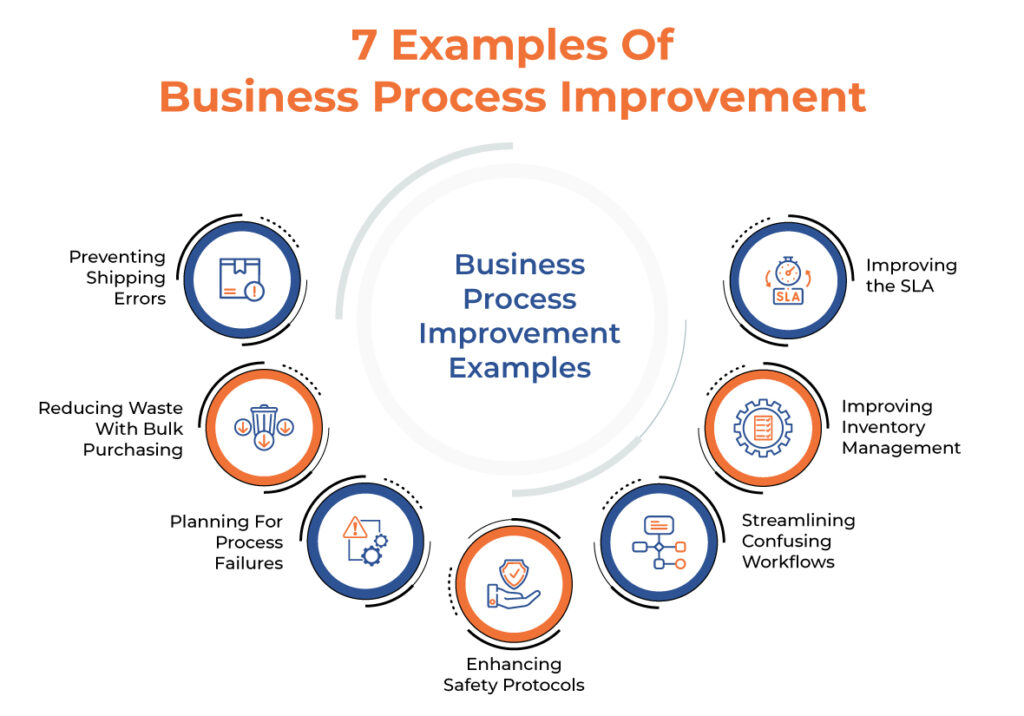
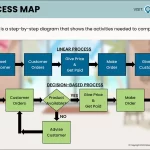
In today’s fast-paced business world, staying ahead means constantly evolving. Process improvement initiatives are essential tools that can transform your organization’s efficiency and effectiveness. By identifying areas for enhancement, you’re not just solving problems; you’re paving the way for innovation and growth.
Curious about how these initiatives can make a real difference? This article dives into practical examples of successful process improvement strategies across various industries. From streamlining workflows to enhancing customer satisfaction, you’ll discover actionable insights that can elevate your operations.
Understanding Process Improvement Initiatives
Process improvement initiatives focus on enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of organizational workflows. These initiatives play a critical role in driving innovation and growth, helping companies adapt to changing market demands.
Definition and Importance
Process improvement initiatives refer to efforts aimed at identifying inefficiencies and enhancing processes within an organization. They help streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. For example:
- Lean Manufacturing: This approach minimizes waste while maximizing productivity by optimizing production processes.
- Six Sigma: A data-driven methodology that reduces defects in products or services through rigorous quality management practices.
These examples illustrate how process improvement initiatives create significant value for organizations.
Historical Background
The concept of process improvement has evolved over decades, influenced by various methodologies. In the early 20th century, pioneers like Frederick Taylor introduced scientific management principles. Later, in the mid-1900s, quality control concepts emerged from Japan’s manufacturing sector.
The introduction of Total Quality Management (TQM) in the 1980s further emphasized continuous improvement across all areas of business. Today, organizations utilize diverse strategies tailored to their specific goals and challenges.
Types of Process Improvement Initiatives
Process improvement initiatives come in various forms, each designed to enhance efficiency and effectiveness within organizations. Understanding these types helps identify the best fit for your needs.
