Criminal records can seem daunting, but understanding them is crucial. Have you ever wondered what types of offenses might appear on a criminal record? In this article, you’ll discover various examples of criminal records that can impact someone’s life and opportunities.
Understanding Criminal Records
Criminal records contain detailed information about an individual’s criminal history. These documents provide insight into various offenses, which can range from minor infractions to serious felonies. Here are some common examples of what you might find on a criminal record:
- Misdemeanors: Offenses like petty theft, vandalism, or simple assault fall into this category. They usually carry lighter penalties than felonies.
- Felonies: Serious crimes such as robbery, murder, or drug trafficking result in harsher punishments. Felony convictions often lead to imprisonment for over one year.
- Traffic Violations: Incidents like driving under the influence (DUI) or reckless driving may appear as part of your record and affect insurance rates.
- Sex Offender Registrations: Certain convictions require individuals to register as sex offenders. This impacts employment opportunities and housing options significantly.
- Arrests Without Convictions: Even if charges don’t lead to a conviction, arrests remain on your record and can be accessed by employers and others.
Understanding these examples helps you grasp how criminal records function in society. You should consider how they impact job applications or other legal situations.
Types of Criminal Records
Understanding the different types of criminal records is essential for grasping how these documents impact individuals. Each type carries specific information and implications that can affect various aspects of life.
Arrest Records
Arrest records document instances where law enforcement agencies have detained individuals. These records include details such as the date of arrest, location, and charges filed. For example, if someone gets arrested for theft, that incident will appear on their arrest record regardless of whether they were convicted. It’s crucial to note that an arrest does not imply guilt; many arrests do not lead to convictions.
Conviction Records
Conviction records indicate a formal judgment against an individual after a legal trial or plea agreement. This includes outcomes from both misdemeanor and felony cases. For instance, if a person pleads guilty to drug possession, this conviction will show up on their record permanently unless expunged under specific conditions. These records often carry significant weight during background checks for employment or housing applications.
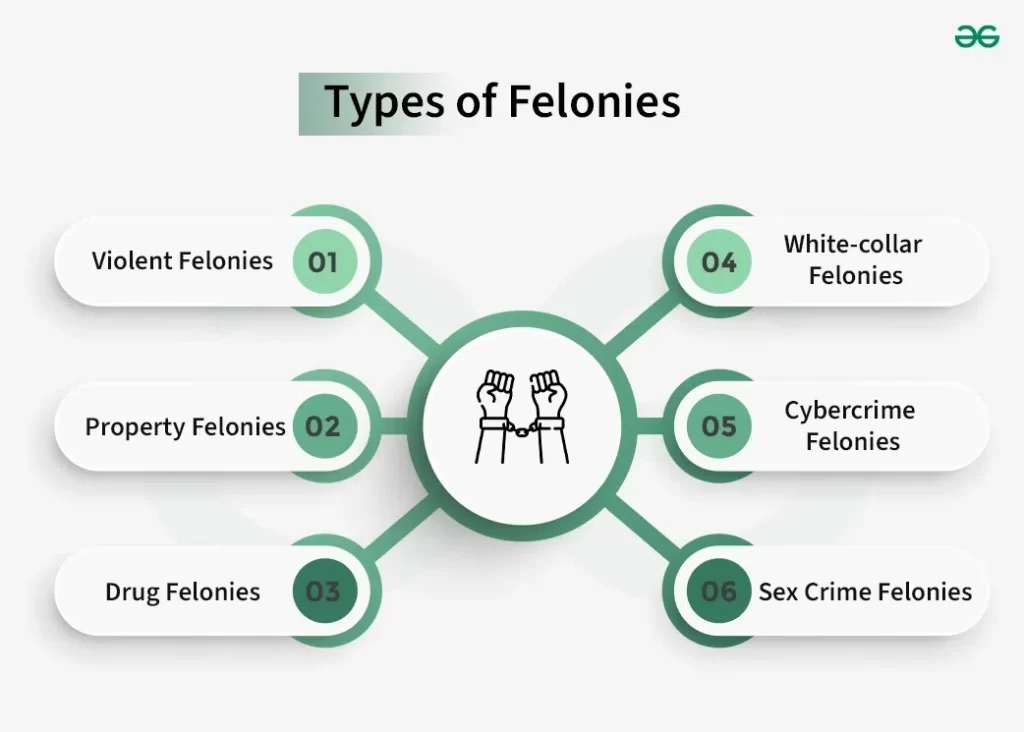
Felony Records
Felony records represent serious crimes resulting in harsher penalties. Common felonies include murder, sexual assault, and robbery. A felony conviction typically results in imprisonment for more than one year and may limit voting rights or job opportunities afterward. For example, an individual convicted of aggravated assault could face years behind bars along with lasting repercussions on their professional life due to this felony record.
