Have you ever wondered how the world around you is organized? Understanding the relationship between structures and functions can unlock insights into everything from biology to architecture. Every element in nature or design serves a purpose, and recognizing this connection helps us appreciate their complexity.
Overview of Structures and Functions
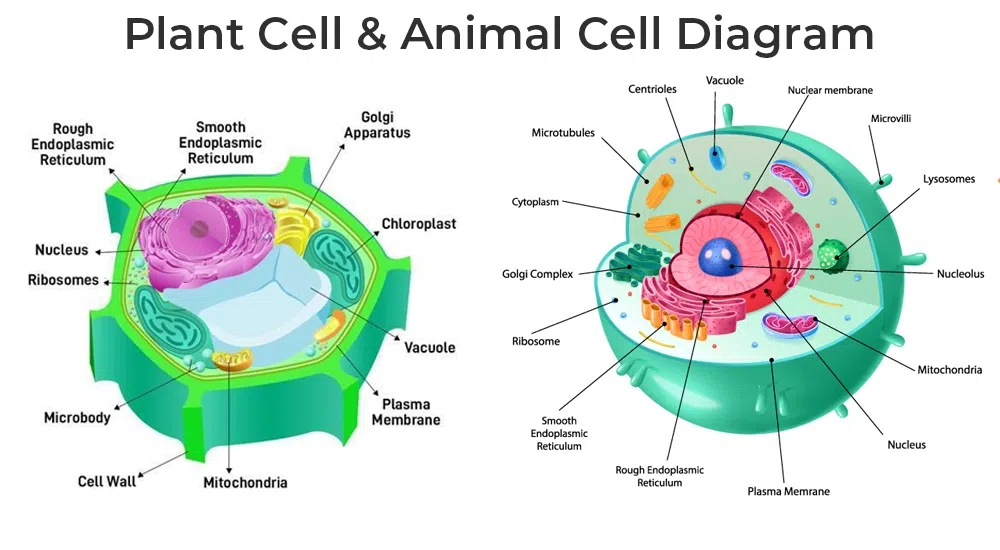
In various fields, the relationship between structures and functions plays a critical role. Structures exist for specific reasons, and their design often dictates how they perform. For instance, in biology, the structure of a cell directly influences its function.
- Cell Membrane: The flexible structure of the cell membrane allows it to regulate what enters and exits the cell effectively.
- Bird Wings: The unique shape of bird wings facilitates flight by allowing for optimal lift and maneuverability.
- Human Heart: The four chambers of the heart ensure efficient blood circulation throughout the body.
Each example illustrates how effective design enhances functionality. Recognizing this connection can deepen your understanding of both natural systems and engineered designs.
Types of Structures
Understanding various types of structures helps clarify their functions and significance in different contexts. Below are key categories illustrating this relationship.
Biological Structures
Biological structures play crucial roles in the survival and efficiency of living organisms. Here are some examples:
- Cell Membrane: The flexible barrier regulates what enters and exits a cell, maintaining homeostasis.
- Bird Wings: Their unique shape allows for efficient flight, showcasing adaptation to environmental demands.
- Human Heart: With four chambers, it ensures effective blood circulation, vital for transporting oxygen throughout the body.
These examples highlight how specific designs enhance functionality within biological systems.
Architectural Structures
Architectural structures reflect human ingenuity while serving practical purposes. Consider these notable examples:
- Skyscrapers: Designed to maximize space in urban environments, they facilitate dense population living.
- Bridges: They connect separated areas, allowing for transportation and trade across obstacles like rivers or valleys.
- Domes: Utilized in many religious buildings, domes distribute weight evenly while providing spacious interiors.
These architectural elements demonstrate how design influences utility and aesthetics in human-made environments.
Importance of Structures
Understanding the significance of structures in various contexts enhances your appreciation for their functions. Structures serve as the foundation upon which systems operate, whether biological or architectural.
Functional Roles
Structures exhibit specific functional roles that directly impact efficiency and performance. For instance:
- Cell membranes regulate what enters and exits a cell, maintaining homeostasis.
- Bird wings are shaped to maximize lift, enabling flight.
- Human hearts possess four chambers to ensure efficient blood circulation throughout the body.
Each example illustrates how structure correlates with function, emphasizing effective design in nature.
Structural Integrity
Structural integrity ensures stability and safety across different fields. Consider these examples:
- Skyscrapers utilize steel frames to withstand wind forces, preventing collapse.
- Bridges employ arch designs to distribute weight evenly, enhancing durability.
- Domes, like those in cathedrals, use curved surfaces to support heavy loads without internal supports.
Strong structures contribute not only to functionality but also to longevity and resilience in both natural and designed environments.
Relationship Between Structures and Functions
Understanding the connection between structures and functions is crucial in various contexts. This relationship demonstrates how design directly impacts utility and effectiveness.
Examples in Nature
In nature, structures serve specific functions that enhance survival and efficiency. Here are some notable examples:
- Cell Membrane: The flexible structure of the cell membrane regulates what enters and exits, maintaining homeostasis.
- Bird Wings: Unique shapes of bird wings allow different species to achieve flight, adapting to their environments.
- Human Heart: Four chambers in the human heart ensure efficient blood circulation, optimizing oxygen delivery throughout the body.
These examples show that nature employs effective designs that enhance functionality.
Applications in Technology
Technology mirrors nature by utilizing structural designs for practical applications. Consider these instances:
- Skyscrapers: Steel frames provide strength to withstand wind forces while maximizing space.
- Bridges: Arch designs distribute weight evenly, increasing stability and durability.
- Domes: Curved surfaces support heavy loads without internal supports, showcasing innovation.
Through these technological advancements, structures have been engineered for safety and efficiency.