Imagine stepping into a world where your identity is stripped away and you’re molded into something new. Prisons and military boot camps are examples of what Erving Goffman calls total institutions. These environments share a common goal: to control the behavior and thoughts of individuals within their confines. But what does that really mean for those who experience them?
In this article, you’ll explore how these institutions operate under strict rules and regulations, transforming lives in profound ways. You’ll discover the psychological impact they have on individuals, as well as the similarities and differences between these two seemingly disparate settings. Are they effective tools for rehabilitation or merely systems of oppression? Dive deeper to uncover the complexities behind Goffman’s theories and understand their relevance in today’s society.
Prisons and Military Boot Camps: An Overview
Prisons and military boot camps serve as prime examples of what Erving Goffman calls total institutions. These environments share common characteristics that shape the lives of individuals within them.
In prisons, inmates experience a loss of autonomy. Their daily routines are strictly regulated, from wake-up times to meal schedules. This control aims to enforce discipline but often leads to feelings of isolation and despair.
Military boot camps also impose strict rules on recruits. They undergo rigorous training designed to build teamwork and obedience. While this prepares individuals for military life, it can also strip away personal identity.
Both settings utilize similar techniques for behavior modification:
- Surveillance: Constant monitoring ensures compliance.
- Uniformity: Standardized clothing diminishes individuality.
- Harsh Discipline: Punishments reinforce authority.
These methods raise questions about their effectiveness in fostering positive change versus perpetuating systems of oppression. How do they impact mental health? Understanding these dynamics is crucial for evaluating the role such institutions play in society today.
Erving Goffman’s Concepts
Erving Goffman’s theories about total institutions provide valuable insights into how environments like prisons and military boot camps function. These institutions significantly reshape individuals’ lives, often leading to profound psychological impacts.
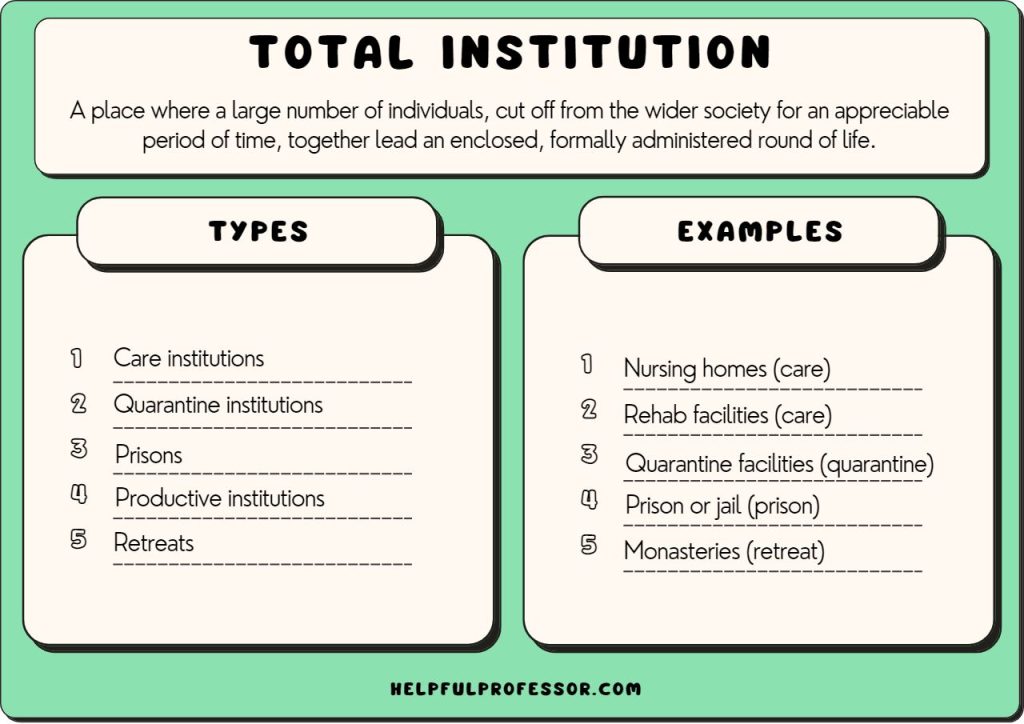
Total Institutions Defined
Total institutions are places where individuals are cut off from broader society. In these settings, daily life is tightly regulated, impacting personal freedom. Prisons confine inmates within walls, while military boot camps enforce a strict regimen for recruits. Both contexts share the aim of controlling behavior and thoughts through structured environments.
