Imagine navigating a world where data management feels effortless. Tables, queries, and forms are examples of Access that transform how you interact with information. These essential components streamline your workflow, making it easier to organize and retrieve data efficiently.
Overview of Access in Database Management
Microsoft Access serves as a powerful tool for database management, featuring key components like tables, queries, and forms. These elements work together to streamline data organization and retrieval.
Tables store your data in a structured format. Each table consists of rows and columns. For example, you might have a “Customers” table with fields for names, addresses, and contact numbers.
Queries allow you to extract specific information. You can create queries to filter or sort data based on certain criteria. For instance, if you want to find all customers from New York, simply set up a query that targets that location.
Forms provide an intuitive interface for data entry. They enable easy input of information into tables without needing to interact directly with the raw data structure. You could design a form that simplifies adding new customer records.
These components enhance user experience by allowing seamless interaction with your database while maintaining accurate and organized information storage.
Understanding Tables in Access
Tables serve as the backbone of Microsoft Access, offering a structured way to store data. By organizing information into rows and columns, tables make it easier for you to manage and retrieve data efficiently.
Importance of Tables
Tables are essential for effective data management. They allow you to categorize information logically, which enhances accessibility. For example, if you’re managing customer information, a table can include fields like Name, Email, and Phone Number. This structure helps in quick searches and updates.
Additionally, tables support relationships between different datasets. You can link related tables using primary keys and foreign keys. This capability ensures data integrity across your database.
Structure of a Table
The structure of a table is straightforward yet powerful. Each table consists of fields (columns) that define the type of data stored and records (rows) that hold individual entries.
- Fields: Define what information is collected.
- Examples include:
- Text
- Numbers
- Dates
- Records: Contain all entries under each field.
- Each record corresponds to one unique entry in the dataset.
This organized format allows for easy addition or modification of data without disrupting existing structures. It also simplifies querying processes when seeking specific insights from your datasets.
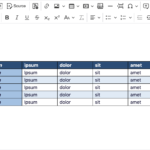
Exploring Queries in Access
Queries in Microsoft Access allow you to retrieve specific data from tables, providing essential insights without the need to sift through extensive datasets. With queries, you can filter and sort information based on your criteria, making them a powerful tool for data analysis.
Types of Queries
You can create several types of queries in Access, each serving distinct purposes:
- Select Query: This type retrieves data from one or more tables and displays it in a datasheet format. For example, if you want to see all customers from New York, a Select Query filters that information effectively.
- Action Query: Action Queries perform operations such as updating records or deleting entries. If you need to change the status of multiple orders at once, an Action Query simplifies this process.
- Parameter Query: This query prompts users for input before running, allowing tailored results. You might use it when searching for products within a specified price range.
- Crosstab Query: Crosstab Queries summarize data in a matrix format, ideal for comparing values across categories. For instance, analyzing sales by product category and month provides quick insights into trends.
Creating and Modifying Queries
Creating queries in Access is straightforward. Start by selecting the “Create” tab and choosing “Query Design.” From there:
- Add Tables: Choose which tables contain the data you want to analyze.
- Select Fields: Drag relevant fields into the grid below.
- Set Criteria: Define any conditions under which you’d like to filter your results.
Modifying existing queries allows further refinement of your data retrieval process. You can adjust criteria directly in the query design view or add new fields as needed. Making changes helps ensure that your queries meet evolving business needs efficiently.
By leveraging these various types of queries and knowing how to create or modify them effectively, you enhance your ability to manage and analyze data within Microsoft Access with ease.
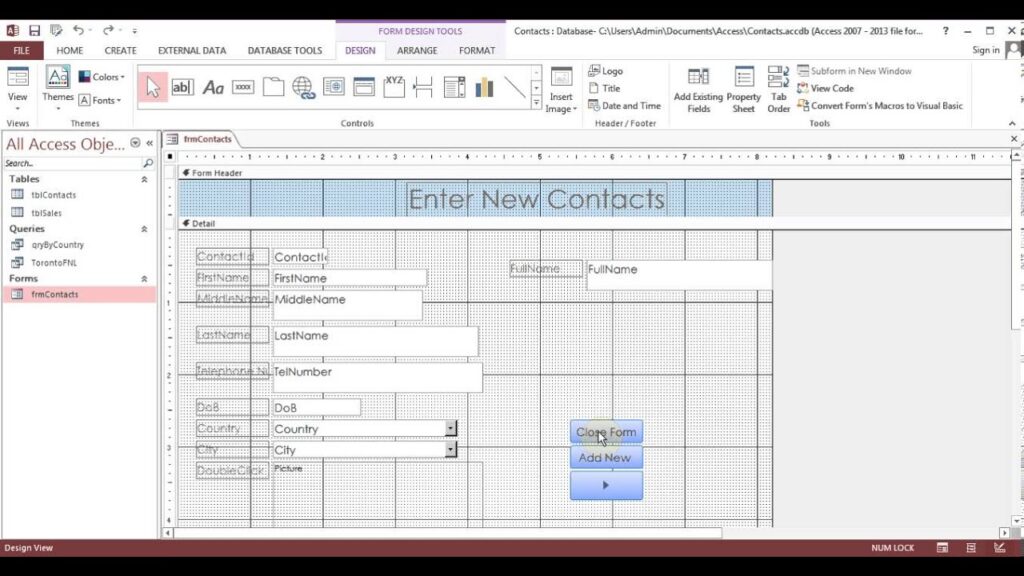
Utilizing Forms in Access
Forms in Microsoft Access serve as a user-friendly interface for data entry and management. They simplify the process of interacting with databases, allowing you to input, edit, and navigate data without directly dealing with tables.
Purpose of Forms
Forms enhance user experience by providing an intuitive method for data entry. Instead of working directly with complex table structures, forms present fields in a clear layout. You can also apply validation rules within forms to ensure accurate data input. Moreover, they facilitate easier navigation through records, enabling users to move between entries seamlessly.
Designing User-Friendly Forms
Designing effective forms requires attention to both functionality and aesthetics. Start by organizing fields logically; group related information together. Use labels that clearly describe each field’s purpose. Additionally, consider including drop-down lists or checkboxes for common inputs; this speeds up data entry and reduces errors.
To ensure accessibility:
- Keep the form layout simple and uncluttered.
- Add navigation buttons for quick record movement.
- Implement search functions if your database is extensive.
Incorporating these elements makes forms more engaging and easy to use.