Have you ever wondered how companies can thrive by venturing into completely different industries? Unrelated diversification examples showcase the bold strategies businesses use to expand their horizons and mitigate risks. By exploring these diverse ventures, organizations not only tap into new markets but also leverage their core competencies in unexpected ways.
Understanding Unrelated Diversification
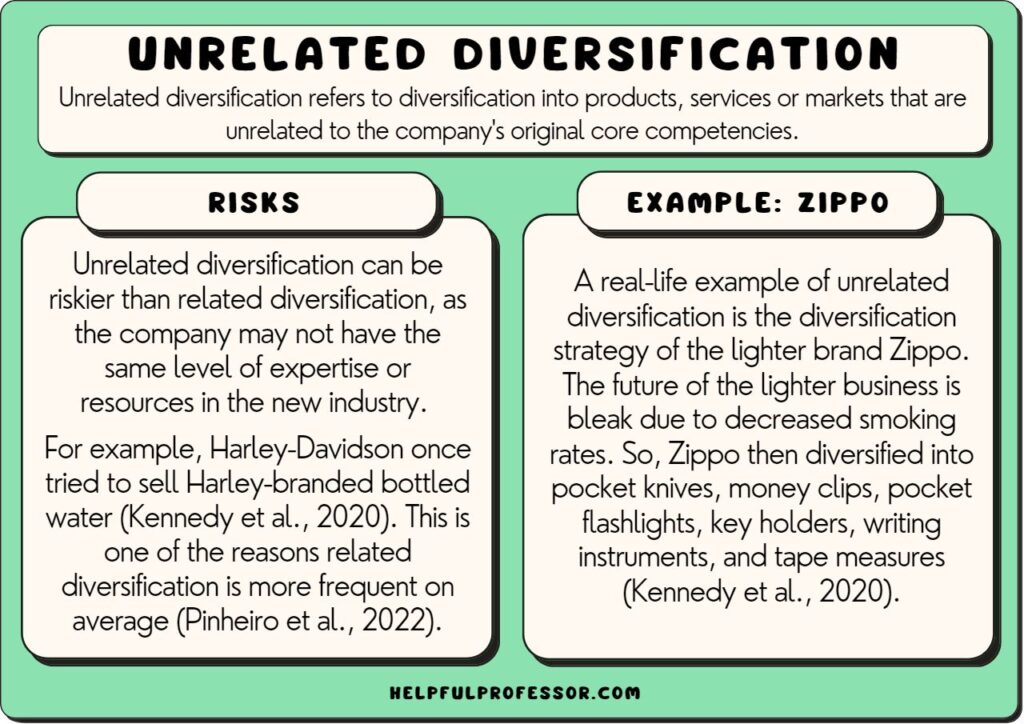
Unrelated diversification occurs when a company expands into industries that bear no direct connection to its core business. This strategy helps reduce risks by spreading investments across various sectors. Here are some notable examples:
- General Electric (GE): Initially focused on electrical equipment, GE ventured into diverse areas like healthcare and aviation, showcasing its broad capabilities.
- Disney: While known for entertainment, Disney has entered sectors such as travel with resorts and streaming services, effectively leveraging its brand.
- Amazon: Starting as an online bookstore, Amazon now operates in cloud computing with AWS and even grocery retail through Whole Foods.
Such strategies enable businesses to tap into new revenue streams while minimizing dependency on a single market. Engaging in unrelated diversification allows firms to utilize their existing resources creatively.
Benefits of Unrelated Diversification
Unrelated diversification offers several advantages for businesses looking to expand their operations. By entering different industries, companies create opportunities that can lead to significant growth and stability.
Risk Mitigation
Risk mitigation becomes a key benefit of unrelated diversification. When you engage in multiple industries, downturns in one sector don’t necessarily affect your entire business. This strategy spreads risk across various markets, reducing vulnerability. For instance:
- General Electric diversified from appliances to healthcare, minimizing risks associated with fluctuating consumer demand.
- Disney ventured into streaming and travel, safeguarding against declines in traditional media revenue.
By diversifying, you can stabilize your income streams and protect your investments.
Capitalizing on New Markets
Capitalizing on new markets is another significant advantage of unrelated diversification. Entering different sectors opens doors to untapped customer bases. Companies leverage their existing expertise while exploring innovative products or services. Consider these examples:
- Amazon’s expansion from bookselling into cloud computing has transformed its market presence.
- Apple, originally focused on computers, now excels in music streaming and wearables.
These moves allow businesses like yours to seize growth opportunities that would otherwise remain inaccessible. By tapping into diverse markets, you increase potential revenues and enhance overall competitiveness.
Notable Unrelated Diversification Examples
Unrelated diversification showcases how businesses can thrive in completely different sectors. Here are some notable examples that illustrate this strategy effectively.
Example 1: General Electric
General Electric (GE) demonstrates successful unrelated diversification by expanding into healthcare and renewable energy. Originally focused on electrical equipment, GE ventured into medical imaging technologies and wind turbine manufacturing. This shift not only spread risks but also opened new revenue streams, allowing GE to leverage its engineering expertise across various industries.
Example 2: Disney
Disney’s expansion into travel and streaming services exemplifies unrelated diversification. While primarily known for animation and entertainment, Disney entered the theme park industry with Disneyland and launched Disney+ for streaming content. These ventures enable Disney to reach a broader audience while enhancing brand loyalty through diverse offerings.
Example 3: Amazon
Amazon illustrates how unrelated diversification can transform a business model. Initially an online bookstore, Amazon diversified into cloud computing with AWS and grocery retail through Whole Foods. This strategic move allowed Amazon to tap into multiple markets, reducing reliance on a single product category while fostering innovation across various sectors.
Challenges of Unrelated Diversification
Unrelated diversification presents various challenges that companies must navigate. Understanding these issues is crucial for any business considering this strategy.
Management Complexity
Management complexity increases significantly when a company diversifies into unrelated industries. Different sectors often require distinct expertise and operational approaches. For example, a firm known for manufacturing electronics may struggle to manage a hospitality division effectively. This can lead to inefficiencies as leadership teams grapple with diverse market dynamics and cultural differences across industries.
Resource Allocation Issues
Resource allocation issues can arise when businesses enter multiple unrelated markets. Companies might face difficulties in determining where to invest financial and human resources most effectively. Take the case of a company branching into both healthcare and automotive sectors; it risks spreading itself too thin, potentially undermining its performance in each area. Prioritizing projects becomes challenging, complicating strategic decision-making processes.