In today’s fast-paced market, understanding how product design and process selection are examples of crucial business strategies can set you apart from the competition. Every successful product starts with a thoughtful design that meets customer needs while considering manufacturing processes. But what makes these elements so vital for your business?
Overview Of Product Design And Process Selection
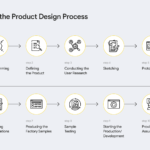
Product design and process selection play crucial roles in creating successful products. Effective product design focuses on user needs and preferences, ensuring the final product meets market demands. For instance, a smartphone’s ergonomic design enhances user comfort while offering essential features.
Process selection complements this by identifying the most suitable manufacturing methods. A company may choose between injection molding or 3D printing based on production volume and material requirements. This decision impacts cost efficiency and product quality directly.
Moreover, various industries showcase these principles effectively:
- Consumer Electronics: Companies like Apple emphasize sleek designs that appeal to tech-savvy users while optimizing assembly processes for efficiency.
- Automotive Industry: Brands such as Tesla focus on innovative designs alongside automated production techniques to enhance sustainability.
- Furniture Manufacturing: Firms often select materials and processes that prioritize both aesthetics and durability, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Understanding the interplay between product design and process selection is vital for achieving business goals. By prioritizing both elements, you can create products that not only meet consumer expectations but also thrive in competitive markets.
Importance Of Product Design
Product design plays a crucial role in the success of any business. It shapes how customers perceive and interact with products, directly influencing customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. Effective product design emphasizes functionality, aesthetics, and usability, ensuring the final offering resonates with target users.
Factors Influencing Product Design
Several key factors shape product design decisions:
- User Needs: Understanding what customers want is vital. Conducting surveys or focus groups helps gather insights.
- Market Trends: Staying updated on industry trends ensures your products remain relevant.
- Cost Constraints: Balancing quality with production costs impacts material selection and manufacturing methods.
- Technology Advances: New technologies can open opportunities for innovative designs that improve efficiency or user experience.
These elements collectively guide designers toward creating successful products.
Design Methodologies
Different methodologies exist to streamline the product design process:
- User-Centered Design (UCD): Focuses on user feedback throughout the development cycle. This approach leads to more intuitive products.
- Agile Design: Encourages iterative testing and refinement, allowing teams to adapt quickly based on feedback.
- Design Thinking: Promotes empathy for users while tackling complex problems creatively. It often includes brainstorming sessions followed by prototyping.
By applying these methodologies effectively, you enhance collaboration among team members and increase the chances of market success.
Understanding Process Selection
Process selection plays a pivotal role in manufacturing and product development. It determines which methods best fit the design and production requirements of a product. Effective process selection optimizes resources while maintaining quality.
Types Of Process Selection
Several types of process selections exist, each suited for different manufacturing needs:
- Job Shop: Ideal for custom products, allowing flexibility.
- Batch Production: Suitable for moderate demand, balancing efficiency with variety.
- Mass Production: Designed for high volumes of standardized products, maximizing efficiency.
- Continuous Flow: Used in industries like chemicals or oil refining, ensuring constant output.
Each type addresses specific operational goals and customer demands.
Impact Of Process Selection On Production
Process selection significantly impacts overall production efficiency. When selecting an appropriate method, consider factors such as cost, time constraints, and resource availability.
Effective choices lead to:
- Reduced waste through optimized workflows.
- Improved quality control by aligning processes with design specifications.
- Enhanced flexibility to adapt to market changes or customer preferences.
Thus, choosing the right process not only saves costs but also enhances product reliability and satisfaction levels among customers.
Connecting Product Design And Process Selection
Product design and process selection work hand in hand to create successful products. Understanding their connection enhances efficiency and meets market demands effectively.
Synergies Between Design And Process
Effective product design directly influences the choice of manufacturing processes. For instance, a sleek electronic device may require precision machining methods, while a bulkier item might benefit from mass production techniques. You can’t overlook how design decisions inform material selection, which can affect costs significantly. Additionally, by integrating user feedback early in the design phase, you ensure that product functionality aligns with the selected process capabilities.
Case Studies Illustrating Successful Integration
Several companies exemplify the successful integration of product design and process selection:
- Apple: Known for its innovative designs, Apple uses advanced CNC machining for aluminum cases. This choice reflects its commitment to aesthetics and durability.
- Tesla: Tesla’s electric vehicles showcase an efficient assembly line process that complements their cutting-edge designs. The streamlined production enables rapid scaling without sacrificing quality.
- IKEA: IKEA’s flat-pack furniture leverages modular design principles and batch production methods. This approach minimizes shipping costs and maximizes storage efficiency.
These examples highlight how aligning product design with suitable manufacturing processes leads to enhanced customer satisfaction and operational excellence.