Have you ever wondered why certain ads resonate with you more than others? That’s the magic of psychographic segmentation. This powerful marketing strategy goes beyond basic demographics, diving into the values, interests, and lifestyles that shape consumer behavior. By understanding what drives your audience on a deeper level, you can tailor your messaging to create lasting connections.
Understanding Psychographic Segmentation
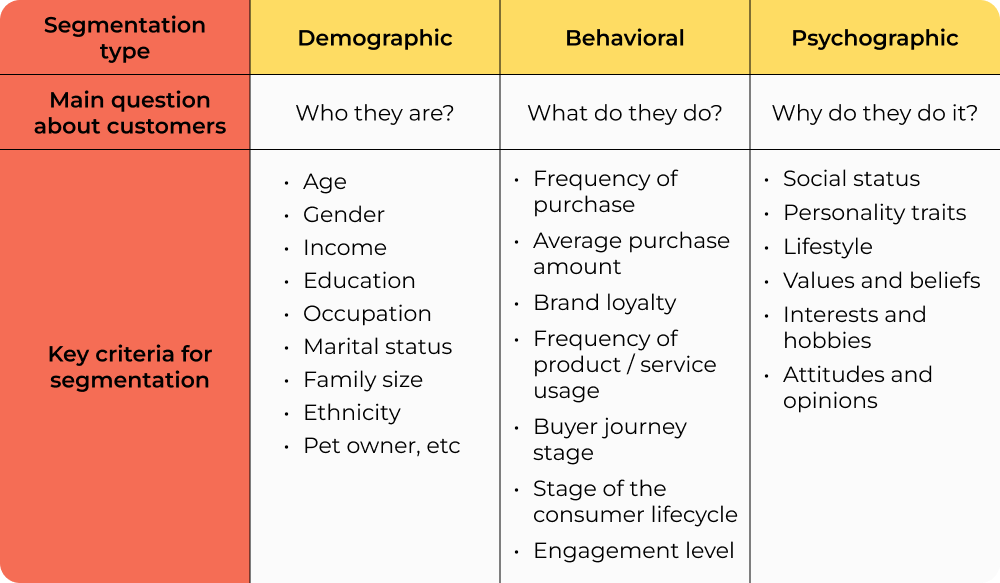
Psychographic segmentation dives deep into the values, interests, and lifestyles of consumers. This approach goes beyond demographics, focusing on what drives consumer behavior.
Definition of Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation categorizes consumers based on psychological attributes. These attributes include:
- Values: Beliefs that guide choices.
- Interests: Hobbies or activities that engage individuals.
- Lifestyles: Daily habits and routines.
This segmentation helps businesses tailor marketing strategies to resonate with specific customer groups.
Importance of Psychographic Segmentation
Understanding psychographics is crucial for effective marketing. It allows you to:
- Create targeted campaigns: Tailor messages that speak directly to your audience’s motivations.
- Enhance product development: Design products that align with consumer values and preferences.
- Build brand loyalty: Foster connections by appealing to shared beliefs and interests.
By leveraging psychographic insights, brands can achieve stronger engagement and drive sales more effectively.
Key Components of Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation involves understanding consumer motivations through various psychological attributes. Focusing on specific components allows businesses to tailor their strategies effectively.
Values and Beliefs
Values and beliefs significantly influence consumer behavior. For instance, a brand promoting sustainability attracts environmentally conscious consumers. By aligning marketing messages with these values, companies foster emotional connections that enhance loyalty. Another example includes brands targeting social responsibility, appealing to customers who prioritize ethical practices in their purchasing decisions.
Lifestyle and Interests
Lifestyle choices and interests play a crucial role in psychographic segmentation. Brands can target fitness enthusiasts by offering health-related products or services. For example, a company selling athletic apparel may focus its campaigns on active lifestyles, highlighting performance benefits. Similarly, travel agencies can appeal to adventure seekers by showcasing unique experiences tailored to their preferences.
Personality Traits
Personality traits also contribute to effective psychographic segmentation. Understanding whether consumers are introverted or extroverted helps tailor communication styles. For instance, a brand aimed at outgoing individuals might use vibrant visuals and engaging content in ads, while one targeting introverts may prefer calm imagery and informative messaging. This approach ensures that marketing resonates with the intended audience’s personalities, enhancing engagement and conversion rates.
Implementing Psychographic Segmentation in Marketing
Implementing psychographic segmentation enhances marketing effectiveness by targeting consumers’ deeper motivations. This approach requires a strategic outline to ensure alignment with audience values and interests.
Data Collection Methods
You can gather psychographic data through various methods:
- Surveys: Use questionnaires to ask about preferences, lifestyles, and values.
- Focus Groups: Conduct discussions to explore consumer attitudes and opinions.
- Social Media Analytics: Analyze interactions on platforms like Facebook or Instagram for insights into interests.
- Customer Interviews: Engage directly with consumers to gain qualitative insights.
Each method provides valuable information that shapes your marketing strategies.
Analyzing Psychographic Data
Once you collect the data, analyze it effectively. Follow these steps:
- Identify Patterns: Look for common themes in responses related to interests and values.
- Segment Audiences: Divide your audience into distinct groups based on psychological traits.
- Create Personas: Develop detailed profiles representing each segment’s characteristics and motivations.
- Tailor Messaging: Adjust your marketing messages to resonate with different segments.
This analysis allows you to craft targeted campaigns that speak directly to consumers’ desires and needs, improving engagement significantly.
Benefits of Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation offers several key advantages for businesses. By understanding consumer motivations, companies can create more tailored and effective marketing strategies.
- Enhances Targeting: This approach allows you to reach specific customer groups with precise messaging that resonates with their values and interests.
- Increases Engagement: When brands align their communications with consumers’ lifestyles, they foster greater emotional connections, leading to higher engagement rates.
- Drives Brand Loyalty: Connecting on a deeper level encourages repeat purchases as customers feel understood and valued by the brand.
- Improves Product Development: Insights from psychographic data guide product design and features that meet the actual needs of your target audience.
- Boosts Marketing Efficiency: Focused campaigns reduce wasted resources by targeting only those most likely to convert, enhancing overall ROI.
By implementing psychographic segmentation effectively, you unlock opportunities for growth and strengthen relationships with your audience.
Challenges of Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation presents several challenges that marketers face. These obstacles can hinder effective implementation and impact overall marketing success.
- Data Collection Difficulties: Gathering psychographic data isn’t straightforward. Often, traditional methods like surveys or interviews may not yield accurate insights since consumers might struggle to articulate their feelings or motivations.
- Complex Analysis Requirements: Analyzing psychographic data requires advanced analytical skills and tools. You need to identify meaningful patterns from qualitative information, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Subjectivity in Interpretation: Interpreting psychographic attributes involves a degree of subjectivity. Different analysts might draw varied conclusions from the same data set, leading to inconsistent segment definitions.
- Dynamic Consumer Behavior: Consumer values and interests can change rapidly due to trends or life events. Keeping segments updated is crucial but often challenging, as it demands ongoing research efforts.
- Integration with Other Data Types: Blending psychographics with demographic data for comprehensive profiles complicates the process further. It’s essential to ensure that all components align seamlessly for effective targeting strategies.
- Cost Implications: Implementing robust psychographic segmentation strategies can require significant investment in research tools and talent acquisition, impacting budget allocation for smaller businesses.
Understanding these challenges helps you navigate the complexities of psychographic segmentation more effectively while creating targeted marketing initiatives that resonate with your audience’s deeper motivations.