When it comes to investing, understanding the difference between systematic risk vs unsystematic risk can make or break your financial strategy. Have you ever wondered why some investments seem to fluctuate with the market while others remain stable? Systematic risk refers to the inherent risks that affect the entire market, such as economic downturns or geopolitical events. On the other hand, unsystematic risk is specific to a particular company or industry, like management decisions or product recalls.
Understanding Systematic Risk Vs Unsystematic Risk
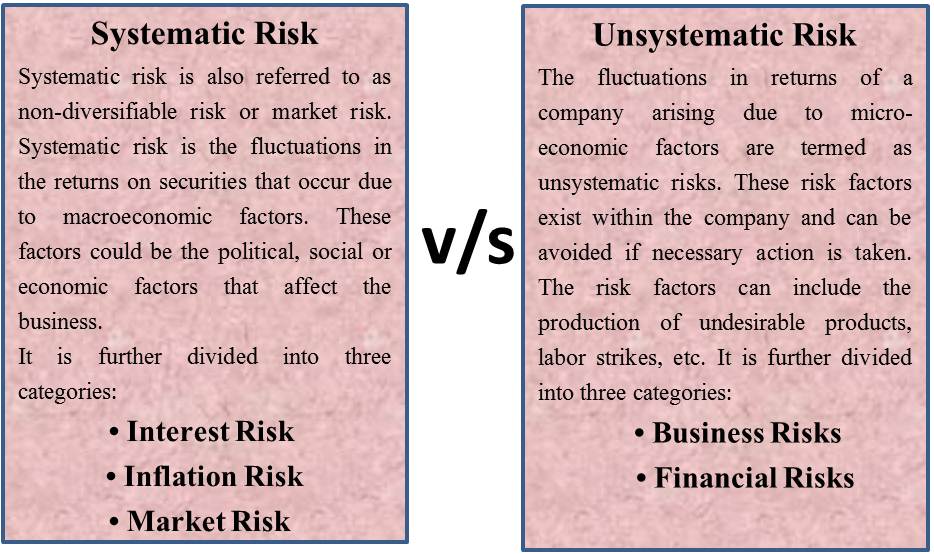
Systematic risk impacts the whole market and cannot be eliminated through diversification. For instance, economic recessions or interest rate changes affect all investments simultaneously. Examples of systematic risk include:
- Market crashes: A sudden drop in stock prices due to negative news.
- Inflation rates: Rising costs that reduce purchasing power.
- Political instability: Events like elections or wars that create uncertainty.
On the other hand, unsystematic risk pertains to individual companies or sectors. This type of risk can be mitigated by diversifying your portfolio. Examples of unsystematic risk include:
- Management decisions: Poor leadership choices impacting a company’s performance.
- Product recalls: Safety issues leading to financial losses for specific businesses.
- Industry competition: New entrants disrupting established firms within a sector.
Recognizing these differences helps you navigate investment strategies more effectively, ensuring better decision-making in volatile markets.
Key Differences Between Systematic And Unsystematic Risk
Understanding the key differences between systematic and unsystematic risk is essential for effective investment strategies. Each type of risk has unique characteristics and impacts on your portfolio.
Definition And Characteristics
Systematic risk refers to the inherent risks that affect the entire market. Factors such as economic recessions, interest rate changes, or global events contribute to this type of risk. It’s unavoidable and cannot be mitigated through diversification.
Unsystematic risk, however, pertains to specific companies or industries. This includes risks like management decisions, product failures, or competitive pressure within a sector. Unlike systematic risk, you can reduce unsystematic risk by diversifying your investments across different assets or sectors.
Impact On Investments
The impact of systematic risk on investments can be profound. Market-wide downturns can lead to significant losses across virtually all asset classes simultaneously. For example, during a financial crisis, stock values may plummet regardless of individual company performance.
Conversely, unsystematic risk affects only particular stocks or sectors. If a company faces legal issues or experiences poor sales results while other companies thrive in different industries, you might still see gains elsewhere in your portfolio. By holding a diverse range of investments, you minimize potential losses from any single entity’s downturn.
