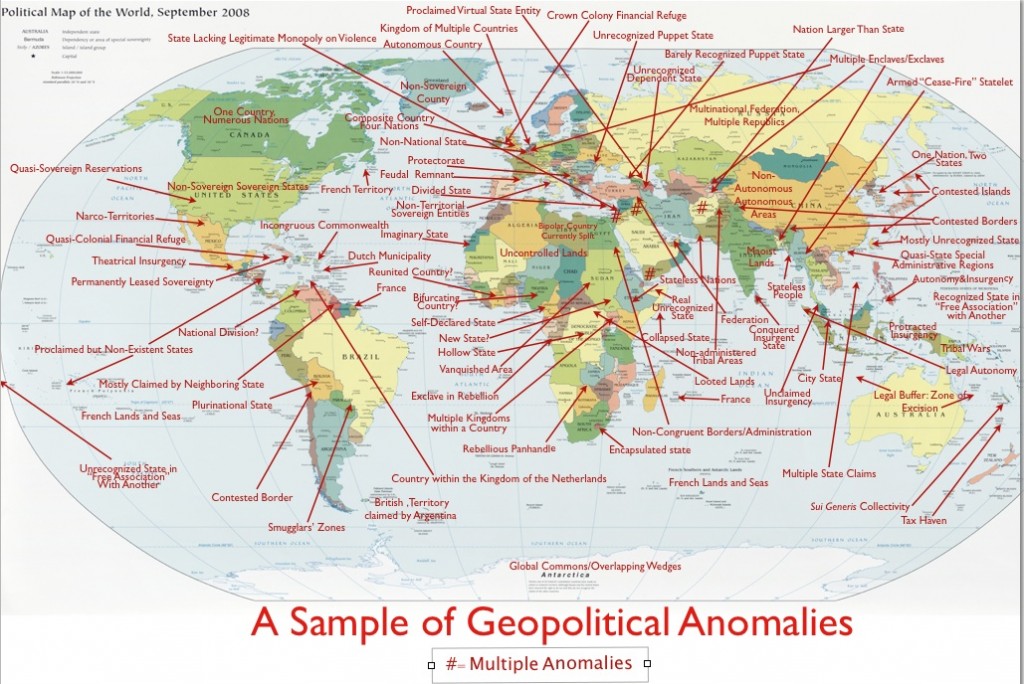
Imagine a country that juts out like a puzzle piece, extending into neighboring territories. This unique geographical formation is known as a prorupted state. But what exactly does this mean for the countries and their interactions? In this article, you’ll explore the fascinating world of prorupted states, where geography shapes politics and culture in unexpected ways.
Understanding Prorupted States
Prorupted states feature unique geographical shapes, extending into territories of neighboring countries. These formations can significantly influence political dynamics and cultural relationships. Here are some notable examples:
- Democratic Republic of the Congo: This state has a significant prorupted area that extends towards the Atlantic Ocean, facilitating access to maritime trade routes.
- Thailand: Thailand’s extension into Malaysia creates not only territorial claims but also affects regional trade agreements.
- Afghanistan: The country’s protrusion into Pakistan impacts its security and diplomatic relations with neighboring nations.
These examples underscore how prorupted states navigate complex interactions due to their geographical configurations. Each state’s unique shape influences its political landscape and economic opportunities.
Characteristics of Prorupted States
Prorupted states exhibit unique features that significantly impact their geographic and political frameworks. These characteristics shape their interactions with neighboring countries.
Geographic Implications
Prorupted states often have irregular shapes, extending into other territories. This distinct geography affects access to resources and trade routes. For example:
- Democratic Republic of the Congo: Its prorupted area allows better access to maritime trade via the Atlantic Ocean.
- Thailand: The extension into Malaysia influences regional connectivity and logistics for trade.
- Afghanistan: The protrusion into Pakistan affects land distribution and resource management.
Such geographical quirks can create advantages or challenges in international relations.
Political Dynamics
Political dynamics in prorupted states often reflect their unique configurations. The shape can lead to complex territorial disputes or alliances. Consider these aspects:
- Border Conflicts: Disputes over borders arise due to the protruded areas, causing tensions with neighbors.
- Regional Influence: Prorupted states may leverage their position for negotiation power in trade agreements or security pacts.
- Cultural Interactions: Protrusions might facilitate cultural exchanges but also lead to competition for resources.
These factors play a crucial role in shaping both internal governance and external diplomacy within prorupted states.
Examples of Prorupted States
Prorupted states provide fascinating insights into how geography shapes nations. Here are notable examples that illustrate the concept.
Historical Context
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is a prime example. Its prorupted shape, extending towards the Atlantic Ocean, emerged from colonial borders drawn in the late 19th century. This configuration aimed to secure access to maritime trade routes and resources like minerals, which remains crucial for its economy today.
Thailand’s extension into Malaysia reflects historical territorial disputes. The British colonization influenced border demarcation, leading to a prorupted state that affects modern political relationships and trade agreements with neighboring countries.
Contemporary Cases
Afghanistan’s protrusion into Pakistan illustrates ongoing security concerns. The unique geographic shape complicates border control and fosters cross-border tensions, impacting diplomatic relations between both nations.
Countries like Angola, which features the Cabinda exclave, showcase another contemporary case. This region extends northward along the coastline, separating it from mainland Angola. Such configurations often lead to resource management challenges and regional autonomy movements.
Prorupted states significantly influence geopolitical dynamics through their distinctive shapes and historical contexts. Understanding these examples highlights how geography directly impacts politics and culture in these regions.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Prorupted states possess distinct advantages and disadvantages that shape their political and economic landscapes. Understanding these factors is crucial for comprehending the dynamics within such countries.
Economic Impact
Prorupted states often experience unique economic opportunities. For instance, a prorupted area can provide direct access to valuable resources or trade routes, enhancing a state’s economic viability. In the case of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, this geographical feature allows better access to maritime trade routes, promoting international commerce.
However, challenges also arise. Economic disparities may occur between prorupted regions and core areas, leading to uneven development. For example, Afghanistan’s protrusion into Pakistan complicates resource distribution and investment in remote areas.
Security Considerations
Security concerns significantly affect prorupted states. The irregular borders might create vulnerabilities that neighboring countries can exploit. Take Thailand as an example; its extension into Malaysia sometimes leads to territorial disputes impacting regional stability.
Moreover, internal security issues frequently emerge due to border complexities. In Afghanistan, tensions with Pakistan continually strain diplomatic relations, affecting national security strategies. These considerations highlight the fragile balance between geographic configuration and safety in prorupted states.