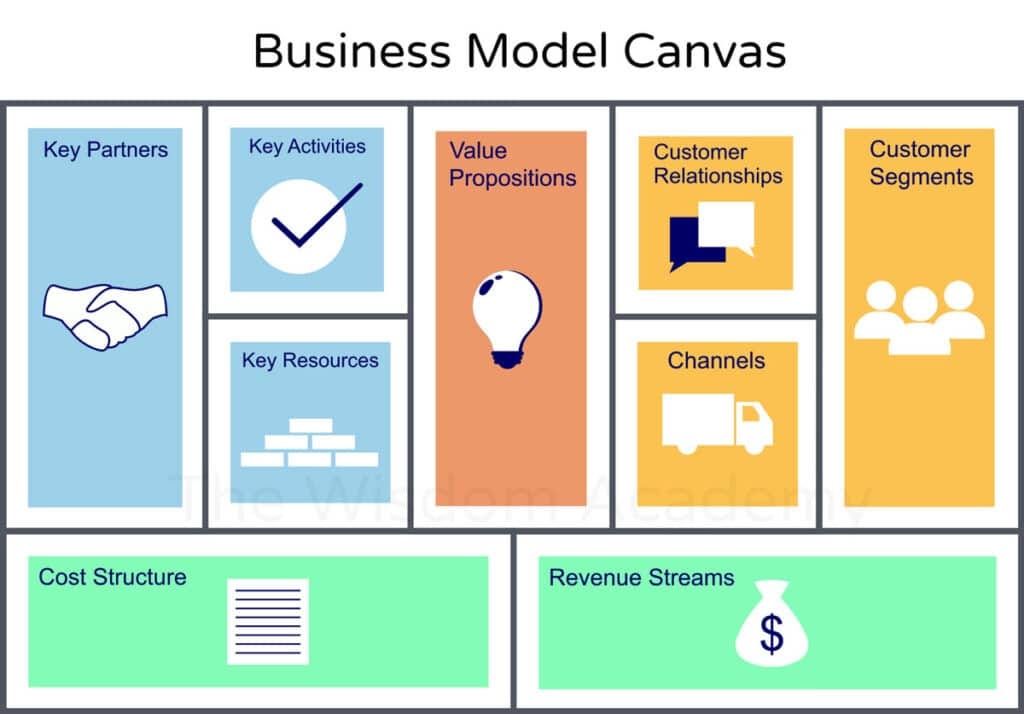
Ever wondered how some companies effortlessly thrive while others struggle to stay afloat? The secret often lies in their business model. A business model defines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. It’s the blueprint that outlines everything from revenue streams to customer relationships.
Understanding Business Models
A business model defines how a company operates and generates revenue. It clarifies the value proposition offered to customers, outlining who those customers are and what needs the product or service fulfills. Here are some common types of business models:
- Subscription Model: Companies like Netflix charge a recurring fee for access to content. This model ensures steady income while keeping customers engaged through regular updates.
- Freemium Model: Platforms such as Spotify offer basic services for free but charge for premium features. This approach attracts users quickly, converting a percentage into paying customers over time.
- E-commerce Model: Amazon exemplifies this by selling products directly to consumers online. By streamlining logistics and offering vast selections, companies can tap into global markets efficiently.
- Marketplace Model: eBay connects buyers with sellers without holding inventory. This model leverages user-generated content and transactions, creating diverse revenue streams through fees.
Each of these models illustrates different strategies for delivering value and making profits. Businesses often adapt or combine models to fit their unique circumstances in the market landscape.
Components of a Business Model
A business model consists of several key components that work together to define how a company operates. Understanding these elements helps you grasp the overall structure and strategy behind a business.
Value Proposition
The value proposition articulates why customers should choose your product or service over competitors’. It highlights the unique benefits that meet customer needs. For instance, strong value propositions can include:
- Quality: Offering superior products, like Apple with its innovative technology.
- Price: Providing lower costs, as seen in Walmart’s everyday low pricing strategy.
- Convenience: Streamlining processes, such as Amazon’s one-click shopping experience.
How well you communicate this proposition influences customer perception and loyalty.
Revenue Streams
Revenue streams are the various sources from which your business earns money. Identifying multiple streams can enhance financial stability. Examples include:
- Sales Revenue: Direct sales of products or services.
- Subscription Fees: Monthly charges for ongoing access, like Netflix’s streaming service.