Lean Methodology
Lean methodology focuses on maximizing value by minimizing waste. This approach aims to optimize processes, ensuring that every step adds value for the customer. For example, a manufacturing company may streamline production by eliminating unnecessary steps in its assembly line. Key principles of Lean include:
- Value Stream Mapping: Identifying all steps in a process and highlighting areas where waste occurs.
- Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): Encouraging small, incremental changes regularly.
- Just-In-Time Production: Reducing inventory costs by producing only what is needed.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma emphasizes data-driven decision-making to reduce defects and improve quality. It uses statistical methods to analyze processes and identify areas needing improvement. A service organization might implement Six Sigma by monitoring customer feedback metrics to refine its offerings. Important components of Six Sigma include:
- DMAIC Framework: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control—this structured approach guides problem-solving.
- Control Charts: Tools for tracking process performance over time.
- Root Cause Analysis: Techniques such as fishbone diagrams help discover underlying issues affecting quality.
Agile Framework
The Agile framework promotes flexibility and responsiveness through iterative development cycles. Teams work in short sprints to adapt quickly based on feedback or changing requirements. For instance, software development teams often use Agile practices to release updates more frequently while responding to user needs effectively. Core elements of Agile include:
- Scrum Meetings: Daily check-ins that foster collaboration among team members.
- User Stories: Short descriptions capturing users’ needs guide development priorities.
- Retrospectives: Regular reflections on team performance encourage continuous learning.
Understanding these types of process improvement initiatives allows you to select the right strategy tailored for your organization’s goals and challenges.
Implementing Process Improvement Initiatives
Implementing process improvement initiatives involves systematic steps that lead to significant organizational enhancements. These initiatives drive efficiency and boost overall performance.
Steps for Successful Implementation
- Identify Objectives: Clearly define what you want to achieve with the initiative, such as reducing costs or improving quality.
- Assemble a Team: Gather a diverse group of stakeholders who can provide different perspectives and expertise.
- Analyze Current Processes: Evaluate existing workflows to pinpoint inefficiencies and areas needing improvement.
- Develop an Action Plan: Create a detailed strategy outlining the steps necessary for implementation, including timelines and resources required.
- Execute Changes: Put your plan into action while ensuring all team members understand their roles and responsibilities.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly track the results of implemented changes against established benchmarks.
- Adjust as Necessary: Be prepared to refine processes based on feedback and performance data.
Common Challenges
You’re likely to face several challenges during implementation:
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist new processes due to fear of the unknown or comfort with current methods.
- Insufficient Training: Without proper training, staff might struggle with adapting to new systems or tools.
- Lack of Resources: Limited budgets or personnel can hinder efforts toward successful implementation.
- Inadequate Communication: Poor communication can lead to misunderstandings about goals, resulting in fragmented efforts.
Navigating these challenges requires proactive strategies that foster engagement and clarity throughout the organization.
Measuring Success in Process Improvement Initiatives
Measuring success in process improvement initiatives involves identifying specific metrics that demonstrate effectiveness. By evaluating these metrics, you can clearly gauge the impact of your efforts.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) serve as measurable values to assess your progress. Examples include:
- Cycle Time: The time taken to complete a process from start to finish.
- Defect Rate: The percentage of products or services that fail to meet quality standards.
- Customer Satisfaction Score: A metric indicating how happy customers are with your product or service.
- Cost Savings: Total financial savings achieved through improved efficiency.
These KPIs provide tangible evidence of enhancements and areas needing further attention.
Continuous Improvement Culture
Fostering a continuous improvement culture enhances long-term success in process initiatives. Encourage employees to identify inefficiencies and suggest improvements regularly. This active participation helps create ownership over processes.
You might implement practices like:
- Regular Training Sessions: Equip teams with skills needed for ongoing improvements.
- Feedback Loops: Establish mechanisms for gathering input on process changes.
- Recognition Programs: Reward innovative ideas and successful implementations.
Such elements cultivate an environment where everyone is invested in optimizing operations, ultimately driving sustained growth and adaptation within the organization.