Ever wondered what makes your favorite songs so memorable? The magic often lies in their song structure examples. Understanding these structures can unlock the secrets behind hit tracks and inspire you to create your own music.
In this article, you’ll explore various song structures that have shaped the music industry, from classic verse-chorus formats to more complex arrangements. Each example will give you insights into how artists craft their narratives and evoke emotions through melody and rhythm. Are you ready to dive into the world of songwriting?
Understanding Song Structure
Understanding song structure is crucial for crafting engaging music. Different structures serve distinct purposes, impacting the listener’s experience. By exploring various examples, you can identify elements that resonate and enhance your songwriting.
Importance of Song Structure
Song structure shapes how listeners perceive and connect with music. It creates familiarity, allowing audiences to anticipate changes and build emotional responses. For instance:
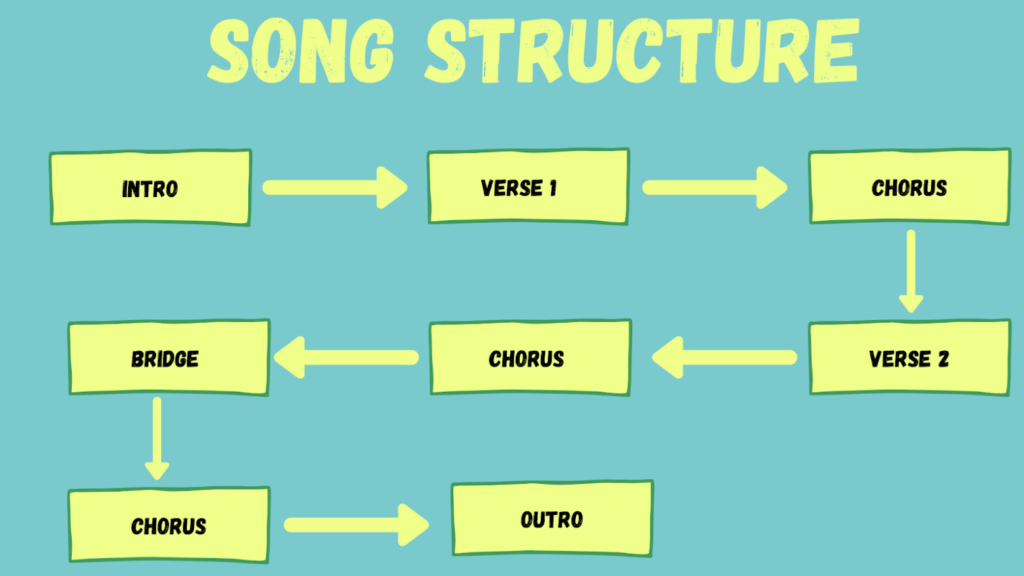
- Verse-Chorus Format: This popular structure supports storytelling, where verses set up a narrative while choruses deliver the emotional punch.
- AABA Pattern: Often found in classic pop songs, this format features two sections followed by a contrasting bridge, creating variation while maintaining cohesion.
Recognizing these patterns helps you create memorable songs that engage your audience effectively.
Common Elements of Song Structure
Key elements define most song structures across genres. Familiarity with these components can streamline your songwriting process. Common elements include:
- Verses: Develop the story or theme.
- Choruses: Present the main message or hook.
- Bridges: Offer contrast and transition between sections.
- Pre-Choruses: Build anticipation before the chorus.
Knowing how to use these elements allows you to experiment within established frameworks, making your music stand out even more.
Popular Song Structure Examples
Understanding popular song structures can enhance your songwriting. Here are some widely used formats in music.
Verse-Chorus Structure
The Verse-Chorus Structure is prevalent in many hit songs. This format typically alternates between verses and a catchy chorus, allowing for storytelling and emotional peaks. For example:
- Verses introduce the narrative, providing details.
- Choruses deliver the main message or hook, creating memorability.
Many artists use this structure to engage listeners effectively, making it one of the most recognizable formats in music today.
ABAB Structure
The ABAB Structure follows an alternating pattern of two different sections. In this setup:
- The first section (A) presents a theme or idea.
- The second section (B) contrasts or complements that idea.
This back-and-forth creates dynamic energy within the song. Classic examples include many pop and rock tracks where themes evolve through repetition and variance, keeping listeners intrigued from start to finish.
Analyzing Different Genres
Understanding how different genres utilize song structures enhances your songwriting skills. Each genre has unique characteristics that shape its musical storytelling, making it vital to explore various examples.
Pop Song Structure Examples
Many pop songs follow a simple yet effective structure. A common format is the Verse-Chorus-Verse-Chorus-Bridge-Chorus layout. This design creates familiarity and keeps listeners engaged.
Here are key elements in pop songs:
For instance, “Shake It Off” by Taylor Swift illustrates this structure well, with verses setting up a story of resilience followed by an infectious chorus.
Rock Song Structure Examples
Rock music often employs variations on classic structures, emphasizing strong instrumentation and emotional intensity. The Verse-Chorus-Verse-Solo-Chorus format is prevalent in many rock hits.
Key characteristics of rock song structures include:
A great example is “Stairway to Heaven” by Led Zeppelin, where intricate guitar solos enhance emotional peaks alongside powerful lyrics.
Creative Variations in Song Structure
Exploring creative variations in song structure reveals how artists push boundaries and innovate within their music. Non-standard formats and experimental approaches add depth and intrigue to songwriting.
Non-Standard Structures
Non-standard structures often deviate from traditional patterns, creating unique listening experiences. For example, the through-composed format features continuous musical development without repeated sections. A notable instance is Radiohead’s “Pyramid Song,” which flows seamlessly, enhancing its ethereal quality.
Another variation is the verse-chorus-less structure, where songs lack a clear chorus altogether. An example includes “Blackbird” by The Beatles; it focuses on storytelling through verses instead of relying on repetitive hooks.
Experimental Approaches
Experimental approaches challenge conventional songwriting norms. Consider the mashup, combining multiple songs into one piece, like DJ Earworm’s annual “United State of Pop.” This technique blends various melodies and lyrics into a cohesive whole, showcasing creativity.
Also noteworthy is the use of polyrhythms, which introduces complex layering of rhythms. In “Take Five” by Dave Brubeck, you experience an unusual time signature (5/4), providing listeners with a fresh auditory experience that breaks away from standard rhythmic patterns.
These variations demonstrate how breaking free from traditional structures can enhance artistry and captivate audiences.