Have you ever wondered why some individuals seem to excel effortlessly in certain areas? Understanding the different types of giftedness can shed light on these remarkable abilities and how they manifest in various forms. Giftedness isn’t just about high IQ scores; it encompasses a range of talents and skills that can be categorized into distinct types.
Overview Of Giftedness
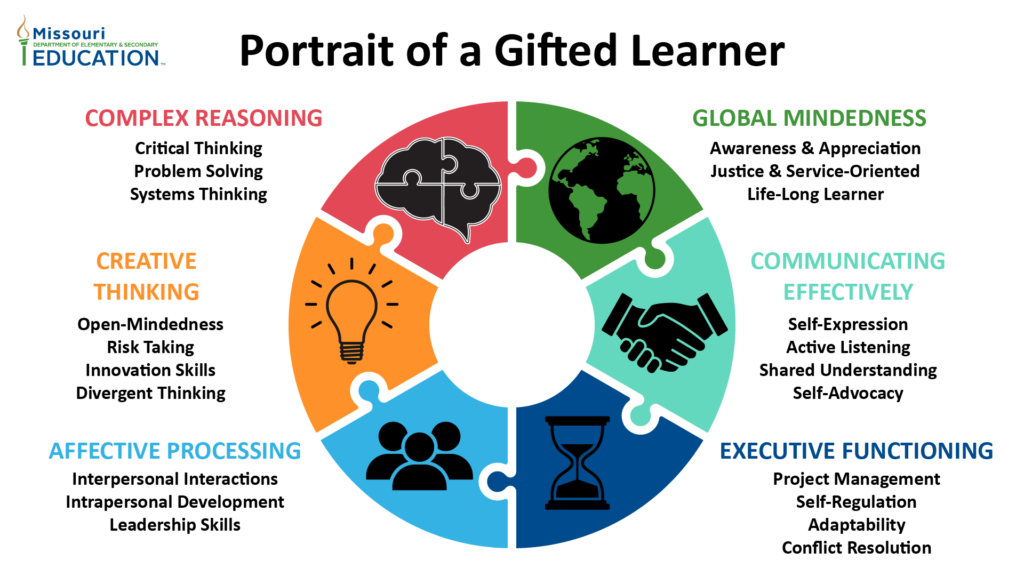
Giftedness encompasses a range of exceptional abilities beyond high IQ scores. It’s crucial to recognize that gifted individuals often exhibit unique talents and skills across various domains. Understanding these types helps identify how they can thrive.
Intellectual giftedness refers to advanced cognitive capabilities, including problem-solving and critical thinking. You might see this in students who grasp complex concepts quickly or excel in academic competitions.
Creative giftedness highlights individuals with original ideas and innovative solutions. These people often express themselves through art, music, or writing, demonstrating their ability to think outside the box.
Artistic giftedness showcases extraordinary talent in visual arts or performing arts. For instance, a child who draws intricate pictures at a young age may possess this type of giftedness.
Leadership giftedness involves strong interpersonal skills and the ability to inspire others. Leaders often show remarkable empathy and communication skills, making them effective group facilitators.
Recognizing different types of giftedness enables tailored support for each individual’s needs. By fostering these abilities early on, you can help them reach their full potential while contributing positively to society.
Major Types Of Giftedness
Giftedness encompasses various talents and abilities that go beyond traditional measures of intelligence. Here are the major types of giftedness, each with distinct characteristics.
Intellectual Giftedness
Intellectual giftedness involves advanced cognitive skills and problem-solving abilities. Individuals in this category often excel in logical reasoning, critical thinking, and academic achievement. For instance, a student who consistently scores in the top 1% on standardized tests demonstrates intellectual giftedness. These individuals may grasp complex concepts quickly or show an exceptional aptitude for mathematics or science.
Creative Giftedness
Creative giftedness is characterized by originality and innovative thinking. People with this type often generate unique ideas or solutions to problems. A well-known example is a young inventor who creates new devices to solve everyday issues. This creativity can manifest in various fields like writing, music composition, or even business innovation.
Artistic Giftedness
Artistic giftedness showcases exceptional talent in visual or performing arts. Individuals may possess skills in painting, sculpture, dance, or theater. For instance, a child recognized for their remarkable ability to draw at an early age illustrates artistic giftedness. These individuals often express deep emotions through their art and can inspire others with their creativity.
Leadership Giftedness
Leadership giftedness highlights strong interpersonal skills and the capacity to inspire others. Those exhibiting this trait naturally take charge in group settings and effectively communicate their vision. An example includes a teenager leading community service projects while motivating peers to participate actively. Such leaders demonstrate empathy and decisiveness that encourage collaboration among team members.
Practical Giftedness
Practical giftedness relates to hands-on problem-solving abilities in real-world scenarios. Individuals might excel in trades such as carpentry or mechanics but also exhibit strong organizational skills in managing projects efficiently. For example, someone adept at fixing machinery without formal training shows practical talent; they apply knowledge practically rather than theoretically.
Identifying Types Of Giftedness
Understanding the various types of giftedness helps in recognizing individuals’ unique strengths. Giftedness manifests differently, requiring tailored approaches for support and development.
Assessment Tools
Assessment tools are essential in identifying giftedness accurately. They provide structured methods to evaluate cognitive abilities and talents. Examples include:
- Standardized tests: Measures IQ or specific skills.
- Achievement tests: Assesses knowledge in subjects like math or reading.
- Creativity assessments: Evaluates innovative thinking through tasks and challenges.
Using these tools offers a clearer picture of an individual’s capabilities, aiding educators and parents in providing appropriate resources.
Observational Methods
Observational methods involve monitoring behaviors and activities to identify gifted traits. These techniques emphasize real-life contexts over formal testing. Key strategies include:
- Classroom observations: Noting interactions, participation, and problem-solving skills during lessons.
- Extracurricular activities: Assessing performance in sports, arts, or clubs shows diverse talents.
- Parent feedback: Parents can offer insights into their child’s interests and achievements at home.
These methods allow for a holistic view of giftedness that complements assessment tools effectively.
Supporting Gifted Individuals
Supporting gifted individuals requires a multifaceted approach, focusing on their unique needs. Effective support fosters growth and helps them thrive in various environments.
Educational Strategies
Implementing tailored educational strategies enhances learning for gifted individuals. Here are some effective methods:
- Differentiated Instruction: Adapt lessons to meet varying ability levels, providing advanced materials for those who excel.
- Acceleration: Allow students to progress faster through subjects or grades based on their readiness and skill level.
- Enrichment Programs: Offer additional challenges beyond the standard curriculum, such as specialized projects or mentorship opportunities.
- Flexible Grouping: Organize students into groups based on skills rather than age, enabling collaboration among peers with similar interests.
These strategies create a stimulating environment that nurtures intellectual curiosity and engagement.
Social-Emotional Support
Addressing social-emotional needs is equally important for gifted individuals. Consider these approaches:
- Peer Interaction Opportunities: Facilitate connections with like-minded peers through clubs or organizations focused on shared interests.
- Counseling Services: Provide access to counselors trained in the issues faced by gifted individuals, helping them navigate social dynamics and emotional challenges.
- Parental Guidance Workshops: Educate parents about fostering resilience and managing expectations, ensuring they understand their child’s experiences.
- Mindfulness Practices: Introduce mindfulness techniques to help manage stress and enhance emotional regulation.
By prioritizing social-emotional support, you promote well-rounded development alongside academic success.