Ever wondered why vitamins and minerals are essential for your health? These tiny yet powerful nutrients play a crucial role in keeping your body functioning at its best. From boosting your immune system to supporting bone health, understanding the importance of vitamins and minerals can transform your overall well-being.
Overview of Vitamins and Minerals
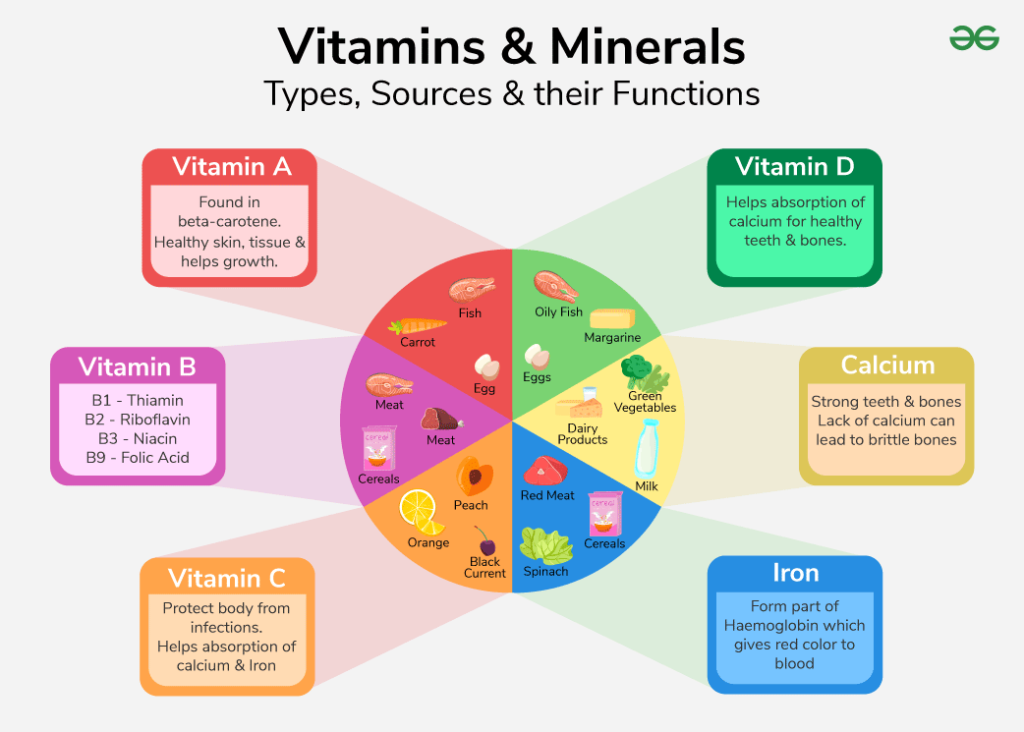
Vitamins and minerals are crucial for your body’s health. They support numerous bodily functions, including metabolism, immunity, and bone strength. Here’s a closer look at some essential vitamins and minerals:
Vitamins
- Vitamin A: Important for vision and immune function. Found in carrots and sweet potatoes.
- Vitamin C: Supports the immune system and aids in collagen production. Citrus fruits like oranges are rich sources.
- Vitamin D: Crucial for calcium absorption and bone health. Sunlight exposure helps your body produce it naturally.
- Calcium: Vital for strong bones and teeth. Dairy products such as milk provide significant amounts.
- Iron: Essential for red blood cell production. Found in meats, beans, and spinach.
- Magnesium: Plays a role in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body. Nuts, seeds, and whole grains contain high levels.
These nutrients work together to maintain your overall well-being. It’s important to consume a balanced diet to ensure you’re getting enough of these vital vitamins and minerals daily.
Types of Vitamins
You can categorize vitamins into two main types: water-soluble and fat-soluble. Understanding these categories helps you recognize how your body uses them.
Water-Soluble Vitamins
Water-soluble vitamins dissolve in water, making it easy for your body to absorb them. These vitamins include:
- Vitamin C: Important for immune function and skin health.
- B-complex Vitamins: This group includes B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B5 (pantothenic acid), B6 (pyridoxine), B7 (biotin), B9 (folate), and B12 (cobalamin). Each plays a unique role, from energy production to brain health.
