Imagine walking through your home and realizing that every item you see is part of your personal property. From the cozy couch to the artwork on the walls, personal property encompasses all assets you own, both tangible and intangible. But have you ever thought about how these items are categorized or valued?
Understanding Personal Property
Personal property encompasses all assets owned by you, including both tangible and intangible items. It’s essential to recognize how these possessions fit into your life and finances.
Definition of Personal Property
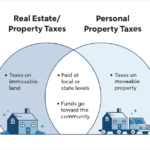
Personal property refers to all movable items that you own. This includes both physical objects, like vehicles or clothing, and non-physical assets, such as stocks or copyrights. Unlike real property, which involves land or buildings, personal property is portable and can be transferred between individuals easily.
Types of Personal Property
You can categorize personal property into various types:
- Tangible Personal Property: Items you can touch or see, such as furniture, electronics, jewelry.
- Intangible Personal Property: Non-physical assets like patents, trademarks, stocks.
- Consumable Goods: Products meant for consumption over time—food items or cleaning supplies fall into this category.
- Collectibles: Items collected for their value or interest—think coins or stamps.
Recognizing the different types helps in managing your assets effectively.
Importance of Personal Property
Personal property plays a significant role in individual wealth and identity. Understanding its importance helps you manage your assets effectively.
Economic Value
Personal property contributes to personal wealth, providing financial security and stability. For instance, tangible assets like vehicles or electronics can be sold or traded for cash if needed. Intangible assets such as stocks increase in value over time, offering potential returns on investment. Additionally:
- Collectibles: Items like rare coins or vintage toys often appreciate significantly.
- Real estate investments: While technically real property, any improvements made through personal property enhance overall asset value.
Legal Implications
The legal aspects of personal property impact ownership rights and responsibilities. You need to know that laws vary by jurisdiction, affecting how properties are bought, sold, or inherited. For example:
- Title transfers: Proper documentation ensures the transfer of ownership is legally recognized.
- Liability issues: Personal liability extends to injuries caused by your belongings.
Understanding these implications protects you from disputes and enhances asset management strategies.
Personal Property Rights
Personal property rights refer to the legal entitlements you possess regarding your owned assets. These rights grant you control over tangible and intangible items, allowing for their use, transfer, or disposal. Understanding these rights is crucial for effective asset management.
Ownership Rights
You hold ownership rights when you legally own personal property. These rights include:
- Possession: You can physically control the item.
- Use: You decide how to utilize the property.
- Transfer: You may sell or gift your assets.
- Exclusion: You can prevent others from using your property without consent.
Recognizing these ownership rights ensures proper management of your assets and helps avoid potential disputes.
Transfer of Personal Property
Transferring personal property involves changing ownership from one party to another. Common methods include:
- Sale: Selling an item for monetary compensation.
- Gift: Giving an item without expecting anything in return.
- Inheritance: Passing on possessions through a will upon death.
Proper documentation during transfers is essential to establish clear ownership and minimize legal issues.
Protecting Personal Property
Protecting personal property involves strategic measures to safeguard your assets. Understanding the various options available ensures effective management and security of your belongings.
Insurance Options
Insurance provides a crucial safety net for personal property. Consider these common types:
- Homeowners Insurance: Covers damage or loss of personal items within your home, such as furniture and electronics.
- Renters Insurance: Offers similar protection for renters, covering personal belongings against theft or damage.
- Auto Insurance: Protects vehicles from accidents and theft while offering liability coverage in case of incidents involving other parties.
- Specialty Insurance: Tailored policies for high-value items like jewelry, art, or collectibles provide additional protection beyond standard policies.
Choosing the right insurance can significantly reduce financial losses related to unforeseen events.
Legal Protections
Legal protections play a vital role in securing ownership rights over personal property. Key aspects include:
- Title Registration: Ensures legal proof of ownership for vehicles and real estate.
- Contracts: Written agreements during sales or transfers protect both parties by outlining terms clearly.
- Wills and Trusts: Establish how personal property will be distributed after death, preventing disputes among heirs.
- Liens: Legal claims on an asset ensure debts are paid before an item is transferred.
Understanding these legal avenues helps maintain control over your assets and mitigates potential conflicts.