Ever wondered why some foods keep you full longer or give you that burst of energy? Understanding what macronutrients are can unlock the secrets to a balanced diet and optimal health. Macronutrients are the building blocks of your nutrition, playing crucial roles in how your body functions daily.
What Are Macronutrients?
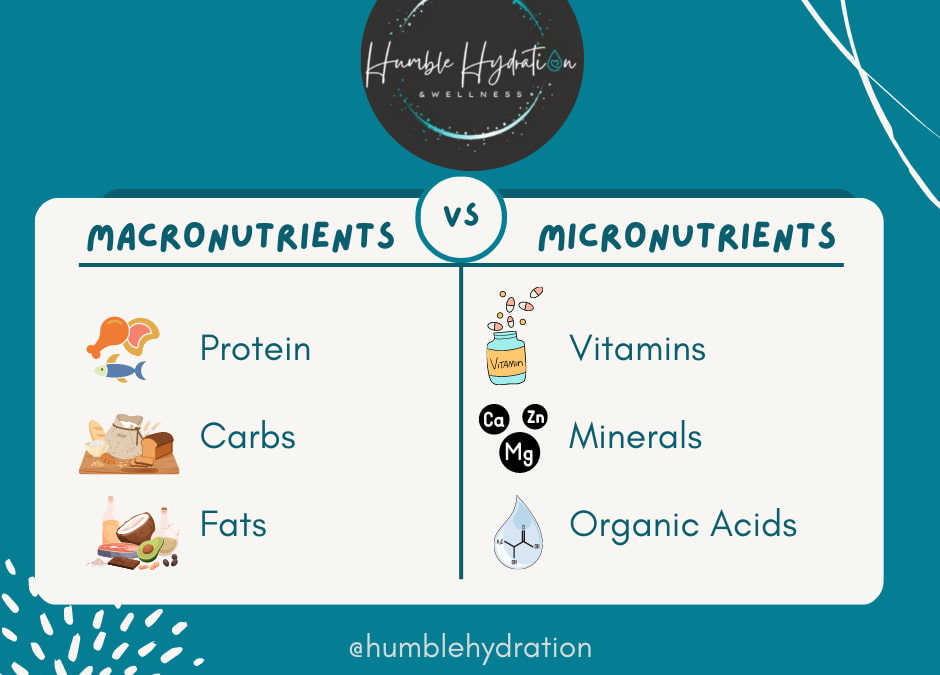
Macronutrients are essential nutrients that provide energy and support various bodily functions. They play a significant role in maintaining health and wellness. Understanding macronutrients helps you make informed dietary choices.
There are three primary types of macronutrients:
- Carbohydrates: These provide quick energy. Common sources include fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes.
- Proteins: Proteins help build and repair tissues. Sources range from meat, fish, eggs to plant-based options like beans and nuts.
- Fats: Healthy fats support cell growth and protect organs. Examples include avocados, olive oil, seeds, and fatty fish.
Each macronutrient serves distinct functions in your body. For instance, carbohydrates fuel your workouts while proteins aid muscle recovery. Fats contribute to hormone production and brain health.
Balancing these macronutrients is crucial for optimal nutrition. A diet rich in diverse foods ensures you receive the right amount of each nutrient to meet your body’s needs.
Types of Macronutrients
Understanding the types of macronutrients is crucial for maintaining a balanced diet. Each type plays a unique role in your body, contributing to overall health and energy levels.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates serve as the primary energy source for your body. They can be categorized into simple and complex carbs. Examples include:
- Simple carbohydrates: Sugary foods, such as candy and soda.
- Complex carbohydrates: Whole grains like brown rice and oats; vegetables like sweet potatoes; legumes such as lentils and chickpeas.
These sources provide quick or sustained energy, depending on their complexity.
Proteins
Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues in your body. They consist of amino acids, which are vital for numerous bodily functions. Common protein sources include:
- Animal-based proteins: Chicken breast, fish, beef, and eggs.
- Plant-based proteins: Tofu, quinoa, beans (black beans or kidney beans), and nuts (almonds or peanuts).
Incorporating a variety of these options helps meet your daily protein needs.
Fats
Fats play an important role in cell growth and protecting vital organs. They come in saturated, unsaturated, and trans forms. Healthy fat examples consist of:
- Unsaturated fats: Avocados, olive oil, nuts (walnuts or hazelnuts), fatty fish (salmon or mackerel).
- Saturated fats: Butter, cheese, coconut oil—these should be consumed in moderation.
Avoid trans fats found in processed snacks; they pose health risks when consumed regularly.
By understanding these macronutrient types better, you can make more informed dietary choices that align with your health goals.
Importance of Macronutrients
Macronutrients play a vital role in your overall health and wellness. They provide energy, support bodily functions, and contribute to growth and repair processes. Understanding their importance helps you make informed dietary choices.
Energy Production
Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are the primary sources of energy for your body. Carbohydrates serve as the quickest energy source. Foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supply immediate fuel for daily activities. Proteins offer a more sustained form of energy. Sources such as lean meats, fish, and legumes help maintain energy levels over time. Fats provide long-lasting energy reserves. Healthy fats found in avocados and nuts support endurance during prolonged physical activities.
Body Function and Repair
Macronutrients also play crucial roles in maintaining various body functions. Proteins are essential for tissue building and repair. They facilitate muscle recovery after workouts through sources like chicken or plant-based options such as lentils. Fats contribute to hormone production. Essential fatty acids found in fish oil support cellular function throughout the body. Additionally, carbohydrates ensure that your brain operates optimally by providing glucose necessary for cognitive functions; without sufficient carbs, mental fatigue can set in quickly.
By understanding how each macronutrient benefits you directly, you’ll find it easier to create balanced meals that promote better health outcomes.
Recommended Macronutrient Ratios
Balancing macronutrients is crucial for achieving optimal health. Generally, a common recommendation suggests the following ratios:
- Carbohydrates: 45-65% of total daily calories
- Proteins: 10-35% of total daily calories
- Fats: 20-35% of total daily calories
For example, if you consume 2,000 calories per day, aim for about 225-325 grams of carbohydrates, 50-175 grams of protein, and 44-78 grams of fat.
Furthermore, these ratios can vary depending on individual goals. If you’re aiming to lose weight or build muscle, adjusting your intake might help. For instance:
Additionally, physical activity levels influence macronutrient needs. Active individuals often require more carbohydrates for energy while having increased protein needs for recovery.
Ultimately, understanding these recommended ratios helps create balanced meals that suit your lifestyle and health objectives.