In today’s fast-paced digital world, understanding software is more crucial than ever. Have you ever wondered how the apps on your phone or the programs on your computer come to life? From simple tools that help with everyday tasks to complex systems driving entire industries, software plays a pivotal role in our daily lives.
Overview of Software
Software plays a crucial role in various aspects of life. It can be categorized into two main types: application software and system software.
Application software includes programs designed for end-users to perform specific tasks. Examples include:
- Microsoft Word for document creation
- Adobe Photoshop for image editing
- Google Chrome for web browsing
These applications enhance productivity and creativity.
System software serves as the backbone of computer operations. It manages hardware resources and provides a platform for application software. Examples are:
- Windows operating system, which facilitates user interaction with computers
- macOS, tailored for Apple devices
- Linux distributions, known for their flexibility and open-source nature
Both categories demonstrate the diverse functionalities that software offers across different industries.
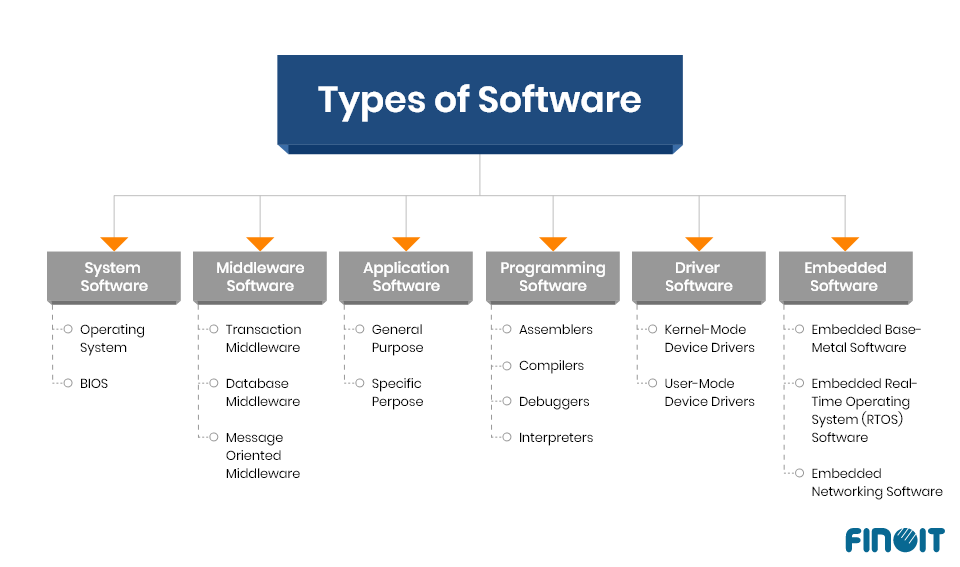
Types of Software
Understanding the different types of software enhances your ability to select the right tools for your needs. The main categories include system software, application software, and development software.
System Software
System software acts as the foundation for computer operations. It manages hardware resources and provides an environment for applications to run. Examples include:
- Operating Systems: Windows, macOS, Linux
- Device Drivers: Printer drivers, graphics card drivers
- Utility Programs: Disk cleanup tools, antivirus programs
These components ensure that your computer functions efficiently and supports various tasks seamlessly.
Application Software
Application software serves specific user tasks or activities. You rely on these programs daily to enhance productivity and creativity. Common examples are:
- Word Processors: Microsoft Word, Google Docs
- Spreadsheets: Excel, Google Sheets
- Web Browsers: Chrome, Firefox
- Graphic Design Tools: Adobe Photoshop, Canva
Each type caters to unique needs in personal or professional settings.
Development Software
Development software facilitates the creation of applications and systems. This category includes a variety of tools that streamline coding and debugging processes. Key examples are:
- Integrated Development Environments (IDEs): Visual Studio, Eclipse
- Version Control Systems: GitHub, Bitbucket
- Text Editors: Sublime Text, Atom
Using these tools can significantly improve efficiency in coding projects while ensuring proper version management.
Key Features of Software
Software encompasses various features that enhance user experience and operational efficiency. Understanding these features helps you choose the right software for your needs.
User Interface
User interface (UI) design significantly impacts how users interact with software. A well-designed UI promotes ease of use and accessibility. For instance, Microsoft Word offers a familiar ribbon layout that simplifies navigation, while Adobe Photoshop uses customizable tool palettes to cater to different workflows. Intuitive interfaces make it easier for users to accomplish tasks without extensive training.
Functionality
Functionality defines what a piece of software can do. Application software like Trello provides task management capabilities, allowing teams to organize projects efficiently. In contrast, system software such as Windows ensures hardware compatibility and resource management, enabling applications to run smoothly. Development tools like GitHub streamline collaboration on code projects by offering version control and issue tracking functionalities.
Performance
Performance measures how effectively software operates under different conditions. High-performance software handles tasks quickly and efficiently without lag or crashes. For example, database management systems like MySQL optimize data retrieval speeds, making them suitable for high-traffic websites. Additionally, graphic design programs like CorelDRAW leverage powerful processing capabilities to handle complex designs seamlessly without compromising speed or quality.
Software Development Lifecycle
The software development lifecycle (SDLC) outlines the stages involved in creating and maintaining software. Understanding this process is crucial for delivering high-quality applications effectively.
Planning
During the planning phase, you identify project goals and define requirements. This stage often involves gathering input from stakeholders to ensure all needs are met. For example, if you’re developing a mobile app, you’ll want to consider factors like target audience and desired features. A well-structured plan sets the foundation for successful development.
Development
In the development stage, programmers write code based on specifications outlined during planning. Teams use various programming languages and tools tailored to project needs. For instance, Java may be preferred for Android apps while Swift is ideal for iOS projects. Collaboration among developers ensures that coding aligns with design principles established earlier.
Testing
Testing comes next to verify functionality and performance. It includes different types of tests such as unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing (UAT). Each test type checks specific aspects; unit tests focus on individual components while UAT assesses overall usability from an end-user perspective. Bugs must be identified and fixed before moving forward.
Deployment
Deployment marks the final step where software is released to users or clients. This phase can involve several activities such as installation, configuration, and training users on new systems. Post-deployment support ensures ongoing maintenance and updates address any emerging issues or feature requests from users over time.