Imagine a world where the price of a product changes, but consumers remain unfazed, purchasing the same quantity no matter what. This scenario illustrates perfectly elastic demand, a concept that reveals how sensitive buyers can be to price fluctuations. In this article, you’ll explore real-life examples that showcase perfectly elastic demand and its implications for businesses and consumers alike.
Understanding Perfectly Elastic Demand
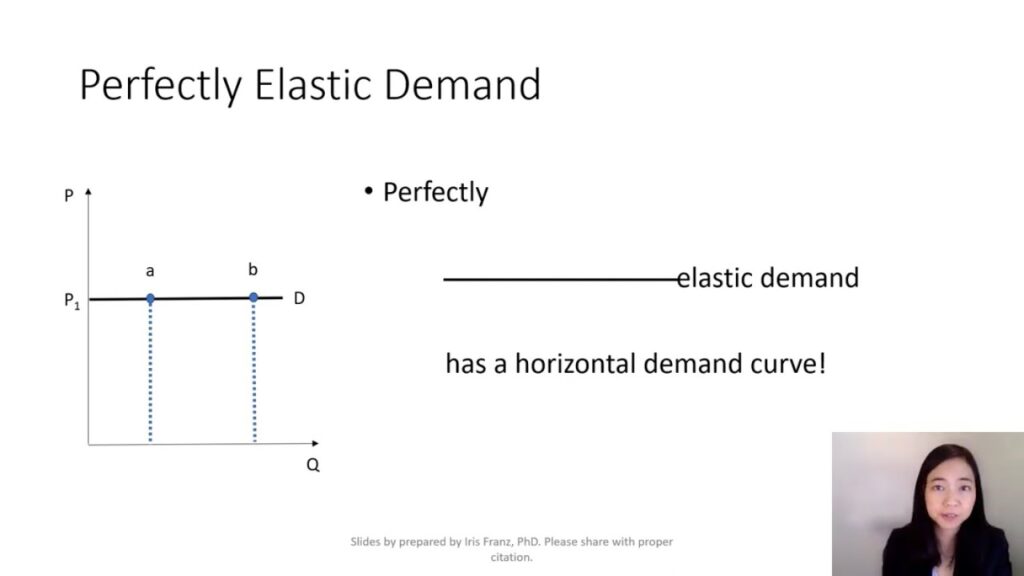
Perfectly elastic demand describes a situation where consumers buy a constant quantity of a product, regardless of price changes. This phenomenon occurs in markets with numerous substitutes and high sensitivity to price.
Definition and Characteristics
Perfectly elastic demand means that even the slightest price increase leads to zero sales; conversely, any decrease results in a significant surge in quantity demanded. Key characteristics include:
- Infinite elasticity: Price changes do not affect the total revenue.
- Horizontal demand curve: The graph appears as a straight line on the horizontal axis.
- Availability of substitutes: Many alternatives exist for consumers, making them very responsive to price fluctuations.
Examples in Real-Life Scenarios
You can find perfectly elastic demand primarily in highly competitive markets. For instance:
- Agricultural products: Farmers selling identical crops often face perfectly elastic demand since buyers can easily switch to competitors if prices rise.
- Currency exchange: In forex markets, small shifts in currency values lead traders to quickly react by buying or selling currencies at prevailing rates.
- Commodities like oil or gold: When suppliers offer similar quality products at different prices, customers will choose the cheaper option instantly.
These examples illustrate how perfectly elastic demand significantly impacts consumer behavior and market dynamics.
Factors Affecting Perfectly Elastic Demand
Perfectly elastic demand hinges on several critical factors that shape consumer behavior. Understanding these elements helps clarify why certain markets exhibit this unique form of demand.
Price Sensitivity
Consumers display a high degree of price sensitivity in perfectly elastic demand scenarios. When prices shift, even slightly, purchasing decisions can change drastically. For instance, if a brand increases the price of its bottled water by just $0.01, customers might opt for a cheaper alternative instead. This behavior underscores how crucial pricing strategies are in highly competitive environments.
- Small price changes lead to significant shifts in quantity demanded.
- Competitors’ pricing directly influences consumer choices.
- Consumer awareness about alternatives heightens sensitivity.
Availability of Substitutes
The availability of substitutes plays a vital role in shaping perfectly elastic demand. In markets where numerous alternatives exist, consumers can easily switch from one product to another based solely on price differences. Take the example of fast food restaurants; if one location raises its prices while others remain stable, customers will flock to competitors offering similar meals at lower costs.
- High substitute availability encourages constant comparison among products.
- Identical goods amplify consumer options and flexibility.
- Market dynamics shift rapidly with new entrants providing additional choices.
Understanding these factors provides insight into how businesses must navigate pricing and competition within their respective markets.
Implications of Perfectly Elastic Demand
Perfectly elastic demand impacts both market dynamics and business strategies significantly. Understanding these implications helps you navigate competitive environments effectively.
Market Competition
In markets with perfectly elastic demand, competition intensifies. Firms must compete on price to attract consumers. If one seller increases prices even slightly, buyers will immediately shift to alternatives. This behavior promotes aggressive pricing tactics among businesses aiming to secure their market share.
Consider the agricultural sector—when corn prices rise, farmers can easily switch to growing soybeans or wheat instead. This flexibility creates a highly competitive landscape where firms continuously monitor pricing trends.
Pricing Strategies for Businesses
Businesses operating in a perfectly elastic demand environment must adopt strategic pricing methods. Implementing dynamic pricing can help maintain competitiveness. This approach involves adjusting prices based on real-time market conditions and competitor actions.
Additionally, offering discounts or promotional deals can attract price-sensitive consumers who might otherwise opt for substitutes. For example:
- Frequent sales events: Regular promotions keep customers engaged.
- Loyalty programs: Rewarding repeat purchases encourages brand loyalty despite lower price offerings from competitors.
By focusing on these strategies, you can enhance your position in a market characterized by perfectly elastic demand while meeting consumer expectations effectively.