Characteristics of Total Institutions
Total institutions exhibit several key characteristics:
- Isolation: Individuals experience separation from the outside world.
- Controlled Environment: Daily routines are dictated by institutional rules.
- Uniformity: Standardized clothing creates a sense of sameness among participants.
- Surveillance: Constant monitoring ensures compliance with rules.
- Disciplinary Measures: Harsh penalties reinforce obedience and conformity.
These elements work together to create an atmosphere that can strip away personal identity, fostering dependence on the institution itself. Understanding these characteristics highlights the significant changes individuals undergo in such settings.
The Function of Prisons
Prisons serve critical roles in society, particularly regarding social control and rehabilitation. These institutions profoundly influence inmates’ lives through their structured environments.
Social Control and Rehabilitation
Prisons primarily function as tools for social control. They regulate behavior by enforcing laws and maintaining order. Inmates face strict routines, limiting personal freedom. Furthermore, the rehabilitation aspect aims to reform individuals. Programs like educational courses or vocational training help prepare inmates for reintegration into society. Yet, the effectiveness varies widely based on resources available and individual engagement.
Perspectives on Incarceration
Perspectives on incarceration differ significantly among stakeholders. Some view prisons as necessary for public safety, arguing that they deter crime. Others critique them as ineffective systems that perpetuate a cycle of recidivism. Statistics indicate that nearly 70% of released prisoners are rearrested within five years. This raises questions about whether prisons truly rehabilitate or merely punish individuals without addressing underlying issues like poverty or addiction.
The Purpose of Military Boot Camps
Military boot camps aim to instill discipline and prepare recruits for service. These environments emphasize conformity, teamwork, and physical endurance. Recruits undergo rigorous training that transforms their identities and fosters a sense of belonging within the military culture.
Disciplinary Practices
Disciplinary practices in military boot camps create an atmosphere of strict adherence to rules. Recruits face consequences for infractions, which reinforces obedience. Common methods include:
- Physical training: Challenging exercises build stamina and resilience.
- Regulated routines: Daily schedules dictate every aspect of life, from wake-up calls to lights out.
- Uniform standards: Wearing identical attire promotes unity and diminishes individuality.
These measures ensure that recruits internalize the values essential for military effectiveness.
Transformation and Readiness
Transformation occurs as recruits adapt to the demands of military life. This process prepares them not just physically but also mentally for future challenges. Key aspects include:
- Identity reshaping: Recruits often shed previous personal identities in favor of a collective one.
- Skill development: Training includes learning specific skills crucial for various military roles.
- Mental resilience: Exposure to high-pressure situations cultivates coping strategies essential during deployments.
Such transformations are intended to foster readiness for the complexities faced in combat or other missions.
Comparative Analysis
Prisons and military boot camps exemplify Erving Goffman’s concept of total institutions, showcasing both similarities and differences in their structures and impacts on individuals.
Similarities Between Prisons and Boot Camps
Both prisons and military boot camps function as total institutions, isolating individuals from broader society. In each setting, routines dominate daily life. For instance:
- Strict schedules dictate wake-up times, meals, and activities.
- Uniforms create a sense of uniformity among participants.
- Surveillance is constant to enforce rules, ensuring compliance at all times.
These elements contribute to a loss of personal autonomy. Participants often experience significant psychological effects like anxiety or depression due to the rigid environments.
Differences in Goals and Outcomes
While both settings control behavior, their objectives diverge significantly. Prisons focus primarily on punishment and deterrence. They aim to manage criminal behavior but often fall short in rehabilitation efforts. Statistics indicate that nearly 70% of released prisoners are rearrested within five years.
Conversely, military boot camps target transformation through discipline and teamwork. Their goal is to prepare recruits for service by instilling values such as loyalty and resilience. This environment promotes camaraderie among recruits but may also lead to mental stress during intense training periods.
Ultimately, the effectiveness of these institutions remains hotly debated. Are they helping individuals reintegrate into society or merely reinforcing negative patterns? Each scenario presents unique challenges affecting individual identity formation.