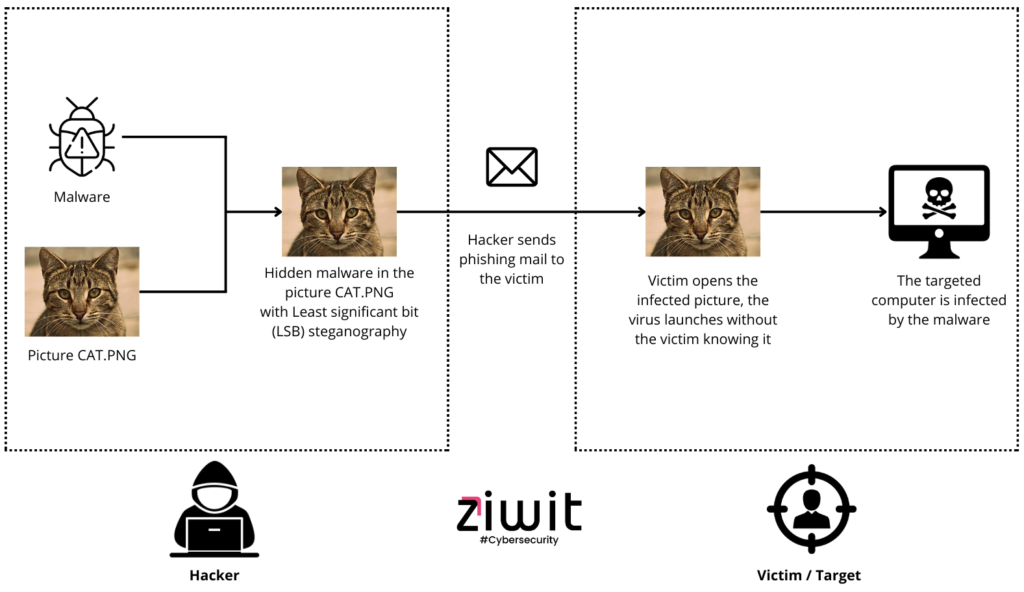
Imagine sending a secret message without anyone knowing it’s there. Steganography examples showcase the art of hiding information in plain sight, making it an intriguing topic for tech enthusiasts and security professionals alike. This technique allows you to conceal data within images, audio files, or even text—transforming ordinary files into covert carriers of sensitive information.
In this article, you’ll explore various steganography examples that demonstrate how easily hidden messages can be embedded in everyday digital content. From classic methods like LSB (Least Significant Bit) encoding to modern applications using advanced algorithms, each example reveals the fascinating ways people keep their communications secure. Are you ready to uncover the secrets behind these stealthy techniques? Dive in and discover how steganography plays a crucial role in today’s digital world.
Overview Of Steganography
Steganography involves concealing messages within other files, providing a method for secure communication. You can find it in various forms, each serving distinct purposes. Here are some notable examples:
- Image Steganography: This technique hides data within the pixels of an image file. For instance, LSB (Least Significant Bit) encoding alters the least significant bits of pixel values to embed secret information.
- Audio Steganography: In this method, you can embed messages within audio files by modifying sound waves or using echo hiding techniques. The changes remain imperceptible to human ears.
- Text Steganography: Techniques include altering font styles or using specific word patterns to conceal messages in text documents. For example, spaces between words can encode binary data.
- Network Steganography: Data is hidden within network protocols or packet headers during transmission. You can manipulate packet timing and size to carry hidden information without raising suspicion.
Understanding these examples illustrates how steganography operates across different media types. It plays a crucial role in maintaining privacy and confidentiality in digital communications today.
Popular Steganography Techniques
Steganography employs various techniques to conceal messages within different media types. Here are some of the most popular methods used today.
Image Steganography
Image steganography hides data within image files by manipulating pixel values. One common technique is Least Significant Bit (LSB) encoding, where the least significant bits of pixels change to store secret information. For instance, altering the last bit in RGB values can embed a message without significantly affecting the image’s appearance. This method works well with formats like BMP and PNG, which accommodate minor changes without noticeable quality loss.
