Imagine a world where valuable resources lie hidden beneath the surface, waiting to be uncovered. Mining is the process that transforms this dream into reality. From precious metals like gold and silver to essential minerals used in everyday products, mining plays a crucial role in our economy and daily lives.
What Is Mining?
Mining is a process that extracts valuable resources from the Earth. This includes various activities aimed at obtaining precious metals and minerals crucial for industries.
Examples of mining include:
- Gold mining: Involves extracting gold from mineral deposits, often using techniques like placer or hard rock mining.
- Coal mining: Focuses on retrieving coal, an essential fossil fuel used for electricity generation and steel production.
- Copper mining: Entails extracting copper ore to produce electrical wiring and plumbing materials.
- Open-pit mining: A surface method where large holes are dug to access minerals near the surface.
- Underground mining: Involves creating tunnels to reach deeper mineral deposits, minimizing surface disruption.
You may also encounter environmental impacts. Mining operations can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water contamination if not managed properly. Regulations exist to mitigate these effects while ensuring resource extraction continues efficiently.
Importance Of Mining
Mining plays a crucial role in modern society, providing essential resources for various industries and daily life. It supports economic growth and development while offering numerous job opportunities.
Economic Impact
Mining significantly contributes to national economies. For instance, in 2025, the mining sector generated over $200 billion in revenue for the United States alone.
- Job creation: Mining employs nearly 600,000 workers in the U.S., supporting families and communities.
- Infrastructure development: Mining activities lead to improved infrastructure—roads, schools, and hospitals often arise where mining takes place.
- Investment attraction: The industry attracts both domestic and foreign investments that boost local economies.
Environmental Considerations
While mining is vital economically, it also poses environmental challenges. Responsible practices are necessary to minimize negative impacts on ecosystems.
- Habitat destruction: Extraction processes can disrupt local wildlife habitats.
- Soil erosion: Activities like open-pit mining can lead to significant soil degradation.
- Water contamination: Chemicals used during extraction may seep into nearby water sources.
You might wonder how these issues are addressed. Regulations exist at federal and state levels aimed at reducing environmental harm while ensuring effective resource extraction.
Types Of Mining
Mining encompasses various techniques, each suited for different geological conditions and resource types. Here are the primary mining methods utilized today.
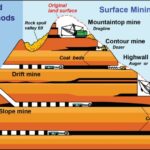
Surface Mining
Surface Mining extracts minerals close to the Earth’s surface. This method includes:
- Open-pit mining: Involves digging a large pit in the ground to access resources like copper and diamonds.
- Strip mining: Removes layers of soil to expose coal or other minerals in horizontal stripes.
This technique is efficient for large-scale operations but can lead to significant environmental disruption.
Underground Mining
Underground Mining targets deposits buried deep within the Earth. It employs methods such as:
- Shaft mining: Creates vertical shafts down to mineral deposits, common for gold and silver extraction.
- Room-and-pillar mining: Extracts materials while leaving pillars of rock for support, often used in coal mines.
Though less disruptive than surface mining, it poses risks such as cave-ins and requires extensive ventilation systems.
Placer Mining
Placer Mining focuses on extracting valuable minerals from alluvial deposits. This method uses water to separate heavier materials like gold from lighter sediments. Common techniques include:
- Panning: A simple manual method using a pan to wash away lighter sediment.
- Dredging: Involves using machinery to scoop up material from riverbeds or lakes.
Placer mining remains popular due to its effectiveness in finding precious metals without extensive equipment or infrastructure.
The Mining Process
Mining involves a systematic approach to uncovering valuable resources from beneath the Earth’s surface. This process consists of three main stages: exploration, extraction, and closure and reclamation.
Exploration
Exploration identifies potential mining sites and assesses their viability. Techniques used include geological mapping, sampling, and geophysical surveys. For example:
- Geological mapping provides insights into rock formations.
- Sampling analyzes soil or rock for mineral content.
- Geophysical surveys detect anomalies indicating resource presence.
These methods allow companies to pinpoint locations rich in minerals like gold, silver, or copper before investing in extraction efforts.
Extraction
Extraction focuses on removing resources from the ground using various techniques suited for specific materials. Common methods include:
- Open-pit mining, which involves digging large pits for minerals near the surface.
- Underground mining, where tunnels are created to access deeper deposits.
For instance, coal is often extracted through open-pit mining due to its proximity to the surface, while precious metals may require underground methods for safer retrieval.
Closure And Reclamation
Closure and reclamation ensure mined areas return to a stable state after resource extraction. This phase includes dismantling equipment and restoring landscapes. Key activities involve:
- Backfilling pits with waste material to minimize disruption.
- Replanting vegetation to revive local ecosystems.
By prioritizing these practices, mining operations can reduce environmental impacts and promote sustainability in affected regions.