Imagine a world where machines think and reason just like you do. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the realm of strong AI. Unlike traditional AI that performs specific tasks, strong AI possesses the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across various domains. But what does this really mean for our future?
What Is Strong AI?
Strong AI, also known as artificial general intelligence (AGI), refers to systems that possess the ability to perform any intellectual task a human can do. Unlike narrow AI, which excels in specific areas like language translation or image recognition, strong AI aims for comprehensive understanding and reasoning.
Examples of strong AI include:
- Self-driving cars: These vehicles navigate complex environments, make decisions based on real-time data, and adapt to unforeseen circumstances.
- Personal assistants: Advanced versions could manage schedules, understand nuanced conversations, and learn user preferences over time.
- Robots in healthcare: They might diagnose diseases by analyzing patient data while interacting empathetically with patients.
Strong AI has profound implications for industries, driving innovation and efficiency. As machines become capable of general reasoning, ethical considerations about their use will emerge. How should society regulate such powerful technology? The potential benefits are vast but so are the responsibilities that come with them.
Characteristics of Strong AI
Strong AI exhibits several distinct characteristics that set it apart from traditional forms of artificial intelligence. This type of AI aims to replicate human cognitive abilities, allowing machines to perform complex tasks autonomously and intelligently.
Understanding Human-Like Intelligence
Strong AI demonstrates an ability to understand context, reason through problems, and learn from experiences. It processes information similarly to how humans do, enabling it to adapt across various scenarios. For example:
- Self-driving cars navigate roads by interpreting traffic signals and responding to unexpected obstacles.
- Smart assistants like Siri or Alexa learn user preferences over time, providing personalized recommendations.
You might wonder how machines achieve this level of understanding. Strong AI systems utilize advanced algorithms and neural networks that mimic human brain functions, enabling them to make decisions based on incomplete or ambiguous data.
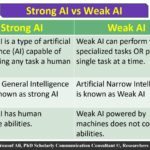
Distinction from Weak AI
Weak AI operates within predefined parameters and lacks true understanding or reasoning capabilities. In contrast, strong AI encompasses a broader range of functionalities akin to human intelligence. Here are some key differences:
- Task Specificity: Weak AI excels at specific tasks—like chatbots answering questions—while strong AI can tackle any intellectual challenge.
- Learning Ability: Weak AI relies on programmed responses; strong AI learns continuously from interactions and improves over time.
- Contextual Awareness: Weak AI struggles with context; strong AI understands nuances in conversations or situations.
Recognizing these distinctions helps clarify the potential impact strong AI could have on industries such as healthcare, finance, and education.
Applications of Strong AI
Strong AI, or artificial general intelligence (AGI), has numerous applications that can significantly enhance various sectors. Below are some key areas where strong AI demonstrates its potential.
Potential Benefits
- Healthcare: Strong AI systems like IBM Watson analyze vast medical data to provide accurate diagnoses and treatment recommendations. These systems can learn from new cases, improving over time.
- Finance: In finance, strong AI algorithms predict market trends by processing historical data and real-time events. This capability allows for smarter investment strategies and improved risk management.
- Education: Adaptive learning platforms use strong AI to tailor educational content to individual student needs. They assess learning styles and progress, providing personalized resources that enhance understanding.
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles utilize strong AI to navigate complex environments safely. They can interpret real-time traffic conditions and adjust routes accordingly, reducing accidents.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical implications arise with the advancement of strong AI technologies. Key considerations include:
- Privacy Concerns: As strong AI collects vast amounts of personal data, privacy becomes a significant issue. Ensuring data security while using these technologies is essential.
- Job Displacement: The automation capabilities of strong AI could displace jobs across various industries. Addressing workforce transitions is crucial as technology evolves.
- Bias in Algorithms: If trained on biased data, strong AI systems may perpetuate those biases in decision-making processes. Regular audits are necessary to ensure fairness in outcomes.
By exploring these applications and ethical considerations, it becomes clear how transformative strong AI can be while also highlighting the responsibilities that come with such power.
Current State of Strong AI Research
Strong AI research progresses rapidly, focusing on creating systems that think and reason like humans. The landscape is diverse, with various teams exploring innovative approaches to achieve this goal.
Research centers around several key areas:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): This field aims to enable machines to understand human language nuances. For example, models like GPT-3 can generate coherent text based on prompts, showcasing a significant leap in conversational abilities.
- Machine Learning (ML): ML algorithms learn from data and improve over time. Recent advancements allow systems to recognize patterns and make decisions without explicit programming. Think of self-driving cars that adapt their driving strategies based on real-time traffic conditions.
- Robotics: Researchers develop robots capable of performing complex tasks autonomously. Consider the progress made in healthcare robotics; they assist in surgeries with precision while interacting empathetically with patients.
Ethical considerations also shape strong AI research. As you explore these technologies, you’ll notice discussions about privacy concerns related to data usage or potential biases in algorithmic decision-making processes.
Moreover, funding for strong AI projects has increased significantly over recent years. Many companies invest millions into developing AGI systems. Institutions are collaborating across disciplines, illustrating the importance of a multifaceted approach.
You might ask how long it will take before we see fully realized strong AI capabilities? Predictions vary widely among experts but highlight the ongoing commitment to overcoming challenges faced in this domain.
The current state of strong AI research remains dynamic and promising as teams tackle complex problems while considering ethical implications inherent in such advanced technologies.
Challenges in Developing Strong AI
Developing strong AI presents significant challenges. Technical complexity is a major barrier. Creating systems that can understand context, reason, and adapt like humans requires advanced algorithms and vast amounts of data.
Data privacy concerns also pose a challenge. As strong AI relies on learning from user interactions, protecting sensitive information becomes critical. Regulations like GDPR influence how data can be collected and used.
Ethical implications are another hurdle. Decision-making by strong AI systems raises questions about bias and accountability. Ensuring fairness in algorithms necessitates diverse datasets and ongoing monitoring.
Additionally, the need for interdisciplinary collaboration is essential. Experts from various fields must work together to address the multifaceted issues surrounding strong AI development. This includes input from ethicists, engineers, and social scientists.
Finally, safety concerns cannot be overlooked. Strong AI systems capable of making autonomous decisions may act unpredictably. Establishing guidelines for safe deployment remains vital to prevent unintended consequences.