Imagine a world where bacterial infections could be treated effectively before the advent of antibiotics. That’s where sulfa drugs come into play, revolutionizing medicine in the early 20th century. These compounds not only paved the way for modern antimicrobial therapies but also saved countless lives during their time.
Overview of Sulfa Drugs
Sulfa drugs, also known as sulfonamides, represent a significant advancement in the treatment of bacterial infections. These compounds inhibit bacterial growth by interfering with folic acid synthesis. Here are some notable examples:
- Sulfamethoxazole: Commonly used in combination with trimethoprim to treat urinary tract infections and respiratory infections.
- Sulfadiazine: Often prescribed for treating toxoplasmosis and certain types of meningitis.
- Sulfisoxazole: Used primarily for treating otitis media and other ear infections.
These medications laid the groundwork for modern antibiotics. They drastically reduced mortality rates from bacterial diseases during their peak usage. While newer antibiotics have largely replaced them, understanding sulfa drugs is crucial for grasping antimicrobial development.
Additionally, it’s important to note that some individuals may experience allergic reactions to sulfa drugs. Symptoms can include skin rashes or fever, which necessitate immediate medical attention. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new medication.
While less common today, sulfa drugs played a pivotal role in early antibiotic therapy and remain relevant in specific clinical scenarios.
History of Sulfa Drugs
Sulfa drugs emerged in the early 20th century, marking a significant advancement in medical treatment for bacterial infections. These compounds laid groundwork for modern antimicrobial therapies and saved countless lives.
Discovery and Development
In 1932, German scientist Gerhard Domagk discovered the first sulfa drug, Prontosil, which effectively treated streptococcal infections. Its success led to further research and development of other sulfonamides like sulfamethoxazole, which became widely used. The discovery shifted medical paradigms, as it introduced a synthetic approach to treating infections that previously relied on natural remedies.
Early Uses in Medicine
Initially, sulfa drugs played a crucial role during World War II by reducing infection rates among soldiers. They treated conditions such as pneumonia and cellulitis effectively. Thanks to their broad-spectrum efficacy, these medications significantly lowered mortality rates from bacterial diseases. While newer antibiotics emerged later, sulfa drugs laid the foundation for antibiotic therapy and remain useful today in specific cases like urinary tract infections or certain skin conditions.
Mechanism of Action
Sulfa drugs function primarily by inhibiting bacterial growth through interference with essential biochemical processes. Understanding their mechanism provides insight into how they treat infections effectively.
Inhibition of Bacterial Growth
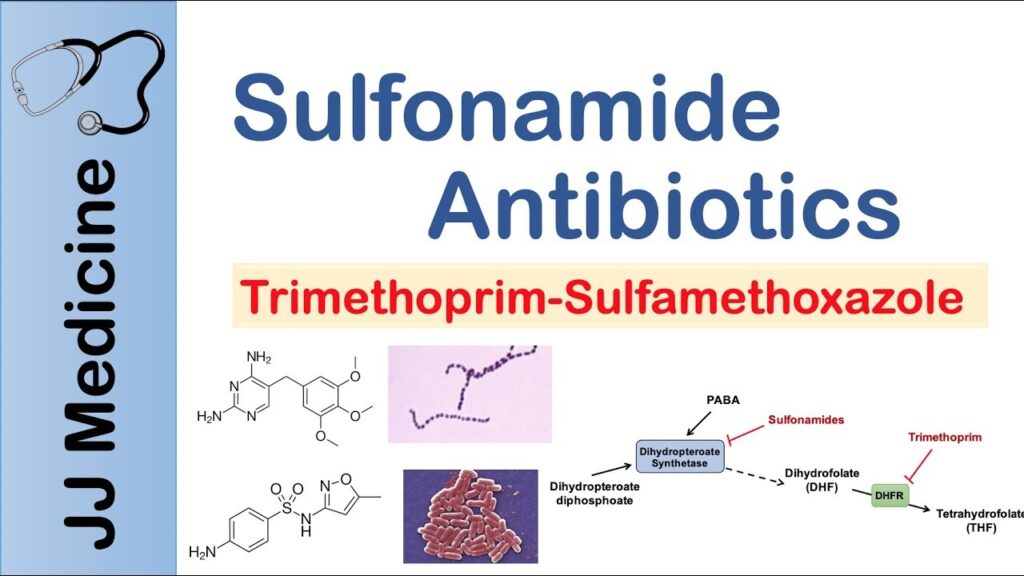
Sulfa drugs disrupt the synthesis of folic acid, a vital nutrient for bacteria. By mimicking para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), these drugs compete for the active site in the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase, which prevents the formation of folate. This inhibition leads to decreased bacterial growth and reproduction. Notably, sulfamethoxazole is frequently prescribed for urinary tract infections due to its effectiveness against common pathogens.
Role of Sulfanilamide
Sulfanilamide serves as a foundational sulfa drug and played a crucial role in antibiotic therapy’s evolution. It demonstrated remarkable efficacy against streptococcal infections and laid groundwork for subsequent sulfonamides. As a competitive inhibitor, it blocks bacterial folate production, leading to cell death. Studies show that combinations like sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim enhance effectiveness by targeting different steps in folate metabolism, making this combination especially potent against various bacterial strains.
Applications and Benefits
Sulfa drugs remain relevant in specific medical applications, providing significant benefits despite the rise of newer antibiotics. Their historical role in treating infections continues to influence current practices.
Treatment of Bacterial Infections
Sulfa drugs effectively treat various bacterial infections. For instance, sulfamethoxazole is commonly used for urinary tract infections (UTIs) due to its ability to inhibit bacterial growth. Additionally, sulfadiazine treats conditions like toxoplasmosis and certain types of pneumonia. These examples showcase their continued importance in managing both common and complex infections.
Impact on Surgery and Medicine
Sulfa drugs have significantly impacted surgical procedures by reducing infection rates post-operation. By preventing bacterial proliferation, they enhance patient recovery times and outcomes. Furthermore, during World War II, sulfa drugs played a crucial role in treating battlefield injuries and infections among soldiers, illustrating their value in emergency medicine settings.
Side Effects and Risks
Sulfa drugs come with potential side effects and risks that users must understand. While these medications have proven effective, awareness of their adverse reactions is crucial for safe usage.
Common Adverse Reactions
Common adverse reactions to sulfa drugs include:
- Gastrointestinal issues: Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea can occur.
- Skin rashes: Some individuals experience mild to severe skin reactions.
- Headaches: A frequent complaint among users, headaches may arise during treatment.
- Dizziness: You might feel lightheaded or dizzy while taking sulfa drugs.
It’s essential to monitor your body’s response and communicate any concerning symptoms with a healthcare professional.
Allergic Reactions and Contraindications
Allergic reactions can range from mild skin rashes to severe anaphylactic responses. If you have a known allergy to sulfonamides, avoid using sulfa drugs entirely. Other contraindications include:
- Pregnancy: Some sulfa drugs pose risks during pregnancy due to potential fetal harm.
- Liver disease: Individuals with liver conditions should consult their doctor before use.
- Kidney problems: Sulfa drugs may exacerbate existing kidney issues.
Always discuss your medical history with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication.