Statistics shape our understanding of the world in powerful ways. Have you ever wondered how data influences decisions in business, healthcare, or even sports? Statistics examples reveal the stories behind the numbers and help us make sense of complex information.
In this article, you’ll explore a variety of statistics examples that illustrate their practical applications across different fields. From analyzing consumer behavior to measuring public health trends, these examples will show you just how integral statistics are to everyday life. Get ready to uncover insights that can transform your perspective on data. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply curious about numbers, understanding these concepts can empower you to interpret data more effectively and make informed choices.
Overview Of Statistics Examples
Statistics offer practical insights across various fields. Here are some notable examples:
- Business Performance: Companies often analyze sales data to identify trends. For instance, a retail store may track monthly sales figures to assess the impact of seasonal promotions.
- Healthcare Research: Medical studies rely heavily on statistics. Researchers frequently use patient data to evaluate treatment effectiveness, often presenting findings through statistical significance metrics.
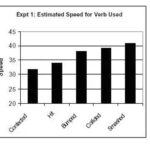
- Sports Analytics: Teams utilize statistics to enhance performance. Coaches might analyze player statistics like shooting percentages or goals scored to develop strategies for upcoming games.
- Education Assessment: Schools assess student performance through standardized tests. These results help educators identify areas needing improvement and tailor curriculum accordingly.
- Public Opinion Polls: Polling organizations conduct surveys to gauge public sentiment on issues. Results can influence political campaigns and policymaking, reflecting community interests and concerns.
These examples illustrate how statistics inform decisions in everyday life, helping you understand complex information effectively.
Descriptive Statistics Examples
Descriptive statistics summarize and describe the characteristics of data. They provide insights that help you understand trends and patterns in various fields. Here are some key examples.
Measures Of Central Tendency
Measures of central tendency include the mean, median, and mode.
- Mean: This is the average value of a data set. For example, if you have test scores of 80, 85, and 90, the mean is (80 + 85 + 90) / 3 = 85.
- Median: This represents the middle value when data points are ordered. In a list like 70, 75, 85, the median is 75 since it’s in the center.
- Mode: This identifies the most frequently occurring value in your data set. If your survey results show responses as 2, 3, 3, and 5, then 3 is the mode.
Understanding these measures helps you interpret data more effectively.
Measures Of Dispersion
Measures of dispersion describe how spread out or varied your data points are.
- Range: The difference between the highest and lowest values gives insight into variability. For instance, if your ages are 20 to 40 years old, then your range is 20 years.
- Variance: This indicates how much individual numbers differ from the mean. A high variance means numbers are widely spread out; a low variance indicates they’re closer together.
- Standard Deviation: It’s a measure that quantifies variability by showing how much scores deviate from the average score on average. For instance, if a dataset has a standard deviation of 5, it suggests that most values lie within ±5 units from the mean.
Each measure provides valuable context for analyzing statistical information effectively.
Inferential Statistics Examples
Inferential statistics draw conclusions about a population based on a sample. Here are some key examples that illustrate its application.
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing evaluates claims using statistical evidence. For instance, consider a company wanting to determine if a new marketing strategy increases sales. The null hypothesis states that the strategy has no effect, while the alternative suggests it does. After analyzing sales data from both periods, you might find p-values indicating whether to reject or accept the null hypothesis. This process helps in making informed decisions regarding marketing efforts.
Confidence Intervals
Confidence intervals provide a range of values within which a population parameter likely falls. For example, if you conduct a survey and find that 60% of respondents prefer product A over product B with a 95% confidence interval of (55%, 65%), you can assert that between 55% and 65% of the entire population prefers product A. This method gives insight into public preferences while acknowledging potential variability in your sample results.
These inferential statistics examples demonstrate how powerful these techniques are for making predictions and guiding decisions across various fields like business and healthcare.
Real-World Applications Of Statistics Examples
Statistics play a vital role across various fields, providing insights that shape decisions and strategies. Here are some practical examples of how statistics are applied in different domains.
Business Analytics
In business analytics, companies leverage statistics to drive growth and optimize operations. For instance:
- Sales Forecasting: Businesses analyze historical sales data to predict future trends. This helps in planning inventory.
- Customer Segmentation: By examining purchasing patterns, companies identify distinct customer groups, allowing for targeted marketing strategies.
- Market Research: Surveys collect consumer opinions on products or services. Statistical analysis reveals preferences that can guide product development.
These applications demonstrate how businesses use statistics for informed decision-making and competitive advantage.
Healthcare Studies
Healthcare relies heavily on statistical methods to improve patient outcomes and evaluate treatments. Key examples include:
- Clinical Trials: Researchers utilize statistics to assess the effectiveness of new medications by comparing results between treated and control groups.
- Epidemiological Studies: Statistics help track disease outbreaks, enabling public health officials to respond effectively based on data-driven insights.
- Patient Outcomes Analysis: Hospitals analyze recovery rates using statistical tools, identifying factors that contribute to successful treatments.
Such examples highlight the importance of statistics in enhancing healthcare practices and ensuring evidence-based approaches.