Imagine sitting in a meeting where complex ideas are tossed around, but you struggle to grasp them. This is where visual aids come into play, transforming confusion into clarity. Whether it’s a chart that illustrates trends or an infographic breaking down statistics, these tools enhance understanding and retention.
In this article, you’ll discover various examples of visual aids, each designed to make information more accessible and engaging. From slideshows that captivate audiences to diagrams that simplify processes, visual aids can elevate your communication skills. Ever wondered how a simple image can convey messages faster than words? Let’s dive into the world of visual aids and explore their powerful impact on learning and presentations.
Understanding Visual Aid
Visual aids play a crucial role in simplifying complex information, making it easier for audiences to grasp concepts quickly. They enhance engagement and retention during presentations or discussions.
Definition of Visual Aid
A visual aid refers to any item that helps convey information visually. Examples include:
- Charts: Bar charts or pie charts illustrate data trends clearly.
- Infographics: These combine graphics and text to represent statistics or processes succinctly.
- Slideshows: PowerPoint presentations allow for organized content delivery with visuals.
- Videos: Short clips can demonstrate processes or showcase products effectively.
These tools help clarify your points and keep your audience focused.
Importance of Visual Aids in Communication
Visual aids significantly enhance understanding by breaking down complicated ideas. People process visuals faster than text, so you capture their attention more effectively.
Using visual aids improves communication by:
- Increasing Retention: Information paired with images sticks better in memory.
- Encouraging Engagement: Audiences are more likely to participate when they see relevant visuals.
- Simplifying Complex Ideas: Charts and diagrams can simplify dense information into digestible formats.
Incorporating these elements into your presentations not only boosts clarity but also fosters a more interactive experience for everyone involved.
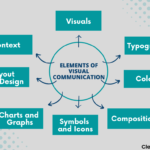
Types of Visual Aids
Visual aids come in various forms, each serving a unique purpose. Understanding these types helps you choose the right one for your presentation.
Charts and Graphs
Charts and graphs effectively display data trends and comparisons. For instance, bar charts can illustrate sales growth over several years, while pie charts show percentage breakdowns of market share. Line graphs are excellent for depicting changes over time, such as stock performance. These visual tools make complex numerical information clearer and more digestible.
Diagrams and Illustrations
Diagrams and illustrations simplify intricate concepts through clear visuals. Flowcharts guide audiences through processes step-by-step, making them ideal for explaining workflows. Venn diagrams highlight relationships between different sets, which is useful in comparative analyses. Additionally, labeled illustrations can clarify complex structures like human anatomy or mechanical systems.
Videos and Multimedia
Videos and multimedia elements enhance presentations by adding dynamic content. Short clips can demonstrate product features or showcase case studies effectively. Interactive slideshows engage viewers by allowing them to explore content at their own pace. Incorporating audio-visual elements not only captures attention but also reinforces key messages in memorable ways.
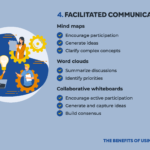
Benefits of Using Visual Aids
Visual aids significantly enhance presentations and meetings. They simplify complex information, making it easier for audiences to understand key points.
Enhancing Understanding
Visual aids clarify complex concepts. For instance, a detailed infographic can break down intricate data into digestible segments. When you use diagrams, they help illustrate relationships among ideas clearly. Additionally, flowcharts guide your audience through processes step-by-step, ensuring everyone stays on the same page.
Improving Retention
Visual aids improve memory retention. Research indicates that people remember 80% of what they see compared to only 20% of what they hear. Incorporating videos or interactive slides engages viewers more effectively and reinforces important messages. Moreover, utilizing consistent colors and themes across visual elements helps create mental associations that aid recall later on.
Best Practices for Creating Effective Visual Aids
Creating effective visual aids requires attention to detail and an understanding of your audience. Focus on making information accessible and engaging.
Clarity and Simplicity
Clarity is crucial when designing visual aids. Use straightforward language, avoid jargon, and ensure that each element serves a clear purpose. For example:
- Limit text: Use bullet points instead of long paragraphs.
- Choose simple images: Select visuals that directly relate to your message.
- Highlight key points: Emphasize important data or concepts with larger fonts or contrasting colors.
These practices help audiences quickly grasp essential information without confusion.
Appropriate Use of Colors and Fonts
The right colors and fonts enhance comprehension. Choose a color palette that aligns with your content while maintaining readability. For instance:
- Use complementary colors: Ensure contrast between text and background for better visibility.
- Stick to 2-3 fonts: Limit font types for consistency; one for headings, another for body text works well.
- Consider accessibility: Avoid color combinations that may be difficult for colorblind individuals to distinguish.
By focusing on these elements, you create visually appealing aids that effectively communicate your message.