Ever wondered why people make the choices they do? Rational choice theory examples offer fascinating insights into decision-making processes, revealing how individuals weigh options to maximize benefits and minimize costs. This theory suggests that when faced with a choice, you evaluate the possible outcomes based on logic and personal preferences.
Overview of Rational Choice Theory
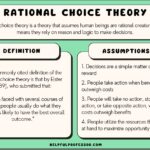
Rational choice theory focuses on the decision-making process individuals use when faced with options. You evaluate choices based on expected outcomes, weighing costs against benefits. This theory assumes that people act logically to maximize their utility.
Examples illustrate how rational choice theory operates in real life:
- Consumer Behavior: When purchasing a smartphone, you compare features like price, brand reputation, and technical specifications before deciding.
- Voting Decisions: In elections, voters assess candidates’ policies and past performances to choose whom they believe will serve their interests best.
- Career Choices: Individuals consider salary, job satisfaction, and growth opportunities when selecting a career path.
Each example highlights how decisions are driven by logical evaluations rather than emotions or social influences.
Common Examples of Rational Choice Theory
Rational choice theory applies to various aspects of daily life, revealing how you make decisions based on logical evaluations. Below are some common examples that illustrate this concept.
Economic Decisions
Economic decisions often reflect rational choice principles. When you decide to purchase a product, you typically compare prices and quality. For instance, when choosing between two smartphones, you assess features like camera quality, battery life, and cost. This evaluation helps maximize your satisfaction while minimizing expenses.
Political Choices
Political choices showcase rational decision-making too. Voters analyze candidates’ policies before casting their ballots. If you’re considering a candidate’s stance on healthcare or taxes, you weigh how these policies affect your life directly. You aim to choose the option that aligns best with your values and interests.
Social Interactions
Social interactions can also be explained through rational choice theory. When deciding whether to attend a social event, you consider factors like potential enjoyment versus time commitment. If the perceived benefits outweigh the costs—like meeting new people or having fun—you’re more likely to go.
Applications in Various Fields
Rational choice theory finds significant application across various disciplines, illustrating how individuals make decisions based on logical evaluations. Here are specific applications in different fields:
Economics
In economics, rational choice theory explains consumer behavior. For instance, when buying a car, you assess factors like price, fuel efficiency, and brand reputation. By comparing these attributes, you aim to maximize utility while minimizing costs. This approach also applies to investment decisions where individuals weigh risks against potential returns.
Sociology
Sociology utilizes rational choice theory to understand social interactions. When deciding whether to attend a social event, you consider factors such as enjoyment versus time commitment. If the perceived benefits of attending outweigh the costs of your time and effort, you’re more likely to participate. This evaluation helps explain trends in social behavior and group dynamics.
Political Science
In political science, rational choice theory plays a crucial role in voter behavior analysis. Voters examine candidates’ policies and past performances before making their choices during elections. For example, if one candidate supports tax cuts that align with your financial interests while another proposes increased taxes for social programs, you’ll likely vote for the candidate whose platform maximizes your economic benefit.
Critiques of Rational Choice Theory
Rational choice theory faces several critiques, particularly regarding its assumptions and applications. Critics argue that the notion of individuals acting purely rationally often doesn’t hold true in real-world scenarios.
Limitations
Rational choice theory relies on a few key assumptions, which can limit its applicability:
- Assumes perfect information: It posits that individuals have access to all relevant information before making decisions. However, this isn’t realistic as people often make choices based on incomplete or biased data.
- Ignores emotional factors: The theory overlooks how emotions significantly influence decision-making. People don’t always act logically; feelings can lead to decisions that deviate from maximizing utility.
- Simplifies complex behaviors: Human behavior is multifaceted; reducing it to pure logic neglects social, cultural, and contextual influences.
Alternative Theories
Several alternatives challenge the premises of rational choice theory:
- Bounded rationality: This concept suggests that while individuals strive for optimal decisions, cognitive limitations hinder their ability to evaluate all options fully.
- Behavioral economics: This field examines how psychological factors impact economic decision-making. It highlights biases and heuristics, showing how they affect choices in ways not accounted for by traditional theories.
- Social choice theory: This approach focuses on collective decision-making processes. It acknowledges the complexities involved when groups must reach a consensus rather than just individual preferences.
These critiques emphasize the need for a more nuanced understanding of decision-making beyond strict rationality.