Examples Of Systematic And Unsystematic Risk
Understanding examples of systematic and unsystematic risk helps clarify their impacts on investments. Here are some key instances for each type.
Systematic Risk Examples
Systematic risk encompasses factors that affect the entire market. Consider these examples:
- Economic Recession: A downturn in the economy leads to reduced consumer spending, impacting all companies.
- Inflation Rates: Rising inflation can erode purchasing power and reduce corporate profits across various sectors.
- Political Instability: Events like elections or conflicts can cause market volatility, affecting investor confidence globally.
- Natural Disasters: Events such as earthquakes or hurricanes disrupt supply chains and impact overall economic performance.
Each of these events demonstrates how systematic risk permeates through the financial landscape.
Unsystematic Risk Examples
Unsystematic risk relates specifically to individual companies or industries. These examples illustrate its nature:
- Management Decisions: Poor choices by a company’s leadership can lead to significant losses, affecting only that firm’s stock price.
- Product Recalls: If a company recalls a defective product, it may face immediate financial repercussions while other firms remain unaffected.
- Industry Competition: New competitors entering the market can reduce a company’s market share and profitability without impacting unrelated businesses.
- Technological Changes: Companies that fail to adapt to new technologies may suffer losses, whereas others thrive.
These cases show how unsystematic risks highlight vulnerabilities at the company level rather than across the entire market.
Importance Of Risk Assessment In Investing
Risk assessment plays a crucial role in your investment strategy. It helps you identify potential threats that could impact your portfolio’s performance. By understanding both systematic and unsystematic risks, you can make informed decisions.
Systematic risk affects all investments equally. Examples include market downturns caused by economic recessions or political instability. This type of risk is unavoidable and necessitates strategies to manage it effectively.
Unsystematic risk, on the other hand, relates to specific companies or industries. For instance, if a company faces management issues or product recalls, its stock may decline independently of the broader market. You can reduce this risk through diversification—spreading investments across various assets.
Here are some examples to consider:
- Economic Factors: Inflation rates rising can decrease purchasing power.
- Market Volatility: A sudden drop in stock prices due to global events.
- Company Performance: Earnings reports missing expectations may lead to sharp declines in individual stocks.
You might ask yourself how these risks affect your portfolio. Understanding them allows you to adjust your investments accordingly, minimizing losses while maximizing gains.
By prioritizing risk assessment, you enhance your ability to navigate uncertain markets. You’ll find that being proactive about these risks leads to more resilient investment choices over time.
Strategies For Managing Risk
Understanding how to manage risk is essential for successful investing. Here are some effective strategies to consider:
- Diversification
Diversifying your portfolio across various asset classes can minimize unsystematic risk. You might invest in stocks, bonds, and real estate to reduce the impact of specific company or sector downturns.
- Asset Allocation
Allocating assets based on your risk tolerance helps balance systematic risk. Adjusting your investments between equities and fixed-income securities can provide stability during volatile market conditions.
- Hedging
Using financial instruments like options or futures contracts allows you to hedge against potential losses from systematic risks. By taking positions that offset potential declines in your primary investments, you create a safety net.
- Regular Monitoring
Keeping an eye on market trends and economic indicators aids in identifying risks early on. Regularly reviewing your investment performance lets you make informed decisions when adjustments are necessary.
- Setting Stop-Loss Orders
Implementing stop-loss orders can help protect profits and limit losses in declining markets. When prices drop below a certain threshold, these orders automatically sell the asset, minimizing further loss exposure.
- Investment Research
Conducting thorough research before investing reduces the likelihood of encountering unsystematic risks linked to poorly performing companies or industries. Understanding fundamentals helps you make better choices.
- Professional Guidance
Consulting with financial advisors offers expert insights into risk management strategies tailored to your needs. Their experience can enhance decision-making while navigating complex markets.
By incorporating these strategies into your investment approach, you’ll be better equipped to handle both systematic and unsystematic risks effectively.