Ever wondered how to enhance your writing and make it more dynamic? Reporting verbs are the secret ingredient that can transform simple statements into engaging narratives. These powerful verbs not only convey what someone said but also reflect the speaker’s attitude and intention, giving depth to your communication.
Overview Of Reporting Verbs
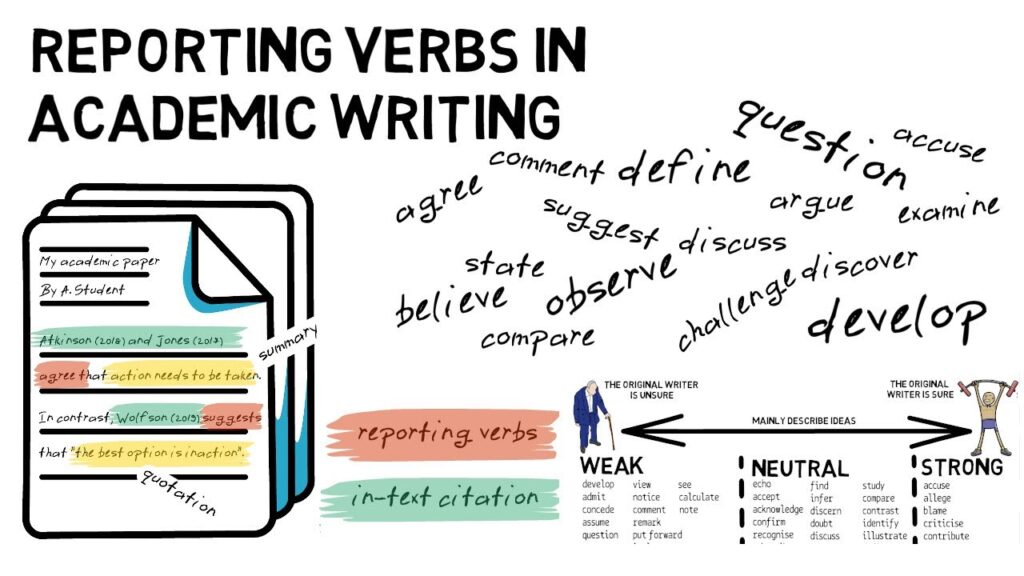
Reporting verbs play a crucial role in enhancing clarity and precision in communication. These verbs help convey not only what was said but also how it was said. You can categorize reporting verbs into different types based on their functions. Here are some common examples:
- Say: This is the most straightforward reporting verb. For example, “She said she would join us later.”
- Tell: This implies giving information directly to someone. An example would be, “He told me about the meeting.”
- Ask: Use this when posing a question or request. For instance, “They asked if I could attend the event.”
- Suggest: This conveys recommendations or proposals. You might say, “She suggested we try that new restaurant.”
Each of these verbs adds a unique flavor to your narrative, allowing for greater nuance and understanding of intent.
Moreover, you can use modifiers with these verbs to express varying degrees of certainty or emotion:
- Insist: It shows strong conviction. For example, “He insisted that we leave early.”
- Admit: This indicates acknowledgment of a fact. You might say, “She admitted she made an error.”
Using reporting verbs effectively enriches dialogue and description in writing while providing insight into characters’ motivations and emotions.
Here’s a summary table showcasing various reporting verbs along with their typical usage:
| Reporting Verb | Usage Example |
|---|---|
| Say | “She said it was raining.” |
| Tell | “He told them about his plans.” |
| Ask | “They asked where the store was located.” |
| Suggest | “I suggest trying the new cafe.” |
| Insist | “She insisted on finishing her work first.” |
| Admit | “He admitted he forgot the appointment.” |
Utilizing these examples enhances your ability to communicate effectively through written language by allowing varied expression of speech acts and intentions.
Types Of Reporting Verbs
Reporting verbs can be categorized into two main types: direct and indirect reporting verbs. Each type serves a distinct purpose in conveying speech or thought.
Direct Reporting Verbs
Direct reporting verbs convey the exact words spoken by a person. You use them to present someone’s statement verbatim, often enclosed in quotation marks. For example:
- “He said,” she explained the situation clearly.
- “I will finish this project,” he insisted with confidence.
These verbs emphasize the speaker’s intention and tone. By using direct reporting, you create immediacy and authenticity in dialogue.
Indirect Reporting Verbs
Indirect reporting verbs paraphrase what someone has said without quoting them directly. This approach allows for summarization while maintaining the essence of their message. Examples include:
- She mentioned that she would attend the meeting.
- He suggested that we consider alternative solutions.
Using indirect reporting helps streamline communication and focuses on the message rather than the exact wording, making it useful for summarizing discussions or relaying information efficiently.
Functions Of Reporting Verbs
Reporting verbs serve multiple functions in writing, enhancing clarity and depth in communication. They not only convey what someone said but also add layers of meaning through tone and intent.
Adding Credibility
Using reporting verbs can enhance the credibility of your statements. For instance, phrases like “according to” or “as reported by” signal that information comes from a reliable source. You might say, “According to experts,” which establishes authority in your argument. Additionally, citing sources such as research studies or expert opinions with reporting verbs strengthens your claims. It shows you’ve done your homework and adds weight to your narrative.
Indicating Attitude
Reporting verbs also indicate the speaker’s attitude towards the statement made. For example, using “argue” implies a strong position on a topic, while “suggest” conveys a softer recommendation. Consider these examples:
- “He argued that climate change is urgent.”
- “She suggested we consider alternative solutions.”
Such choices reveal emotions or biases behind messages, informing readers about underlying motives or feelings tied to those words. By understanding these nuances, you communicate more effectively and engage your audience more deeply.
Common Reporting Verbs
Understanding common reporting verbs enhances communication and enriches writing. These verbs convey statements, attitudes, and intentions, providing clarity and depth to narratives.
Say Vs. Tell
The verbs say and tell serve distinct functions in dialogue. You use say when quoting someone’s exact words or expressing general statements. For example:
- She said, “I’ll join the team later.”
- He says that the project is on track.
Conversely, you use tell when imparting information directly to someone or indicating what a person has communicated. Examples include:
- She told him about the meeting.
- He tells his friends everything he knows.
While they seem similar, using them correctly clarifies your message.
Other Frequently Used Verbs
Many other reporting verbs broaden expression in writing. Here are some frequently used options:
- Ask: To inquire about something.
- Example: She asked if anyone needed help.
- Suggest: To propose an idea or course of action.
- Example: He suggested starting the meeting earlier.
- Admit: To acknowledge something reluctantly.
- Example: She admitted she made a mistake.
These verbs add nuance to your narrative by reflecting attitudes and intentions effectively. By incorporating varied reporting verbs into your writing, you enhance engagement and improve understanding for your audience.