Ever wondered how businesses decide what to charge for their products or services? The pricing model plays a crucial role in shaping a company’s success. It’s not just about numbers; it’s about understanding your market, your customers, and the value you provide.
In this article, you’ll explore various pricing models that can elevate your business strategy. From cost-plus pricing to dynamic pricing and subscription-based models, each approach offers unique advantages and challenges. You’ll learn how different industries apply these strategies effectively and discover which model might be best suited for your own venture.
Overview of Pricing Models
Pricing models play a crucial role in defining how businesses charge for their products or services. Understanding different pricing strategies helps you determine the most effective approach for your offerings.
Definition of Pricing Models
Pricing models refer to the frameworks that businesses use to establish the price of their goods or services. These models take into account various factors like costs, competition, and customer demand. Examples include:
- Cost-plus pricing: Setting prices based on production costs plus a fixed margin.
- Dynamic pricing: Adjusting prices in real-time based on market conditions.
- Subscription-based pricing: Charging customers a recurring fee for access to products or services.
Importance of Pricing Models
Effective pricing models can significantly impact your business’s profitability and market position. They help you align your pricing strategy with customer expectations and competitive dynamics. Key benefits include:
- Maximized revenue: Properly defined pricing can enhance sales performance.
- Customer satisfaction: Fair pricing fosters trust and loyalty among customers.
- Market adaptability: Flexible strategies allow quick responses to changing market conditions.
By choosing the right model, you equip your business with tools for sustained growth and competitiveness.
Types of Pricing Models
Pricing models vary significantly, and each serves a different strategic purpose. Understanding these types helps you determine the best approach for your business.
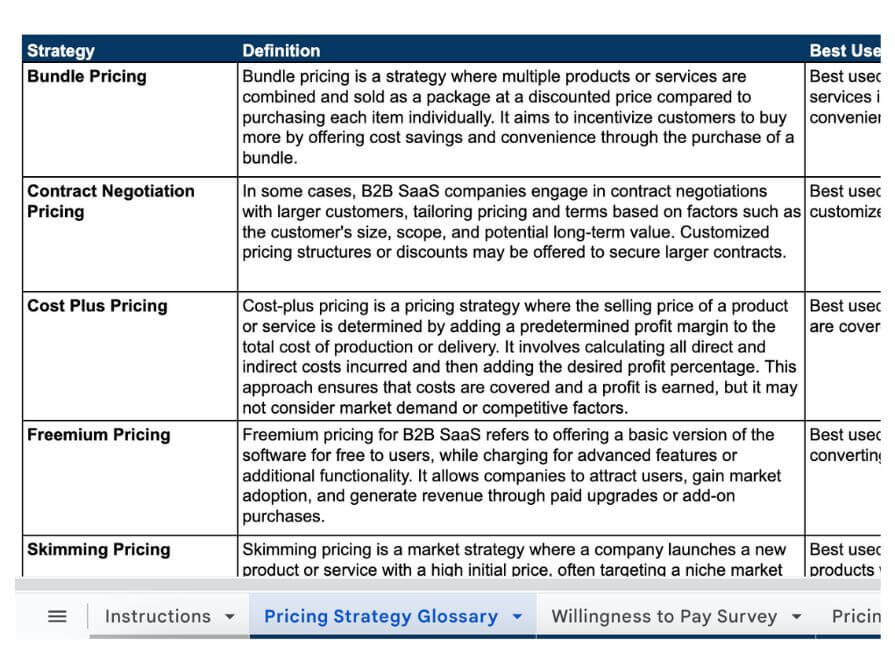
Cost-Plus Pricing
Cost-plus pricing involves calculating total costs and adding a markup percentage for profit. For instance, if your product costs $50 to produce and you add a 20% markup, the selling price becomes $60. This method is straightforward but may not account for market demand or competition effectively.
Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing sets prices based on perceived value rather than cost. For example, if your software saves businesses significant time and money, you can charge based on that savings rather than production costs. This model attracts customers willing to pay more for high-value solutions while maximizing profit margins.
Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing adjusts prices in real-time according to demand fluctuations. Consider airlines: ticket prices change based on factors like booking time and seat availability. This model maximizes revenue during peak times while attracting price-sensitive customers during off-peak periods.
Subscription Pricing
Subscription pricing offers products or services at regular intervals, often monthly or annually. Companies like Netflix use this model successfully by providing continuous access to content for a recurring fee. It creates predictable revenue streams and builds customer loyalty through ongoing engagement with offerings.
Factors Influencing Pricing Models
Several critical factors influence the development of pricing models. Understanding these elements helps you tailor your strategy effectively.
Market Demand
Market demand plays a central role in shaping pricing models. When demand is high, businesses often set higher prices to maximize revenue. Conversely, if demand falls, prices usually decrease to attract customers. For instance, during holiday seasons, retailers frequently increase prices due to heightened customer interest. Recognizing trends in demand allows you to adjust your pricing model proactively.
Competition
Competition impacts pricing strategies significantly. If several competitors offer similar products or services at lower prices, you’ll need to consider how to position yours effectively without sacrificing profit margins. For example, airlines often use competitive pricing for ticket sales during peak travel times—keeping their rates attractive while ensuring profitability. Monitoring competitor actions helps you stay relevant and responsive in the market.
Customer Behavior
Customer behavior shapes how businesses approach their pricing models as well. Preferences and spending habits vary widely among consumer segments; thus, understanding your target audience is essential. For example:
- Price Sensitivity: Some customers prioritize low-cost options over premium features.
- Brand Loyalty: Others might pay more for brands they trust despite alternatives.
- Purchase Frequency: Regular buyers may prefer subscription-based models that offer discounts.
By analyzing these behaviors, you can create a more effective pricing strategy tailored to your audience’s needs.
Implementing a Pricing Model
Implementing a pricing model involves several key steps and considerations. The right approach can enhance profitability and align your offerings with market expectations.
Steps for Implementation
- Conduct Market Research: Understand customer preferences, competitors, and market trends. This research provides insights into what customers value and are willing to pay.
- Define Target Audience: Identify your ideal customers based on demographics, buying behavior, and needs. Tailoring your pricing strategy to this group maximizes relevance.
- Choose the Right Model: Select a pricing model that aligns with your business goals. For example:
- Cost-plus pricing adds a markup to production costs.
- Value-based pricing focuses on perceived worth.
- Dynamic pricing adjusts prices according to demand fluctuations.
- Test Pricing Strategies: Experiment with different price points or models through A/B testing or pilot programs. Gather data on customer responses to refine your approach.
- Monitor Performance: Continuously track sales metrics, customer feedback, and market conditions after implementation. Use these insights to make necessary adjustments over time.
Common Challenges
Implementing a pricing model isn’t without challenges:
- Market Volatility: Rapid changes in demand can disrupt established prices.
- Competition Pressure: Competitors may undercut prices or introduce new strategies that require immediate responses from you.
- Customer Resistance: Customers might resist price increases if they don’t perceive added value or benefits.
- Data Overload: Too much data can complicate decision-making rather than simplify it; focus on relevant metrics instead.
Addressing these challenges proactively ensures smoother implementation of your chosen pricing model while maintaining competitiveness in the marketplace.