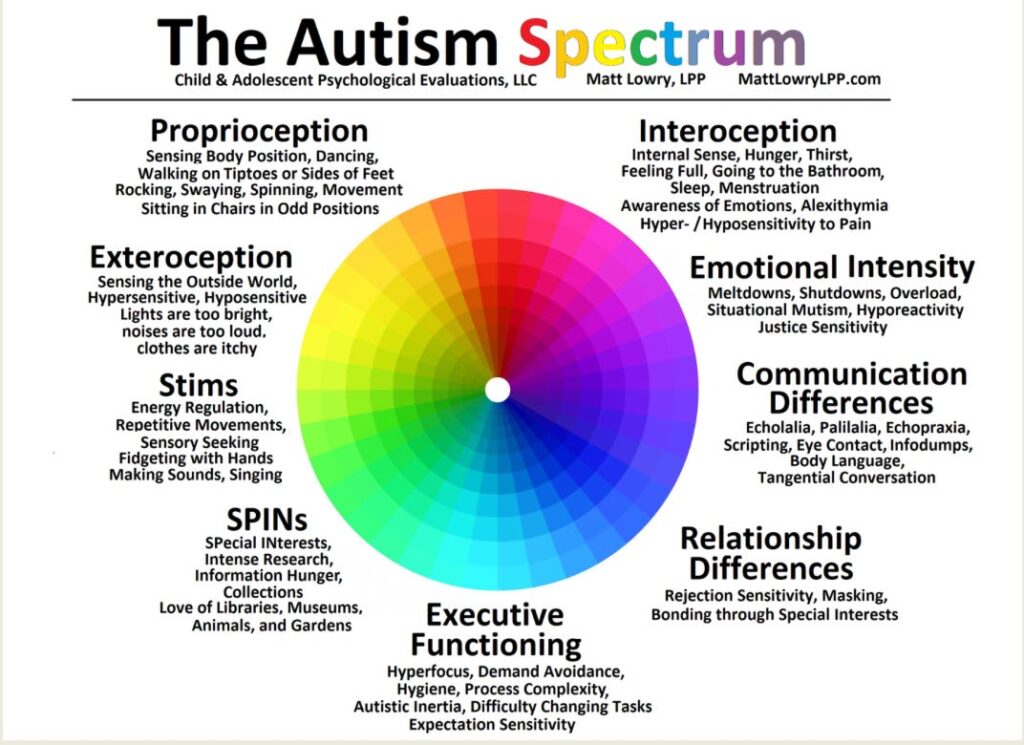
Have you ever noticed how some individuals on the autism spectrum display an extraordinary strong sense of justice? This unique trait often leads them to champion fairness and equality in ways that can be both inspiring and thought-provoking. For many, this unwavering commitment to justice shapes their interactions with others and influences their understanding of the world around them.
Understanding Strong Sense of Justice Autism
Individuals on the autism spectrum often exhibit a strong sense of justice, which influences their perceptions and behaviors. Here are some examples that illustrate this trait:
- Advocacy for Fairness: You might notice individuals passionately defending peers who face bullying or discrimination. Their commitment to fairness drives them to speak out against any perceived injustice.
- Strict Adherence to Rules: Many individuals display a rigid interpretation of rules in games or social situations. They may insist that everyone follows the same guidelines to ensure fairness for all participants.
- Empathy Towards Others: Some show heightened empathy when witnessing unfair treatment, feeling deeply affected by others’ distress. This can lead them to take action or offer support whenever they can.
- Strong Reactions to Unfairness: If you observe someone reacting intensely when encountering an unfair situation, it reflects their desire for equity and balance in interactions with others.
- Interest in Social Justice Issues: Individuals often engage with topics related to human rights or environmental concerns, demonstrating their desire for a more just society through research and activism.
These examples highlight how a strong sense of justice shapes interactions and perspectives among those on the autism spectrum, fostering a commitment to equitable treatment for all.
