Ever wondered how businesses make informed decisions? The answer often lies in effective data gathering. Understanding which activities qualify as data gathering is crucial for any organization aiming to thrive in today’s information-driven world. From surveys to observations, each method plays a vital role in collecting valuable insights.
In this article, you’ll explore various activities that exemplify data gathering. Identifying these examples can help you enhance your own strategies and ensure you’re leveraging the right techniques. Whether you’re a marketer seeking customer feedback or a researcher compiling statistics, knowing the right methods can significantly impact your outcomes. Are you ready to uncover the different ways to gather data effectively? Let’s dive into some practical examples that will sharpen your understanding of this essential process.
Understanding Data Gathering
Data gathering involves various activities aimed at collecting information for analysis. These methods provide businesses and researchers with the data necessary to make informed decisions and develop strategies.
Definition of Data Gathering
Data gathering refers to the systematic collection of information from different sources. This process can include qualitative and quantitative methods, ensuring a comprehensive view of the subject matter. Common techniques encompass surveys, interviews, observations, and experiments. Collecting this data allows you to analyze trends, understand behaviors, and draw conclusions.
Importance of Data Gathering
Data gathering is crucial for effective decision-making in any organization. It helps identify customer preferences, market conditions, and operational efficiencies. By leveraging accurate data, you enhance your strategic planning capabilities. Additionally, informed choices based on solid evidence reduce risks associated with uncertainty.
Here are some key reasons why data gathering matters:
- Informs business strategy: Understand market trends better.
- Enhances customer experience: Tailor services or products to meet needs.
- Supports research: Provides credible statistics for studies.
- Identifies opportunities: Spot gaps in the market before competitors do.
By focusing on these aspects of data gathering, you position yourself for success in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Activities That Are Examples of Data Gathering
Data gathering involves various activities that help you collect essential information. Below are examples of effective methods used in this process.
Surveys and Questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are popular for collecting data directly from respondents. You can utilize online platforms like Google Forms or SurveyMonkey to create and distribute these tools easily. They generally focus on specific topics, allowing you to gather a range of opinions or experiences. For instance:
- Customer satisfaction surveys measure how well your products meet user expectations.
- Market research questionnaires assess trends affecting consumer behavior.
Interviews and Focus Groups
Interviews and focus groups provide deeper insights into individual or group perspectives. You might conduct one-on-one interviews to explore personal experiences or feelings related to a subject. Alternatively, focus groups invite small groups for discussions about your product or service, offering diverse viewpoints. Consider these approaches:
- Structured interviews follow a set list of questions for consistency.
- Unstructured interviews allow more open-ended discussions, leading to richer data.
Observations and Experiments
Observational studies capture behaviors in real-time settings without interference. By observing subjects in their natural environment, you gain valuable context about actions and reactions. Experiments test hypotheses under controlled conditions, enabling you to draw conclusions based on results. Here are key points:
- Field observations occur in everyday settings where people interact with products.
- Laboratory experiments control variables tightly for precise outcomes.
Online Research and Data Mining
Online research uses digital resources to gather existing data relevant to your needs. You can search academic journals, market reports, or news articles for credible information on various topics. Data mining refers specifically to analyzing large datasets using algorithms for patterns that reveal useful insights. Important aspects include:
- Web scraping tools, which automate the collection of web-based information.
- Statistical databases, providing access to historical data across industries.
By engaging in these activities effectively, you enhance your ability to make informed decisions based on solid evidence gathered through systematic processes.
Distinguishing Data Gathering Activities
Data gathering activities fall into different categories, each serving unique purposes. Understanding these distinctions enhances your ability to select the right method for your needs.
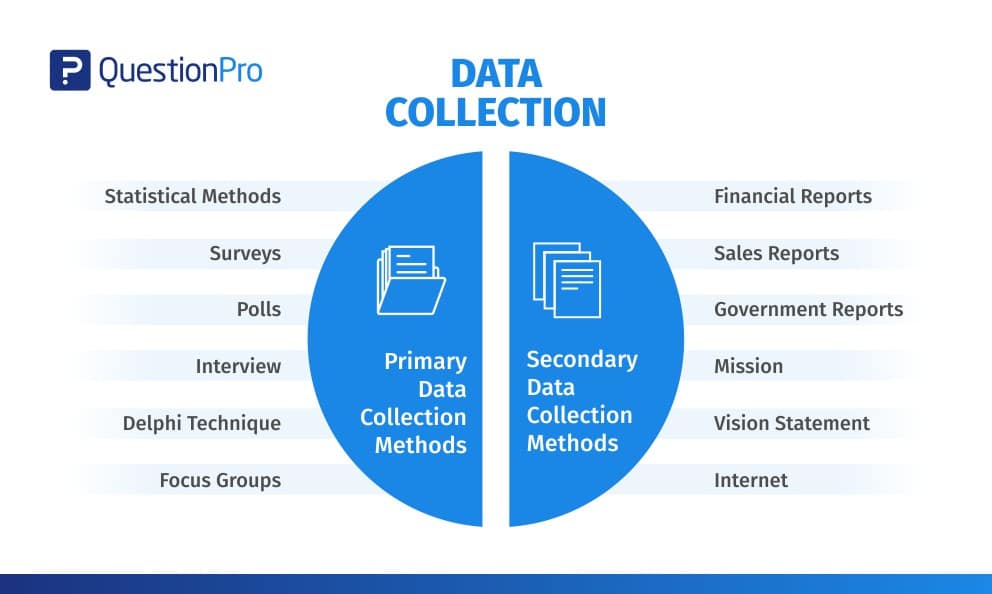
Primary vs. Secondary Data
Primary data refers to information collected directly from original sources. You gather this data through methods such as surveys, experiments, or interviews. For example, conducting a customer satisfaction survey provides insights specific to your business.
Secondary data involves analyzing existing information gathered by others. This can include reports, articles, or databases. For instance, using census data allows you to understand demographic trends without collecting new information yourself.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Methods
Qualitative methods focus on understanding concepts and experiences. You might use focus groups or open-ended survey questions to explore opinions in depth. These insights often reveal underlying motivations and emotions.
Quantitative methods emphasize numerical data and statistical analysis. Examples include closed-ended surveys or experiments yielding measurable results. Analyzing sales figures can highlight trends in product performance over time.
By recognizing these differences in data gathering activities, you enhance decision-making based on precise and relevant information tailored to your objectives.