Imagine running a business where every process flows seamlessly and customer satisfaction skyrockets. That’s the power of a quality management system example in action. Whether you’re a small startup or an established corporation, implementing effective quality management can transform your operations and drive success.
In this article, you’ll discover various quality management system examples that illustrate how organizations effectively maintain high standards while enhancing efficiency. From ISO certifications to Six Sigma methodologies, these frameworks provide practical insights into achieving excellence. Are you ready to elevate your business practices? Dive in as we explore real-world applications that demonstrate the impact of robust quality management systems on performance and growth.
Understanding Quality Management Systems
Quality management systems (QMS) play a crucial role in enhancing organizational efficiency and customer satisfaction. They help businesses maintain high standards through structured processes.
Definition of Quality Management System
A quality management system refers to the organizational structure, procedures, processes, and resources needed to implement quality management. An effective QMS ensures that an organization meets customer requirements and regulatory standards consistently. For example, ISO 9001 provides a framework for maintaining product quality while improving operational performance.
Importance of Quality Management Systems
The significance of quality management systems cannot be overstated. Implementing a QMS leads to improved efficiency and reduced waste, which directly impacts profitability. Additionally, strong QMS practices enhance customer trust by ensuring reliable products and services. Consider these key benefits:
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: A focus on quality improves overall customer experience.
- Regulatory Compliance: A robust QMS helps navigate complex regulations.
- Continuous Improvement: Implementing feedback loops fosters ongoing enhancements in processes.
By prioritizing a well-designed QMS, you position your organization for sustained growth and success in competitive markets.
Key Components of a Quality Management System
A quality management system (QMS) includes several key components that ensure processes run smoothly and customer needs are met. Understanding these components helps you implement effective practices.
Customer Focus
Customer focus drives quality management. Organizations prioritize understanding customer requirements to enhance satisfaction. For example, companies like Amazon gather feedback through surveys and reviews, allowing them to adapt services based on user preferences. This commitment leads to better product offerings and improved loyalty from customers.
Leadership and Commitment
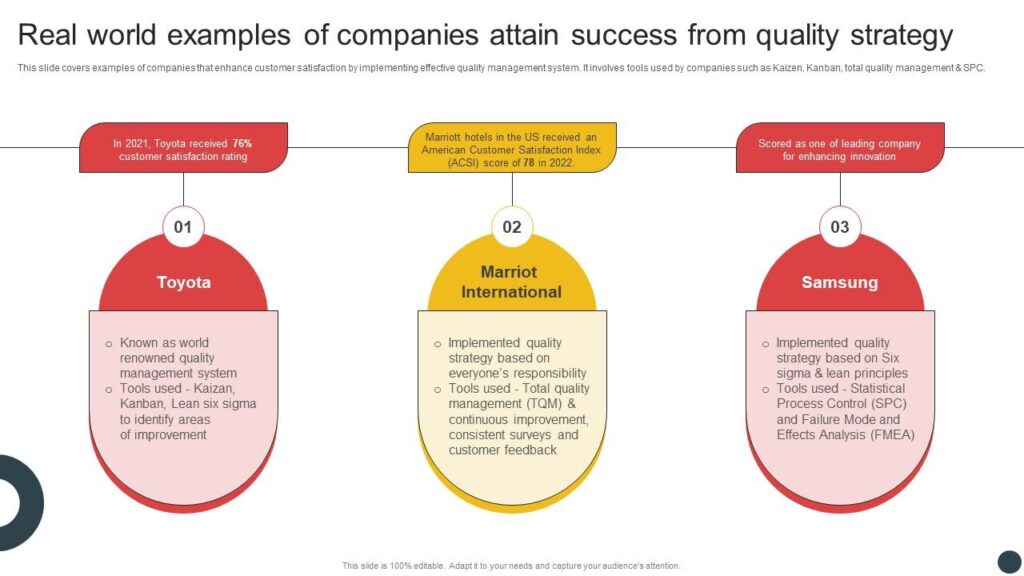
Leadership plays a crucial role in QMS success. Effective leaders establish a culture of quality throughout the organization. Take Toyota as an example; its leaders emphasize continuous improvement and employee engagement in decision-making processes. Such commitment fosters an environment where everyone is accountable for maintaining high standards.
Process Approach
A process approach streamlines operations. By viewing activities as interconnected processes, organizations can identify inefficiencies more easily. For instance, Dell employs this method by mapping out supply chain procedures to reduce lead times and minimize waste. This systematic view enhances productivity while ensuring consistent output quality.
A Quality Management System Example
A quality management system (QMS) can transform your organization’s approach to quality. Here are examples that illustrate effective implementation in real-world scenarios.
Case Study Overview
One notable example is Toyota, known for its Toyota Production System (TPS). This system emphasizes continuous improvement and respect for people, resulting in high-quality vehicle production. Another example is Amazon, which leverages customer feedback through a robust QMS to refine its services continuously. By prioritizing customer satisfaction, both companies demonstrate the effectiveness of structured quality management practices.
Implementation Process
Implementing a QMS involves several key steps:
- Define Objectives: Clearly outline what you aim to achieve with your QMS.
- Engage Leadership: Secure commitment from top management to foster a culture of quality.
- Develop Processes: Establish processes that align with organizational goals and customer needs.
- Train Employees: Provide training sessions so everyone understands their roles within the QMS.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly assess performance metrics to identify areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement: Use data-driven insights to enhance processes continually.
Incorporating these steps ensures a solid foundation for your QMS, leading to improved efficiency and customer satisfaction over time.
Benefits of Implementing a Quality Management System
Implementing a quality management system (QMS) offers several key advantages that can significantly impact your organization. These benefits range from improved efficiency to enhanced customer satisfaction, creating a strong foundation for success.
Improved Efficiency
A QMS streamlines processes and eliminates inefficiencies. By focusing on standardized procedures, you can reduce errors and enhance productivity. For example, companies like Toyota use their Production System to minimize waste while maintaining high standards. You may notice reduced operational costs and faster turnaround times as workflows become more efficient.
- Standardization: Establishes consistent practices across departments.
- Process Mapping: Helps identify bottlenecks in operations.
- Data Analysis: Provides insights into performance metrics for continuous improvement.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction improves when organizations prioritize quality management. When you consistently deliver reliable products or services, trust builds with your customers. Amazon exemplifies this by using feedback loops to adapt its offerings based on customer preferences. Satisfied customers often lead to repeat business and positive referrals, contributing to long-term growth.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Allow real-time adjustments based on customer input.
- Quality Assurance: Ensures products meet established standards before reaching consumers.
- Personalized Services: Tailor experiences based on individual customer needs.
Embracing these benefits through an effective QMS positions your organization favorably in today’s competitive landscape.