Since your body doesn’t store these vitamins, regular intake through food is essential. Foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes provide ample sources.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins
Fat-soluble vitamins require dietary fats for absorption. These include:
- Vitamin A: Supports vision and immune system functionality.
- Vitamin D: Essential for calcium absorption and bone health.
- Vitamin E: Acts as an antioxidant that protects cells from damage.
- Vitamin K: Vital for blood clotting and bone metabolism.
These vitamins can be stored in the liver and fatty tissues. Consume foods like nuts, seeds, dairy products, fish oils, and leafy greens to ensure adequate intake.
Essential Minerals
Minerals play a crucial role in your body, supporting various functions and maintaining overall health. They can be categorized into major minerals and trace minerals, each with specific benefits.
Major Minerals
Major minerals are essential for numerous bodily processes. These include:
- Calcium: Vital for strong bones and teeth, calcium also supports muscle function and nerve signaling. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods are excellent sources.
- Potassium: This mineral helps regulate fluid balance, muscle contractions, and nerve signals. Foods rich in potassium include bananas, oranges, potatoes, and spinach.
- Magnesium: Important for over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, magnesium contributes to energy production and muscle relaxation. Nuts, seeds, whole grains, and legumes offer good amounts.
Trace Minerals
Trace minerals are needed in smaller quantities but remain critical for health. Key examples include:
- Iron: Necessary for red blood cell production and oxygen transport throughout the body. Red meat, beans, lentils, and spinach provide ample iron.
- Zinc: Supports immune function and wound healing while playing a role in protein synthesis. Sources of zinc include meat, shellfish, dairy products, nuts, and whole grains.
- Selenium: Acts as an antioxidant that protects cells from damage while supporting thyroid function. Brazil nuts are one of the richest sources of selenium along with seafoods like tuna or shrimp.
By incorporating these essential minerals into your diet through diverse food choices like fruits vegetables or whole grains you can support your body’s vital functions effectively.
Health Benefits of Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals play crucial roles in your overall health. They support various bodily functions, influencing everything from energy levels to immune response. Here are some key benefits:
- Vitamin A: This vitamin is vital for maintaining healthy vision and a robust immune system. Foods like carrots, sweet potatoes, and spinach provide ample Vitamin A.
- Vitamin C: Known for its role in boosting immunity, it also aids collagen production, essential for skin health. Citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers are excellent sources.
- Vitamin D: It promotes calcium absorption, which is critical for bone strength. Sunlight exposure helps your body produce Vitamin D; fatty fish and fortified foods offer additional sources.
- Calcium: Essential for strong bones and teeth, calcium also supports muscle function. Dairy products like milk and yogurt deliver high amounts of this mineral.
- Iron: Necessary for red blood cell production, iron helps transport oxygen throughout your body. You can find it in red meat, beans, lentils, and fortified cereals.
- Magnesium: This mineral plays a role in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body. Nuts, seeds, whole grains, and leafy greens supply magnesium effectively.
Incorporating a variety of these vitamins and minerals into your diet ensures you meet nutritional needs effectively. Eating colorful fruits and vegetables alongside whole grains helps maintain balance while promoting overall well-being.
Sources of Vitamins and Minerals
Understanding where to find vitamins and minerals is essential for maintaining optimal health. A well-rounded diet ensures you receive these nutrients naturally, while supplements can also help fill any gaps.
Dietary Sources
Various foods provide a rich array of vitamins and minerals. Here are some key examples:
- Fruits: Citrus fruits like oranges and grapefruits supply Vitamin C, while bananas offer potassium.
- Vegetables: Leafy greens such as spinach and kale are packed with Vitamins A, C, K, and magnesium.
- Whole grains: Foods like brown rice and quinoa deliver B-complex vitamins along with iron.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds provide Vitamin E, while chia seeds contain omega-3 fatty acids.
- Dairy products: Milk and yogurt are excellent sources of calcium and riboflavin.
These foods not only contribute to your daily nutrient intake but also support overall health through diverse benefits.
Supplementation
While getting nutrients from food is ideal, supplementation can be useful in certain cases. Consider the following points:
- Multivitamins: These can help cover various deficiencies if your diet lacks specific nutrients.
- Vitamin D supplements: Useful during winter months or for those with limited sun exposure.
- Calcium supplements: Beneficial for individuals who don’t consume enough dairy products or leafy greens.
Consulting a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen is wise to ensure it aligns with your individual needs.