Misdemeanor Records
Misdemeanor records cover less severe offenses but still hold importance in legal contexts. Examples include petty theft and simple assault which usually result in lighter sentences like fines or short jail time (often less than one year). Even though misdemeanors are viewed as less serious than felonies, they can still impact your employment prospects significantly if discovered during background checks. Individuals with misdemeanor convictions should be aware of how these might affect various opportunities moving forward.
Specific Examples of Criminal Records
Criminal records can vary widely based on the nature of offenses. Here are specific examples that illustrate different types of criminal activities.
Drug Offenses
Drug offenses often include various illegal activities related to controlled substances. Common examples are:
- Possession: Holding illegal drugs like marijuana, cocaine, or heroin.
- Distribution: Selling or distributing narcotics to others.
- Manufacturing: Producing illicit drugs in a home lab.
Each type carries serious legal consequences, affecting employment and personal freedom.
Theft Crimes
Theft crimes encompass a range of unlawful acts involving taking someone else’s property. Examples include:
- Burglary: Breaking into a building with intent to commit theft.
- Shoplifting: Stealing items from a retail store.
- Robbery: Taking property from someone through force or intimidation.
The repercussions for theft can lead to significant penalties, impacting your future opportunities.
Violent Crimes
Violent crimes involve harm or the threat of harm against individuals. Some examples consist of:
- Assault: Physically attacking another person.
- Homicide: Intentionally causing someone’s death.
- Kidnapping: Unlawfully seizing and carrying away a person by force.
Being charged with violent crimes often results in severe legal outcomes, including imprisonment.
Domestic Violence Offenses
Domestic violence offenses occur within intimate relationships and can take many forms. Key examples are:
- Physical Abuse: Hitting, slapping, or otherwise harming an intimate partner.
- Emotional Abuse: Manipulating or controlling behavior towards a partner.
- Stalking: Repeatedly following or harassing someone, creating fear for their safety.
Such offenses not only affect relationships but also carry heavy legal consequences.
Importance of Criminal Records
Criminal records serve as official documentation of an individual’s legal history. They play a significant role in various aspects of life, influencing decisions made by employers, landlords, and even governmental agencies. Understanding these records is crucial for navigating potential challenges.
Criminal records can affect job opportunities. Employers often conduct background checks to assess candidates’ suitability. A record may limit access to certain positions, particularly in sensitive fields like education or healthcare.
Housing applications can also be impacted by criminal records. Landlords frequently check applicants’ backgrounds before approval. A negative record might lead to denial or higher rental costs.
Court proceedings rely on the accuracy of criminal records. Whether it’s for sentencing or parole considerations, judges use these documents to make informed decisions about individuals’ futures.
Types of offenses listed include:
- Misdemeanors: Minor crimes that still influence employment chances.
- Felonies: Serious crimes with long-lasting repercussions on personal freedom and opportunities.
- Traffic violations: Even these can lead to increased insurance rates and other penalties.
Being aware of your own criminal record empowers you to address any issues proactively. You gain insight into how this information shapes perceptions and may alter life’s path.