Have you ever noticed someone tapping their fingers or rocking back and forth? These repetitive movements are known as stimming, a term that describes self-stimulatory behavior often seen in individuals with autism and other neurodiverse conditions. Understanding stimming is essential for fostering empathy and awareness in our communities.
In this article, we’ll explore what stimming really means, its purpose, and why it matters. You’ll discover various examples of stimming behaviors—from hand-flapping to spinning objects—and learn how these actions can serve as coping mechanisms for sensory overload or emotional regulation. By the end, you’ll gain valuable insights into how recognizing and respecting stimming can create more inclusive environments for everyone. Are you ready to dive deeper into this fascinating topic?
What Is Stimming?
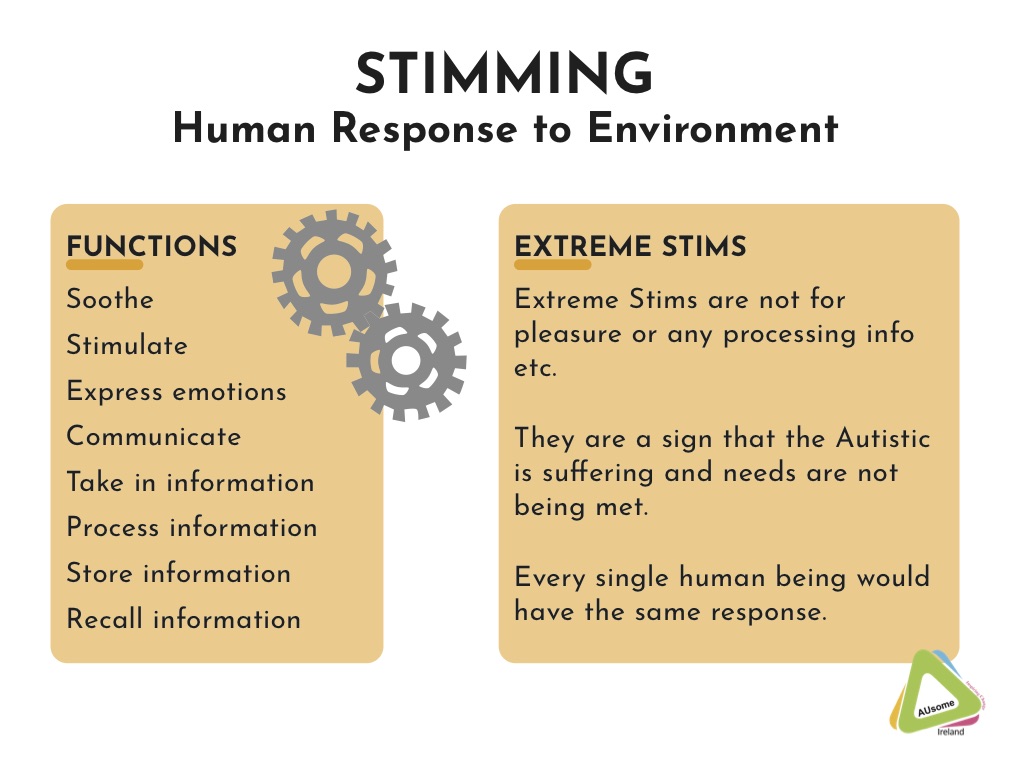
Stimming refers to a range of self-stimulatory behaviors often observed in individuals with autism and other neurodiverse conditions. These actions serve various purposes, including sensory regulation and emotional relief.
Examples of stimming behaviors include:
- Hand flapping: Many people engage in hand flapping when excited or anxious.
- Rocking back and forth: This can provide comfort during overwhelming situations.
- Repeating phrases or sounds: Some may repeat their favorite lines from movies or songs to soothe themselves.
- Fidgeting with objects: Using stress balls or fidget spinners helps maintain focus.
Understanding stimming is important for fostering empathy. Recognizing these behaviors allows communities to support individuals who stim, creating more inclusive environments.
Understanding Stimming in Autism
Stimming refers to a variety of self-stimulatory behaviors commonly seen in individuals with autism. Recognizing and understanding these actions enhances empathy and support for those who engage in them.
Types of Stimming Behaviors
Several distinct types of stimming behaviors exist. Some examples include:
- Hand flapping: Rapidly moving your hands up and down or side to side.
- Rocking: Repeatedly swaying back and forth while sitting or standing.
- Fidgeting: Manipulating small objects, like stress balls or fidget spinners.
- Repetitive vocalizations: Making sounds or repeating phrases consistently.
These behaviors can vary widely among individuals, showcasing unique preferences and patterns.
The Purpose of Stimming
Stimming serves multiple purposes for those who engage in it. It often provides:
- Sensory regulation: Helping manage overwhelming sensory input by offering a predictable outlet.
- Emotional relief: Reducing anxiety during stressful situations through familiar movements.
- Focus enhancement: Improving concentration on tasks by channeling excess energy.
Understanding the purpose behind stimming fosters greater acceptance within communities, promoting supportive interactions with neurodiverse individuals.
Stimming in Different Age Groups
Stimming behaviors manifest differently across age groups, shaped by developmental stages and individual needs. Understanding these variations aids in fostering acceptance and support.
Stimming in Children
Children often engage in stimming as a way to cope with overwhelming sensations or emotions. Common examples include:
- Hand flapping: This behavior helps children express excitement or manage anxiety.
- Rocking back and forth: Many kids find rhythmic movements calming, especially during stressful situations.
- Spinning objects: Fidgeting with toys can provide sensory input that some children crave.
- Vocalizations: Repetitive sounds or phrases may emerge when they seek comfort or focus.
Recognizing these actions is essential for creating supportive environments at home and school.
Stimming in Adults
Adults also exhibit stimming behaviors but may do so less visibly due to social norms. Examples include:
- Fidgeting with pens or stress balls: These tactile activities help maintain concentration.
- Tapping feet or fingers: Such movements can relieve tension during meetings or while working.
- Repetitive speech patterns: Some adults use specific phrases to self-soothe under pressure.
- Engaging in hobbies like knitting or drawing: These activities provide structured stimulation and relaxation.
Understanding adult stimming promotes empathy within workplaces and social settings, enhancing overall inclusivity.
The Impact of Stimming on Daily Life
Stimming behaviors significantly influence daily life for individuals who engage in them. Understanding how these actions affect various aspects of existence is crucial.
Social Interactions
Stimming can impact social interactions in multiple ways. Some individuals may find it difficult to connect with others while stimming. For instance, someone flapping their hands might distract others or lead to misunderstandings about their emotional state. However, stimming often provides comfort, which allows many to feel more secure during social situations. Recognizing that stimming serves as a communication tool can foster better connections among peers.
Coping Mechanisms
Stimming acts as an effective coping mechanism for many people. It helps regulate sensory overload and manage stress levels. Common examples include tapping fingers when anxious or rocking back and forth during overwhelming moments. These repetitive actions create a sense of predictability amid chaos, promoting calmness. Acknowledging the role of stimming in managing emotions enhances understanding and support from family and friends.