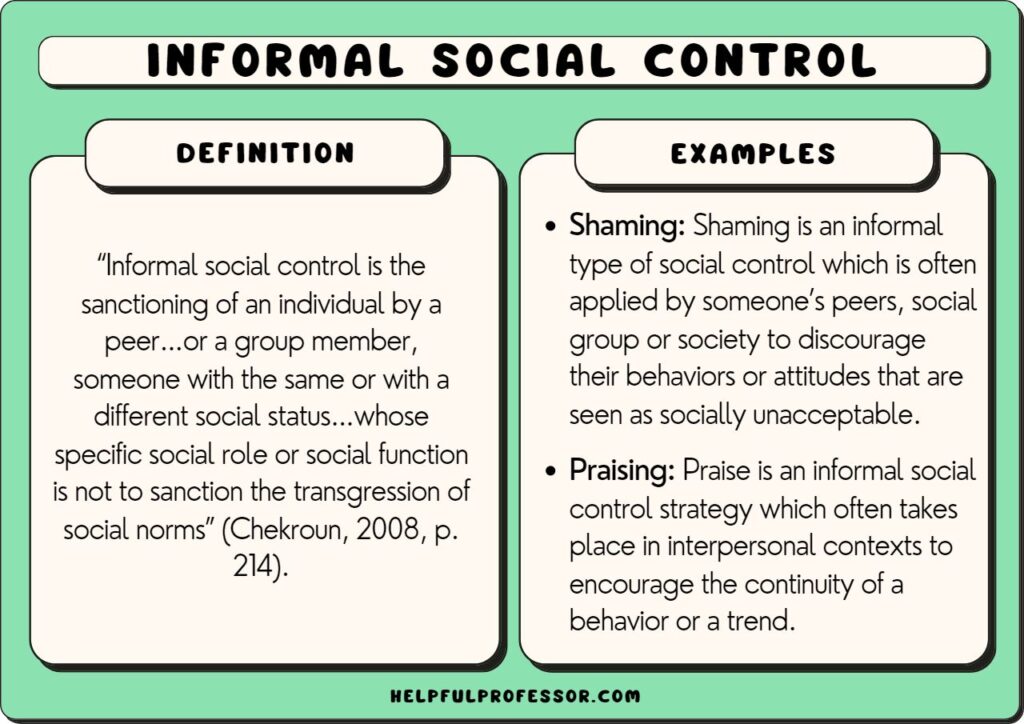
Informal social control refers to the unwritten rules and expectations that influence behavior in society. It encompasses various mechanisms that guide individuals on what is acceptable or unacceptable conduct.
Definition of Informal Social Control
Informal social control involves societal norms, values, and peer influences rather than formal laws. This type of control shapes behavior through socialization processes within families, schools, and communities. Examples include:
- Peer pressure, where friends encourage conformity.
- Family expectations, guiding children’s behaviors.
- Cultural traditions, which dictate appropriate actions.
Importance in Society
The impact of informal social control is profound. It helps maintain order and cohesion within communities by promoting shared values. Key points include:
- Encouragement of conformity leads to stability.
- Prevention of deviance minimizes conflicts.
- Promotion of positive behaviors enhances community well-being.
You can see how these elements work together to foster a sense of belonging while discouraging actions that may disrupt harmony.
Examples of Informal Social Control
Informal social control manifests through various everyday interactions and expectations. Here are key examples that illustrate how it operates within society.
Family Influence
Family plays a crucial role in shaping behavior. Strong family values instill norms that guide actions. For instance, parents often express disappointment when children misbehave, leading to guilt or shame that encourages conformity. When families celebrate achievements, they reinforce positive behaviors, making kids more likely to repeat them.
Peer Pressure
Peer pressure significantly influences decisions and actions among individuals, especially youths. Friends can motivate each other to conform to group standards or discourage deviant behavior. When a group collectively disapproves of certain actions—like skipping school—members may feel compelled to align with the group’s expectations for acceptance and belonging.
Cultural Norms
Cultural norms dictate acceptable behaviors within communities. Shared beliefs about morality shape individual conduct in profound ways. For example, traditions around respect for elders promote courteous behavior while discouraging disrespectful attitudes. Participation in cultural events reinforces these values, guiding people toward socially accepted practices and away from those deemed inappropriate.
The Role of Community in Informal Social Control
Community plays a crucial role in informal social control, influencing behavior through shared values and expectations. This influence fosters a sense of belonging and encourages adherence to societal norms.
Neighborhood Watch Programs
Neighborhood watch programs exemplify informal social control by promoting safety and community involvement. Residents collaborate to monitor suspicious activities, enhancing security through vigilance. These programs create stronger bonds among neighbors, fostering communication and cooperation. Regular meetings help establish collective goals, reinforcing accountability. When everyone is aware of each other’s actions, it discourages deviant behavior within the community.
Local Organizations and Clubs
Local organizations and clubs contribute significantly to informal social control by providing structured environments for interaction. These groups set standards for conduct, helping members feel connected while encouraging positive behaviors. For example:
- Sports teams instill discipline through regular practice.
- Book clubs promote discussion around shared values.
- Volunteer groups foster empathy towards others.
Participation in these organizations creates social networks that reinforce acceptable behaviors, guiding individuals toward positive contributions to society.
Comparison with Formal Social Control
Informal social control differs significantly from formal social control, shaping behavior through unwritten rules rather than enforced laws. While both mechanisms aim to maintain order within society, their methods and effectiveness can vary.
Differences and Similarities
Formal social control relies on established laws and regulations enforced by institutions like the police or courts. Examples include legal penalties for theft or driving violations. In contrast, informal social control employs societal expectations and norms that guide behavior without official enforcement. Instances of this include family teachings about manners or peer disapproval of rule-breaking actions.
Both types share a common goal: maintaining societal order. However, informal social control often operates at a community level, relying on relationships and shared values to influence individuals.
Effectiveness of Each Type
The effectiveness of each type varies based on context. Informal social control often proves more effective in small communities where close interpersonal ties exist. For instance:
- Close-knit neighborhoods encourage residents to monitor one another’s behaviors.
- Families instill values that dictate acceptable conduct from an early age.
On the other hand, formal social control becomes essential in larger societies where individual actions may threaten public safety. Laws against violent crimes provide necessary boundaries that informal measures cannot enforce alone.
Ultimately, both forms complement each other; without either system, maintaining societal order would be challenging.