Have you ever found yourself in a debate where your opponent seems to misrepresent your argument? That’s often the straw man fallacy at work. This tactic involves distorting someone’s position to make it easier to attack, leading to confusion and frustration. Understanding this fallacy is crucial for anyone looking to engage in meaningful discussions.
Overview of Straw Man Fallacy
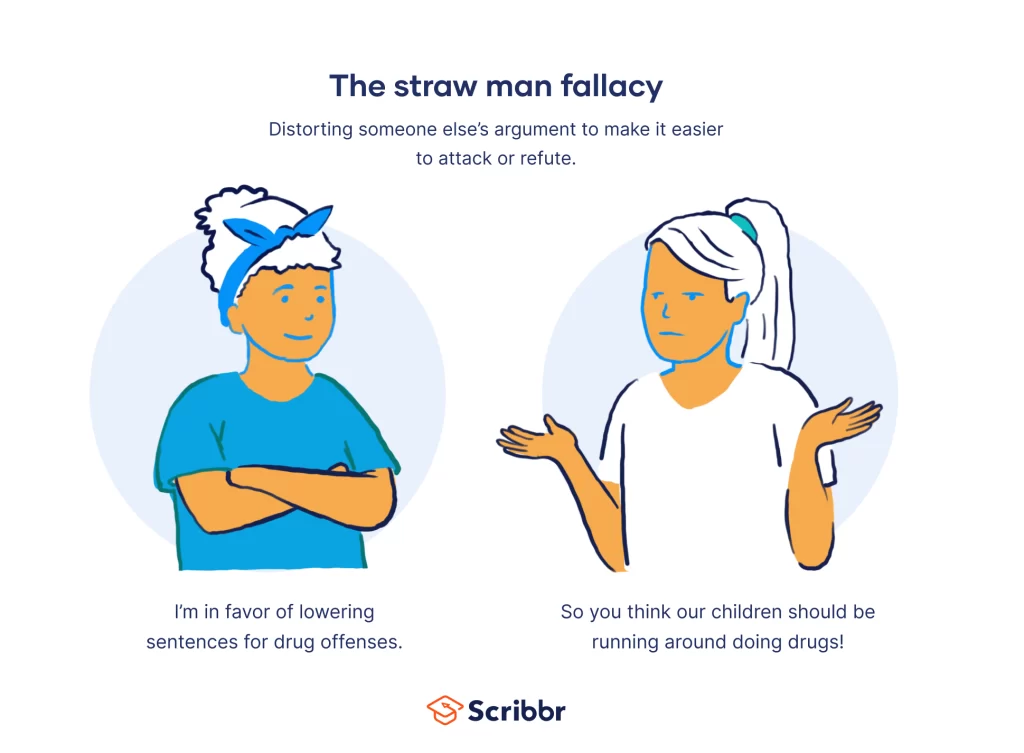
The straw man fallacy occurs when someone misrepresents another person’s argument to make it easier to attack. You might see this in debates or discussions where one party exaggerates or distorts the other’s position. This tactic often leads to confusion and detracts from the actual issue at hand.
- Environmental Debate: Person A advocates for reducing plastic use. Person B claims, “Person A wants everyone to stop using any plastics, which is impractical.” Here, Person B simplifies and misrepresents Person A’s argument.
- Health Discussion: If someone argues for a balanced diet, you might hear, “You just want people to starve themselves by cutting out sugar completely.” This oversimplifies the original point about moderation.
- Political Argument: During political discussions, if Candidate X promotes healthcare reforms, their opponent might say, “Candidate X wants to eliminate all private health insurance.” This ignores the nuances of Candidate X’s proposal.
Recognizing these examples helps clarify arguments and fosters productive dialogue. By addressing the actual points raised instead of creating misleading versions, discussions become more meaningful and focused.
Common Straw Man Fallacy Examples
Recognizing straw man fallacies enhances your understanding of arguments. Here are some specific instances where this fallacy often appears.
Example in Political Debate
In political debates, a common occurrence involves one candidate misrepresenting another’s stance. For instance, if Candidate A advocates for reducing military spending, Candidate B might say, “Candidate A wants to leave our country defenseless.” This simplifies and distorts Candidate A’s argument. Such tactics distract from the original point and can manipulate public perception.
Example in Everyday Arguments
Everyday conversations also feature straw man fallacies frequently. Imagine a discussion about healthy eating where one person suggests reducing sugar intake. The response could be, “So you think we should all eat tasteless food?” This exaggerates the initial suggestion and shifts focus away from the true issue—finding balance in diet. Addressing such distortions helps maintain clarity in discussions.
Analyzing the Impact of Straw Man Fallacy
Understanding the impact of the straw man fallacy is crucial for effective communication and critical thinking. Misrepresenting arguments can lead to significant misunderstandings and hinder productive discussions.
Consequences in Communication
Miscommunication often arises from straw man fallacies. When someone distorts an opponent’s argument, it triggers confusion and frustration, making constructive dialogue nearly impossible. Consider these potential consequences:
- Distrust: Repeated use of straw man tactics breeds skepticism among participants.
- Polarization: Conversations become more divisive as individuals cling to misrepresented views.
- Stagnation: Discussions fail to progress when focus shifts away from actual issues.
Recognizing these impacts encourages clearer communication and fosters a healthier exchange of ideas.
Effects on Critical Thinking
The straw man fallacy undermines critical thinking skills by diverting attention from valid arguments. You may find that addressing misrepresentations leads to poor reasoning habits. Here are some effects:
- Lack of Clarity: When arguments are twisted, it becomes difficult to assess their validity.
- Weakens Arguments: Responding to mischaracterizations distracts from addressing real concerns.
- Discourages Engagement: Individuals might disengage if they feel their points aren’t respected or understood.
Awareness of these effects promotes stronger analytical abilities and enhances overall discourse quality.
Strategies to Avoid Straw Man Fallacies
Recognizing and avoiding straw man fallacies enhances the quality of discussions. Here are effective strategies to ensure clarity in your arguments:
- Understand the Opponent’s Argument: Make sure you fully grasp the points your opponent raises. This helps prevent misrepresentation.
- Restate Before Responding: Restate your opponent’s argument in your own words before offering a rebuttal. This shows you’re listening and provides an opportunity for clarification.
- Focus on Specifics: Address specific claims rather than generalizations. This keeps the conversation grounded and relevant.
- Ask Questions: If something seems unclear, ask open-ended questions to draw out more context from the other party.
- Avoid Exaggeration: Stick to what was actually said without inflating or distorting its meaning.
- Clarify Misunderstandings Immediately: If someone misrepresents your stance, correct them as soon as possible to maintain clarity in discussion.
- Practice Active Listening: Engage with empathy by truly listening to others’ viewpoints before formulating responses.
Implementing these strategies promotes respectful dialogue and encourages constructive discourse while minimizing misunderstandings associated with straw man tactics.