Have you ever wondered what drives your decisions? Understanding rational motives can unlock the secrets behind why you choose one option over another. These motives are rooted in logic and reason, guiding us toward choices that seem most beneficial. Whether it’s selecting a product or making a career move, recognizing these underlying factors can enhance your decision-making skills.
Understanding Rational Motives
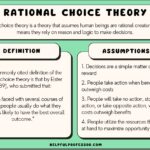
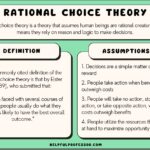
Rational motives are driven by logic and reason, influencing your decisions in a significant way. When you recognize these motives, you can make choices that align with your best interests.
Definition of Rational Motives
Rational motives refer to the reasons behind decisions that rely on factual information and logical reasoning. They often involve weighing pros and cons before making a choice. For instance, when purchasing a car, you might consider factors like fuel efficiency, safety ratings, and price. These elements guide your decision-making process based on objective criteria rather than emotional impulses.
Importance in Decision Making
Understanding rational motives enhances your ability to make informed choices. They help you evaluate options systematically and minimize impulsive decisions. For example:
- Job Selection: You may analyze salary benefits, work-life balance, and career growth opportunities.
- Investment Choices: You could assess market trends, potential returns, and associated risks before investing.
- Purchasing Decisions: You might compare product specifications and customer reviews to select the best item.
By focusing on rational motives during decision-making processes, you increase the likelihood of achieving favorable outcomes aligned with your goals.
Types of Rational Motives
Understanding the various types of rational motives helps clarify decision-making processes. Two primary categories include economic and social motives, each influencing choices in distinct ways.
Economic Motives
Economic motives focus on financial factors that drive decisions. These motives emphasize cost-effectiveness and value for money. For instance, when you choose a product, you might consider:
- Price: Does it fit within your budget?
- Quality: Is the product durable and reliable?
- Value: Are you getting more features for a similar price?
You often assess these elements to ensure your purchase is wise financially.
Social Motives
Social motives relate to the influence of societal factors on your choices. These motives highlight how relationships and social status impact decisions. When selecting a brand or service, you might think about:
- Brand Reputation: Is it well-regarded by peers?
- Social Acceptance: Will using this product enhance your status among friends?
- Peer Pressure: Are others in your circle choosing this option?
You frequently weigh these aspects to align with social norms or expectations.
Rational Motives in Consumer Behavior
Rational motives significantly shape consumer behavior, guiding decisions based on logic rather than emotion. Understanding these motives can enhance your purchasing strategies and lead to better outcomes.
Influence on Purchasing Decisions
Rational motives directly influence your purchasing decisions by emphasizing logical reasoning. For example:
- Cost Efficiency: When selecting a smartphone, you might compare prices and features to find the best value.
- Quality Assurance: Choosing a washing machine often involves researching durability ratings and energy efficiency.
- Functionality Needs: If you’re buying a laptop, you likely evaluate processor speed and memory size against your specific usage requirements.
These factors encourage you to make informed choices that align with your practical needs.
Role in Marketing Strategies
Marketers leverage rational motives to appeal to consumers’ logical faculties. They often highlight objective facts that resonate with potential buyers. Consider these strategies:
- Comparative Advertising: Brands may showcase side-by-side comparisons of their products against competitors, focusing on superior features or pricing.
- Data-driven Claims: Many businesses utilize statistics or studies demonstrating the effectiveness or efficiency of their products, appealing directly to rational decision-making.
- Value Messaging: Companies often emphasize long-term savings associated with their offerings, such as reduced energy costs for appliances.
Such approaches effectively capture attention while reinforcing the importance of rational thinking in consumer choices.
Theories Related to Rational Motives
Rational motives are deeply rooted in various psychological theories that explain decision-making processes. Understanding these theories enhances your grasp of how rational motives influence choices.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs outlines a model that prioritizes human motivations. At its base, strong economic factors drive decisions related to physiological needs, like food and shelter. As you move up the hierarchy, social motives gain importance. For example:
- Individuals seek safety in their jobs for financial security.
- People choose brands based on reputation and social acceptance.
Thus, both economic and social rational motives play crucial roles throughout the hierarchy.
The Theory of Planned Behavior
The Theory of Planned Behavior emphasizes how intention influences behavior through rational thinking. Your decisions depend on three components:
- Attitude toward the behavior: If you believe a product is effective, you’re more inclined to buy it.
- Subjective norms: Social pressures can push you toward certain choices, such as opting for popular brands.
- Perceived behavioral control: If you feel confident in making informed choices about products or services, you’re likely to act on those beliefs.
Altogether, this theory illustrates how rational motives guide your actions by combining personal beliefs with external influences.
Practical Applications of Rational Motives
Rational motives play a vital role in various aspects of life, influencing decisions in both business and personal development. Understanding these applications enhances your ability to make informed choices.
Rational Motives in Business
In the business realm, rational motives drive strategic decision-making. For instance, companies often focus on profit maximization by evaluating cost-effectiveness. They consider factors like:
- Market demand: Analyzing customer needs helps tailor products effectively.
- Operational efficiency: Streamlining processes reduces waste and increases productivity.
- Competitive analysis: Examining competitors’ strengths and weaknesses informs pricing strategies.
Data-driven decisions lead to better outcomes. Businesses that prioritize logical reasoning can adapt quickly to market changes while maintaining profitability.
Rational Motives in Personal Development
When it comes to personal development, rational motives guide you toward self-improvement goals. You might evaluate options based on:
- Skill acquisition: Identifying skills that enhance career prospects can direct your learning efforts.
- Health choices: Assessing nutritional information helps you make better dietary decisions.
- Financial planning: Creating budgets based on income and expenses ensures financial stability.
Setting clear objectives enables effective progress tracking. By applying rational thinking, you align daily actions with long-term aspirations, fostering continuous growth.