Audio Steganography
Audio steganography conceals messages in audio files through various techniques. Echo hiding is one effective approach, where echoes are added at carefully calculated intervals, making them imperceptible to listeners but readable by software. Another method involves modifying frequencies or amplitudes subtly so that human ears can’t detect it. Common audio formats like MP3 and WAV support these alterations while preserving sound quality.
Video Steganography
Video steganography extends the concepts of image and audio steganography into video files. This technique often combines both visual and auditory elements to hide data effectively. For example, you might embed information in specific frames or adjust certain audio tracks subtly throughout a video stream. Formats like AVI and MP4 allow for robust embedding methods due to their complex structures, accommodating large amounts of hidden data without degrading playback quality.
These techniques illustrate how steganography adapts across different media forms, ensuring secure communication in an increasingly digital world.
Practical Applications Of Steganography Examples
Steganography finds numerous practical applications in digital communication, enhancing security and privacy. Here are some notable examples:
Data Security
Data security plays a vital role in protecting sensitive information. Steganography conceals confidential data within files, preventing unauthorized access during transmission. For instance, you might embed a critical message within an image or audio file, making it accessible only to authorized recipients who know how to extract it. This technique is especially useful for:
- Secure communications in government sectors
- Protecting intellectual property in businesses
- Safeguarding personal data from cyber threats
By employing steganographic methods, organizations can ensure that their valuable information remains hidden even if the carrier file is intercepted.
Digital Watermarking
Digital watermarking serves as another significant application of steganography. This method embeds copyright information into digital media, ensuring ownership and authenticity. You often see watermarking used in images and videos to deter unauthorized use or reproduction. Key aspects include:
- Indicating ownership of creative content
- Providing traceability for licensing agreements
- Preventing piracy by embedding unique identifiers
With digital watermarking, creators maintain control over their work while deterring infringement, making it essential for artists and publishers alike.
Limitations And Challenges
Steganography presents intriguing possibilities, but it also faces notable limitations and challenges. One significant challenge is the detection of hidden information. As steganographic techniques evolve, so do methods for uncovering them. Tools designed to detect anomalies in files can expose embedded data.
Another limitation lies in capacity constraints. Each media type has a maximum amount of data it can conceal without noticeable distortion. For instance, LSB encoding in images alters only a small fraction of pixel values, restricting how much data you can hide.
Additionally, there’s an issue with robustness. If the carrier file undergoes modification—like resizing an image or compressing audio—the hidden information may become corrupted or lost entirely. This vulnerability makes reliable communication challenging.
You might also consider the legal and ethical implications of using steganography. While it serves legitimate purposes like privacy protection, it could facilitate illicit activities such as hiding malware or illegal content.
While steganography offers unique benefits for secure communications, its limitations require careful consideration when implementing these techniques effectively.
Future Trends In Steganography
Steganography continues to evolve, responding to technological advancements and increasing security demands. Emerging trends illustrate how this technique adapts in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI enhances steganography by automating the embedding and extraction processes. With machine learning algorithms, systems can identify optimal data hiding methods that improve efficiency while maintaining imperceptibility.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain offers decentralized solutions for secure data transmission. By incorporating steganography within blockchain networks, users can hide messages in transactions, ensuring confidentiality without altering the integrity of the chain.
- Cloud Computing: As cloud storage becomes prevalent, steganography applies to protect sensitive information stored online. Data is hidden within files uploaded to cloud services, adding an extra layer of security against unauthorized access.
- Digital Watermarking Integration: The integration of steganography with digital watermarking further secures content ownership. This dual approach embeds copyright information while concealing additional messages in media files.
As these trends develop, expect increased focus on enhancing security measures through sophisticated algorithms and techniques. How will organizations adapt their strategies? They’ll likely invest in research and tools that leverage these innovations for better protection against data breaches and unauthorized surveillance.