Imagine a figure that perfectly embodies the harmony of art and science. The Vitruvian Man, created by Leonardo da Vinci, isn’t just a stunning piece of art; it’s a profound exploration of human proportions and their connection to the universe. This iconic drawing has captivated minds for centuries, serving as a symbol of the Renaissance’s quest for knowledge.
In this article, you’ll discover how the Vitruvian Man reflects principles of geometry and anatomy while influencing various fields from art to architecture. Have you ever wondered why this image remains so relevant today? By delving into its historical context and significance, we’ll uncover the layers behind this masterpiece. Join us as we explore examples that highlight its impact on culture and design, revealing why the Vitruvian Man continues to inspire creativity in our modern world.
Overview of the Vitruvian Man
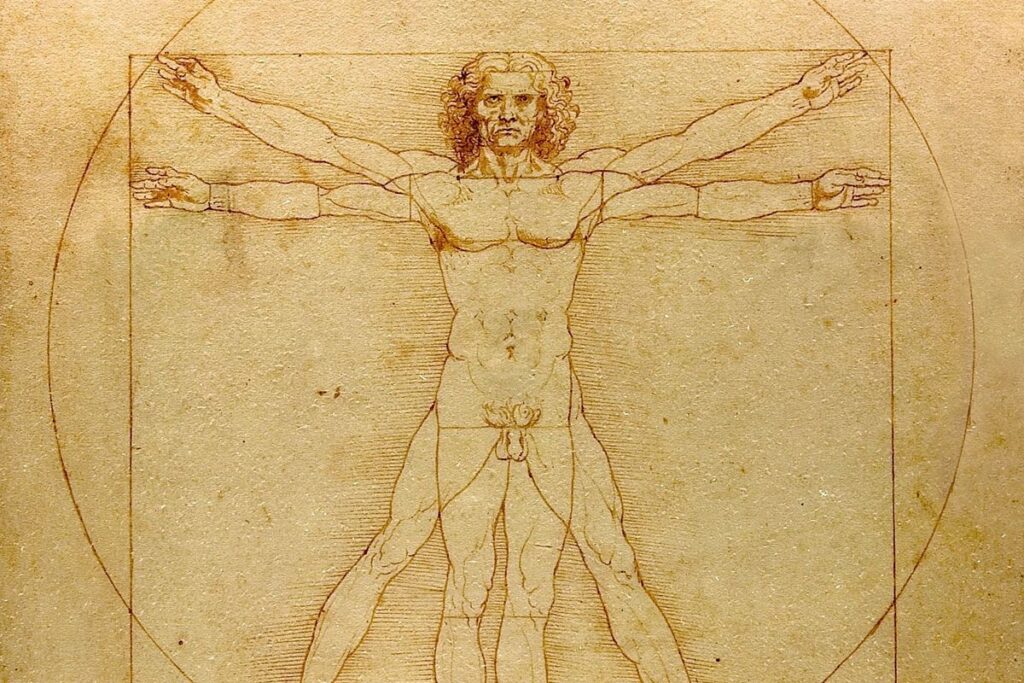
The Vitruvian Man represents a fusion of art and science, illustrating human proportions based on the work of the ancient Roman architect Vitruvius. This drawing, created by Leonardo da Vinci around 1490, showcases how ideal human measurements relate to geometric shapes.
Key aspects include:
- Proportions: Da Vinci emphasized specific ratios, such as the distance from the top of the head to the chin being one-eighth of total height.
- Geometry: The circle and square surrounding the figure symbolize harmony and balance in nature.
- Influence on Art: Artists like Michelangelo drew inspiration from this work for their representations of human form.
The impact extends beyond art into fields like architecture and design. Modern architects reference these proportions when creating functional spaces that resonate with beauty. The enduring relevance reflects society’s ongoing fascination with symmetry and proportion in both natural forms and man-made structures.
Historical Context
The Vitruvian Man emerged during a time of significant cultural and intellectual transformation. Its creation reflects the Renaissance’s emphasis on humanism, mathematics, and nature.
Leonardo da Vinci’s Life and Works
Leonardo da Vinci, born in 1452, exemplified the Renaissance ideal of a polymath. His diverse interests spanned art, science, engineering, and anatomy. The Vitruvian Man illustrates his obsession with proportion and symmetry. You can see this in other works like the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper, where he meticulously studied human emotion and posture.
Influence of Ancient Roman Art
Ancient Roman art profoundly impacted Da Vinci’s work. The principles from Vitruvius’ writings emphasized balance and harmony in design. For example:
- Proportions: Vitruvius outlined ideal human measurements that inspired Da Vinci.
- Architecture: Roman structures showcased geometric precision that influenced Renaissance architects.
- Sculpture: The focus on realism in Roman sculptures set standards for portraying the human form.
These elements combined shaped Da Vinci’s artistic vision, making the Vitruvian Man not just an artwork but a symbol of timeless beauty rooted in ancient wisdom.
Symbolism and Interpretation
The Vitruvian Man embodies deep symbolism, reflecting the harmony between human existence and the universe. This iconic drawing illustrates key themes around proportions and relationships.
Proportions of the Human Body
The proportions depicted in the Vitruvian Man follow specific mathematical ratios. Leonardo da Vinci based them on Vitruvius’ work, emphasizing that a well-proportioned human body fits perfectly within a circle and a square. For instance:
- The nail length equals one-tenth of total height.
- The arm span matches the height, showcasing balance.
These measurements underscore how ideal dimensions relate to beauty and functionality.
Relationship Between Art and Science
The Vitruvian Man serves as a bridge between art and science. Da Vinci’s meticulous attention to anatomical detail reveals his scientific inquiry into human form. He studied anatomy extensively, integrating artistic skills with empirical observation. This fusion enhances our understanding of both disciplines:
- Artists draw inspiration from its aesthetic qualities.
- Scientists reference it for insights into human anatomy.
By merging these fields, the drawing highlights humanity’s quest for knowledge through creativity.
The Vitruvian Man in Modern Culture
The Vitruvian Man continues to resonate in contemporary culture, influencing various fields like art, design, and branding.
References in Art and Design
You can find the Vitruvian Man referenced in numerous artworks and designs. For instance, contemporary artists often reinterpret Da Vinci’s drawing to explore themes of human proportion and symmetry. Graphic designers frequently incorporate the figure into logos or promotional materials, emphasizing balance. Notably:
- Fashion: Designers utilize its proportions for clothing patterns.
- Architecture: Architects reference it when creating harmonious structures.
- Digital Media: Animators draw upon its structure for character design.
These adaptations showcase how Da Vinci’s work remains relevant by inspiring new interpretations.
Use in Branding and Logos
Many brands leverage the symbolic power of the Vitruvian Man to convey ideals of precision and harmony. Companies use this image to communicate values such as innovation and quality. For example:
- Health & Fitness Brands: Use it to promote balanced lifestyles.
- Technology Firms: Incorporate it into their logos for a modern look.
- Educational Institutions: Embrace it as a symbol of knowledge integration.
By using the Vitruvian Man, brands connect with audiences through shared values of beauty and proportionality. It’s fascinating how a 15th-century drawing still influences our visual language today.