Have you ever bought a product because of its catchy jingle or an influencer’s recommendation? That’s the magic of peripheral route persuasion at work. This psychological concept explains how people can be influenced by superficial cues rather than logical arguments, making it a powerful tool in marketing and communication.
Understanding Peripheral Route Persuasion
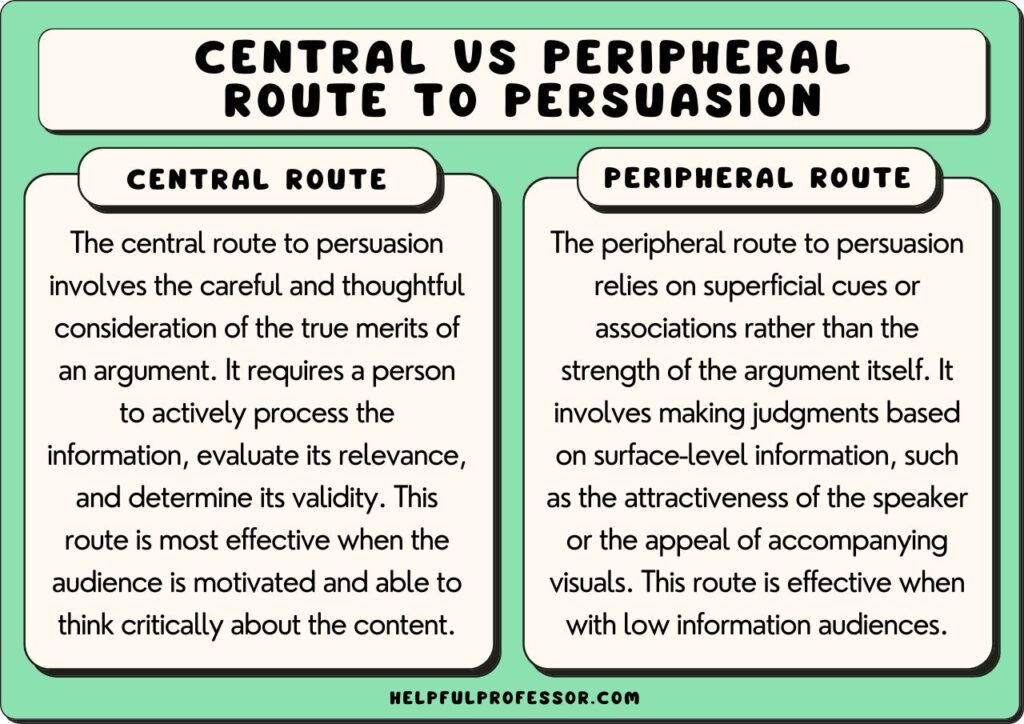
Peripheral route persuasion relies on superficial cues rather than deep processing of information. It often occurs in situations where you may lack motivation or ability to scrutinize arguments. Here are some clear examples:
- Celebrity Endorsements: When a popular athlete promotes a sports drink, you might choose it not for its benefits but because you admire the athlete.
- Catchy Jingles: You remember a product more easily due to its memorable tune, influencing your purchasing decision without considering its quality.
- Visual Appeal: A product’s attractive packaging can grab your attention and sway your choice, even if you know little about what’s inside.
- Social Proof: Seeing many people using a particular brand can lead you to believe it must be good, simply based on popularity.
These elements trigger emotions and quick judgments, steering decisions without engaging in critical thinking. This approach is prevalent in advertising and social media marketing.
Key Elements of Peripheral Route Persuasion
Peripheral route persuasion relies on specific elements that influence decision-making without deep cognitive engagement. Understanding these key components helps clarify how superficial cues can affect choices.
Influence of Cues
Cues play an essential role in peripheral route persuasion. These cues can include:
- Celebrity endorsements: When a well-known figure promotes a product, their popularity often sways consumer decisions.
- Catchy jingles: Memorable tunes stick in your mind, making products more recognizable and appealing.
- Visually appealing packaging: Attractive designs draw attention and can create positive associations with the product.
You might find these cues effective even if you haven’t researched the product thoroughly. Their impact often leads to quick judgments based on immediate impressions rather than informed analysis.
Role of Emotion
Emotion significantly influences peripheral route persuasion. Here’s how emotional appeals work:
- Positive feelings: Advertisements that evoke happiness or nostalgia tend to foster favorable attitudes toward brands.
- Fear appeals: Messages highlighting potential negative outcomes might prompt you to act quickly for reassurance.
- Social proof: Seeing others endorse a brand creates a sense of belonging and validation, encouraging similar choices.
Emotional triggers bypass critical thinking, allowing you to connect with brands on a deeper level. This connection shapes decisions based on feelings rather than logic, reinforcing the effectiveness of peripheral route persuasion in marketing strategies.
Examples of Peripheral Route Persuasion
Peripheral route persuasion appears prominently in various contexts, especially advertising and social media. Let’s explore some examples to illustrate this concept.
Advertisements
In advertisements, you often see elements designed to grab attention rather than engage in deep reasoning. For instance:
- Celebrity endorsements: When a popular actor promotes a drink, their fame can sway your choice more than the product’s features.
- Catchy jingles: You might remember a brand because its jingle sticks in your mind, even if you can’t recall specific benefits.
- Visually appealing packaging: Bright colors or unique designs can attract you to products on shelves without considering quality.
These strategies rely on quick impressions rather than thorough analysis.
Social Media Influencers
Social media influencers play a significant role in shaping opinions through peripheral route persuasion. Think about how they operate:
- Lifestyle showcasing: Influencers often display products seamlessly integrated into their lives. This creates an aspirational image that influences your preferences.
- Engagement with followers: Their relatable content fosters trust, leading you to consider products endorsed by them without much scrutiny.
- Hashtag promotions: Simple hashtags can generate buzz around brands, making popularity itself a persuasive factor.
You might find yourself swayed by these tactics without realizing it.
Effectiveness of Peripheral Route Persuasion
Peripheral route persuasion proves effective in various contexts. It often relies on superficial cues to shape opinions, especially when individuals lack motivation or ability to process information deeply. Here are some key examples illustrating its effectiveness:
- Celebrity endorsements: When a well-known figure promotes a product, their popularity can sway consumer choices significantly. People often trust recommendations from celebrities they admire.
- Catchy jingles: Memorable tunes make products stick in people’s minds. A catchy jingle can lead to brand recall during shopping, influencing purchasing decisions without much thought.
- Visually appealing packaging: Attractive design captures attention immediately. Consumers may choose one product over another solely based on its packaging, bypassing detailed evaluation.
- Social proof: Seeing others use and recommend a brand creates a sense of trust. Positive reviews and high follower counts on social media can persuade you to try something new simply because others do.
Each example highlights how quick judgments replace thorough analysis, allowing brands to connect emotionally with consumers. This emotional engagement fosters loyalty and enhances brand perception effectively without relying heavily on logical arguments or extensive research.