Understanding demographic information is crucial for businesses, marketers, and researchers alike. But what exactly does it encompass? Demographic information includes various characteristics that help define a population. From age and gender to income levels and education, these details can significantly impact decision-making processes.
Understanding Demographic Information
Demographic information includes various characteristics that help define a population. Some key examples of demographic information are:
- Age: Knowing the age range of your target audience helps tailor products and services effectively.
- Gender: Gender distribution can influence marketing strategies and product development.
- Income Levels: Understanding income levels allows businesses to price their offerings appropriately.
- Education Level: Education insights inform how you communicate with your audience and what types of content resonate.
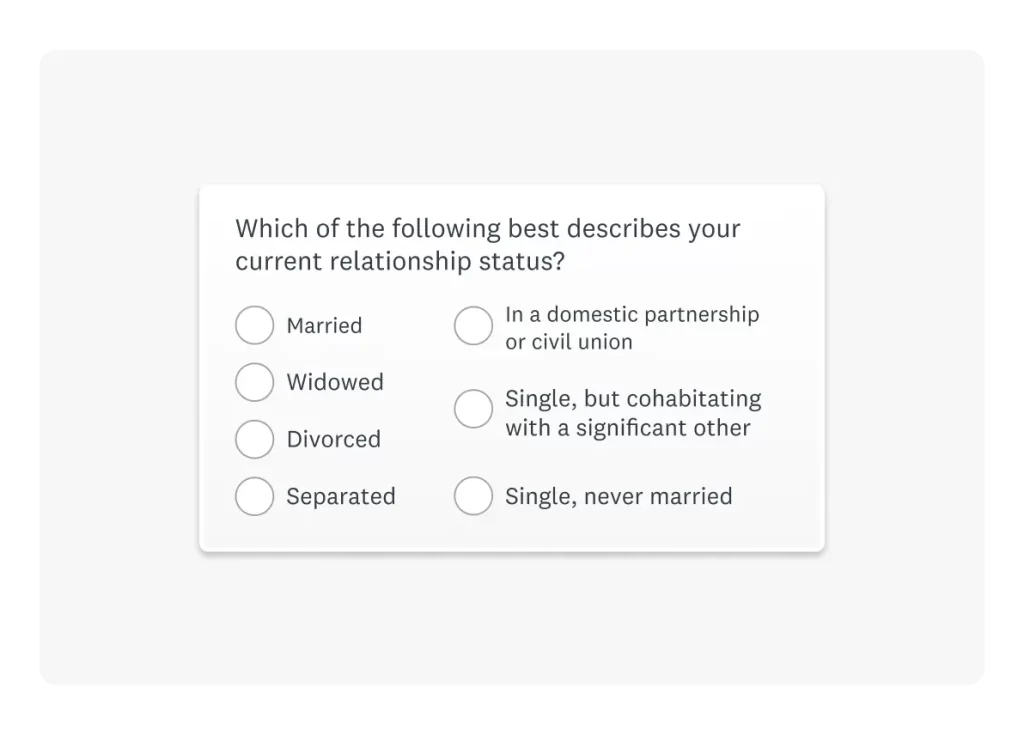
- Marital Status: Whether individuals are single, married, or divorced can affect purchasing decisions.
- Occupation: Occupation data provides insights into lifestyle choices and spending habits.
- Ethnicity: Ethnic backgrounds may influence cultural preferences and community engagement.
These demographic factors play a significant role in shaping market research, advertising campaigns, and overall business strategies. By analyzing this information, businesses can enhance targeting efforts and improve customer satisfaction.
Types of Demographic Information
Demographic information consists of various characteristics that help define a population. Understanding these types aids businesses and researchers in tailoring their strategies effectively.
Age
Age is a vital demographic factor that influences consumer behavior. For example, millennials may prefer digital products, while older adults might favor traditional marketing methods. Collecting age data allows businesses to target specific groups efficiently.
Gender
Gender plays a significant role in shaping preferences and purchasing habits. Products like skincare or clothing often cater to different genders. By analyzing gender demographics, companies can create tailored marketing campaigns that resonate with their audience.
Ethnicity
Ethnicity provides insights into cultural backgrounds and values. Different ethnic groups may have unique buying patterns or preferences for certain products. For instance, food brands often adapt flavors based on regional ethnicities to appeal to diverse consumers.
Education Level
Education level affects income potential and purchasing power. Consumers with higher education levels tend to spend more on luxury items. Businesses can leverage this information by crafting messages that align with the educational background of their target market.
Income Level
Income level significantly impacts spending habits and lifestyle choices. Higher-income individuals may seek premium products, whereas lower-income consumers prioritize affordability. Understanding income demographics helps in setting appropriate pricing strategies for different market segments.
Importance of Demographic Information
Demographic information provides essential insights for businesses and policymakers. Understanding the characteristics of a population shapes effective strategies and decisions.
Impacts on Marketing
Demographic data significantly influences marketing strategies. For instance, age groups determine preferred communication channels. Younger audiences may favor social media ads, while older generations often respond better to traditional media. Additionally, gender impacts product promotion; men and women frequently have different preferences. Ethnicity can guide cultural messaging in campaigns. By analyzing these factors, you can create targeted marketing that resonates with your audience.
Impacts on Policy Making
Demographic information plays a crucial role in crafting public policies. Policymakers use this data to identify community needs accurately. For example, understanding income levels helps allocate resources effectively. Education demographics inform initiatives aimed at improving literacy rates among specific groups. Moreover, age statistics assist in planning healthcare services tailored for various populations. By leveraging demographic insights, you can ensure policies address real-world challenges faced by communities.
Common Misconceptions
Many people confuse demographic information with other types of data. For instance, demographic information specifically refers to characteristics that define a population. These include age, gender, income level, education, and marital status. However, some might mistakenly believe that preferences or opinions fall under this category.
Additionally, demographic information isn’t static; it changes over time. You might think your audience remains the same indefinitely, but shifts in demographics can significantly impact marketing strategies. For example:
- Age groups evolve as new generations emerge.
- Income levels fluctuate due to economic factors.
- Educational attainment increases over years.
It’s also common to overlook the importance of geographic location in demographic analysis. While many focus on individual traits like age or gender, location influences purchasing behavior and market segmentation.
Moreover, some assume that collecting demographic data is unnecessary or invasive. Yet gathering this information aids businesses and policymakers alike by tailoring services and products to meet specific needs effectively. Understanding your audience’s demographics fosters better engagement.
Lastly, don’t forget about intersectionality—how different demographic factors interact with one another. For example:
- An individual’s buying habits may differ based on both their age and income level.
- Marketing strategies may vary for women versus men within the same age group.
Recognizing these nuances enhances your approach to utilizing demographic information efficiently.