Characteristics of Strong Sense of Justice
Individuals on the autism spectrum often exhibit a strong sense of justice that shapes their interactions and perspectives. This characteristic manifests in various ways, including heightened empathy, strict adherence to rules, and a commitment to fairness.
Empathy and Moral Reasoning
A deep sense of empathy influences your moral reasoning. You might react strongly when witnessing unfairness or injustice, whether in social settings or through media narratives. For example:
- Advocacy for Peers: If you see someone being bullied, you likely feel compelled to speak up for them.
- Emotional Reactions: You may experience intense emotions when encountering stories about discrimination or inequality.
This emotional engagement fosters a drive towards social justice efforts, reflecting your desire for equitable treatment.
Rules and Fairness
Strict adherence to rules is another hallmark of a strong sense of justice. You value structure and clarity in social situations. Common examples include:
- Enforcing Guidelines: In group activities, you ensure that everyone follows the same set of rules.
- Challenging Unfair Practices: If someone bends the rules for personal gain, you’re likely to confront them directly.
Such behaviors emphasize your commitment to fairness and equality within your community and beyond.
Impact on Daily Life
Individuals with a strong sense of justice often experience unique challenges and strengths in their daily lives. This impact is evident in social interactions and educational environments.
Social Interactions
In social settings, you may notice individuals on the autism spectrum actively advocating for others. For example, when witnessing bullying, they often intervene to defend the victim. They might say things like, “That’s not fair; everyone deserves respect.” Their unwavering commitment to fairness can lead to intense emotional responses during discussions about equality or injustice. Consequently, this can create both meaningful connections and potential conflicts with peers who don’t share the same values.
Educational Environments
In educational contexts, students with a strong sense of justice typically exhibit a deep commitment to rules and fairness. For instance, they may insist that teachers enforce classroom rules consistently for all students. This adherence helps create an environment where everyone feels treated equally. Additionally, these individuals might take on roles as advocates for school policies that promote inclusivity. Their passion can inspire classmates to engage in discussions about equity or participate in activities supporting social justice initiatives within the school community.
Challenges Faced
Individuals on the autism spectrum with a strong sense of justice encounter various challenges that affect their daily interactions and experiences. These hurdles can stem from misunderstandings, emotional responses, and social dynamics.
Misunderstandings and Stereotypes
Misunderstandings about autism often lead to stereotypes that overlook the unique perspectives of individuals. Many people assume that those on the spectrum lack empathy, which isn’t true. In fact, they may express empathy in intense ways when they witness unfairness. For example:
- Advocating for classmates who face bullying.
- Reacting strongly to stories of discrimination in media.
- Challenging perceived injustices during discussions or debates.
These actions can create misconceptions about aggressive behavior instead of highlighting their commitment to fairness.
Emotional Responses
Emotional responses can be heightened for individuals with a strong sense of justice. They often feel compelled to act when witnessing unfair situations. This passion sometimes leads to frustration or distress in social settings. Common scenarios include:
- Feeling overwhelmed by injustice portrayed in movies or news.
- Experiencing anxiety when rules are enforced inconsistently.
- Struggling with peer reactions when advocating for fairness.
These emotional challenges can impact relationships and social engagement, as others may not fully understand their motivations or feelings.
Supporting Individuals with Strong Sense of Justice
Supporting individuals with a strong sense of justice requires understanding their unique perspectives and needs. These strategies can foster positive interactions and environments.
Effective Communication Strategies
Use clear, direct language when discussing rules or expectations. This helps avoid misunderstandings. For example, instead of saying “be nice,” specify “treat everyone with respect.”
Encourage open dialogue. Ask them how they feel about certain situations. This validates their feelings and promotes trust.
Provide visual aids. Charts or diagrams can clarify complex ideas or social situations, making communication easier.
Encouraging Positive Outlets
Create safe spaces for expression. Whether through art, writing, or discussion groups, providing opportunities for creative expression helps channel intense emotions productively.
Highlight role models. Introduce individuals who advocate for justice in various fields—like activists or public figures—to inspire action and connection to larger causes.