Have you ever stopped to think about how much of your daily life is influenced by products made from petroleum? From the fuel that powers your car to the plastic in your smartphone, petroleum plays a crucial role in modern society. It’s not just about gasoline; this versatile resource is the backbone of countless items we often take for granted.
Overview of Petroleum Products
Petroleum products play a crucial role in everyday life. These products, derived from crude oil, encompass a wide range of items you likely use daily.
Fuel types include gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. Gasoline powers most vehicles on the road, while diesel fuels trucks and machinery. Jet fuel keeps airplanes flying.
Plastics are another significant category. Items like bottles, containers, and packaging materials rely heavily on petroleum-based plastics. They offer durability and versatility for countless applications.
Synthetic rubber, used in tires and footwear, also comes from petroleum. This material provides strength and flexibility in various products we depend on.
Cosmetics, such as lipsticks and lotions, often contain petroleum derivatives that contribute to their texture and moisture-retaining properties.
In addition to these examples:
- Asphalt, essential for roads,
- Lubricants, for machinery operation,
- Fertilizers, supporting agriculture,
All derive from petroleum processes.
Understanding these products highlights just how integral petroleum is to your daily activities. Each item serves a specific purpose rooted in the versatility of this natural resource.
Common Products Made From Petroleum
Petroleum is a vital resource that contributes to various everyday products. Here are some common examples of petroleum-derived items.
Fuels
Fuels derived from petroleum power modern transportation and machinery. Key examples include:
- Gasoline: Used in cars, motorcycles, and small engines.
- Diesel: Powers trucks, buses, and trains.
- Jet fuel: Essential for airplanes during flight.
These fuels enable efficient travel and commerce across the globe.
Plastics
Plastics are ubiquitous in daily life, primarily made from petrochemicals. Notable products include:
- Polyethylene: Found in plastic bags and bottles.
- PVC (polyvinyl chloride): Used for pipes and vinyl flooring.
- Polystyrene: Common in disposable cups and food containers.
These plastics make packaging lightweight and cost-effective.
Chemicals
Many essential chemicals originate from petroleum refining processes. Examples encompass:
- Fertilizers: Such as ammonium sulfate for agriculture.
- Solvents: Like benzene used in cleaning products.
- Synthetic fibers: Including nylon for clothing production.
Environmental Impact of Petroleum Products
Petroleum products significantly affect the environment, contributing to pollution and waste. Understanding these impacts helps in recognizing the need for sustainable practices.
Pollution and Waste
Petroleum products generate various forms of pollution. For instance, air pollution arises from burning fossil fuels like gasoline and diesel, releasing harmful emissions into the atmosphere. Additionally, water contamination occurs when oil spills happen or when wastewater from refining processes is improperly managed. This can harm aquatic life and disrupt ecosystems. Lastly, solid waste results from plastic products that often end up in landfills or oceans, taking hundreds of years to decompose.
- Air pollutants include:
- Carbon monoxide
- Nitrogen oxides
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
- Water contaminants consist of:
- Heavy metals
- Hydrocarbons
- Toxic chemicals
Sustainable Alternatives
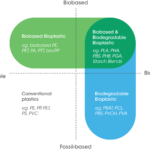
Finding sustainable alternatives to petroleum products is crucial for minimizing environmental damage. For example, biofuels, derived from organic materials like plant oils or animal fats, offer renewable energy sources that reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional fuels. Moreover, using bioplastics, made from natural substances such as cornstarch or sugarcane, can help decrease dependence on traditional plastics.
You might also consider other options like:
- Electric vehicles (EVs): These produce zero tailpipe emissions and promote cleaner air.
- Recycling programs: They reduce plastic waste by reprocessing materials into new products.
Exploring these alternatives not only aids in reducing pollution but also fosters a more sustainable future for everyone.
Economic Aspects of Petroleum Products
Petroleum products significantly influence the global economy. Their demand shapes markets, impacts production costs, and drives innovation in various sectors.
Market Demand
Market demand for petroleum products remains high due to their essential roles. Gasoline, for instance, powers vehicles, while jet fuel supports air travel. In 2025, global gasoline consumption reached approximately 1.2 billion metric tons. Additionally, plastics derived from petroleum find uses in packaging and consumer goods. With the growth of urbanization and industrial activities, you can expect continual demand for these versatile products.
Production Costs
Production costs of petroleum products directly affect pricing and availability. Crude oil prices, influenced by geopolitical events and supply chain dynamics, play a crucial role here. For example:
- A 10% increase in crude oil prices may raise gasoline prices by about 3% at the pump.
- Refining processes incur operational expenses that impact overall product pricing.
Understanding these costs helps consumers anticipate price fluctuations and make informed choices regarding energy use and purchasing decisions.