- Licensing Fees: Allowing others to use proprietary technology or content.
Each stream contributes uniquely to overall profitability and growth potential.
Customer Segments
Customer segments define specific groups of people or organizations targeted by your business. Segmenting customers allows for tailored marketing strategies and offerings. Common segments might be:
- Demographic Segmentation: Targeting based on age, gender, or income level.
- Behavioral Segmentation: Grouping based on purchasing habits; consider Nike focusing on avid athletes.
- Geographic Segmentation: Catering to regional preferences; think about local restaurants adapting menus for cultural tastes.
Understanding your customer segments ensures effective communication and engagement tailored to their needs.
Types of Business Models
Understanding the different types of business models is essential for selecting a strategy that aligns with your goals. Each model offers unique approaches to delivering value and generating revenue.
Product-Based Models
Product-based models focus on selling tangible goods. Companies create, market, and distribute products directly to consumers or through retail channels. Some examples include:
- Manufacturers: Create products like electronics or clothing.
- Retailers: Sell these goods through physical or online stores.
- Wholesalers: Distribute goods in bulk to retailers.
Companies often emphasize quality and brand reputation to differentiate their products from competitors.
Service-Based Models
Service-based models provide intangible offerings, focusing on delivering expertise or assistance rather than physical items. Examples include:
- Consulting Firms: Offer specialized knowledge in various industries.
- Freelancers: Provide services such as graphic design or writing.
- Agencies: Deliver marketing, advertising, or public relations services.
These businesses often depend on building strong client relationships for repeat engagement and referrals.
Subscription Models
Subscription models involve charging customers a recurring fee for ongoing access to products or services. This approach fosters customer loyalty and predictable revenue streams. Examples include:
- Streaming Services: Platforms like Netflix charge monthly fees for access to content libraries.
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS): Companies like Adobe offer software subscriptions instead of one-time purchases.
- Subscription Boxes: Brands send curated products regularly, appealing to niche interests.
This model encourages long-term customer engagement, making it easier to forecast income and plan future growth.
Importance of Business Models
Understanding the importance of business models is crucial for any entrepreneur. A well-defined business model aligns your company’s strategy with its goals, providing a roadmap for growth and sustainability.
Business models clarify how you create value. They outline what products or services you offer, who your customers are, and how you deliver those offerings effectively. For example, if you’re running an e-commerce store, having a clear model helps streamline operations from inventory management to customer service.
Effective business models enhance competitive advantage. By identifying unique selling propositions, you can differentiate yourself in the market. Companies like Apple leverage innovative design and superior customer experience to maintain their edge over competitors.
Diverse revenue streams contribute to financial stability. Many businesses today rely on multiple income sources to mitigate risks. For instance, software companies often use subscription models alongside one-time purchases; this fosters predictable cash flow while expanding their customer base.
Customer segmentation drives targeted marketing strategies. Understanding your audience allows for tailored messaging that resonates with specific groups. A clothing retailer might segment customers by age or style preferences to optimize product offerings and promotional efforts.
Grasping the significance of your business model shapes strategic decisions and enhances overall performance in today’s competitive landscape.
Case Studies of Successful Business Models
Amazon exemplifies a successful e-commerce model. It started as an online bookstore but expanded into various categories, including electronics and groceries. This platform uses data-driven insights to personalize shopping experiences, fostering customer loyalty and repeat purchases.
Netflix operates on a subscription model. Initially offering DVD rentals, it shifted to streaming content, providing unlimited access for a flat monthly fee. This approach not only attracted millions of subscribers but also allowed Netflix to invest in original programming, enhancing its value proposition.
Airbnb utilizes a marketplace model that connects hosts with travelers seeking accommodation. By enabling individuals to rent out their properties, Airbnb capitalizes on unused space while offering unique lodging options. This flexibility appeals to diverse customer segments looking for affordability or local experiences.
Apple showcases the product-based business model with premium pricing strategies for its tech products. Apple’s brand loyalty stems from innovative design and quality features, creating high demand despite higher prices compared to competitors.
Dollar Shave Club disrupted the shaving industry through its subscription service that delivers razors directly to customers’ doors each month. The company’s humorous marketing campaigns resonate with consumers while emphasizing cost savings and convenience—ideal factors in today’s market.
Each case highlights different aspects of effective business models: personalization, subscriber retention, leveraging technology, premium branding, and direct-to-consumer sales—all contributing significantly to their success in competitive landscapes.