In today’s digital landscape, securing your online accounts is more crucial than ever. Have you ever wondered why password complexity, password history, and password reuse are all examples of security practices? These elements play a vital role in protecting your personal information from cyber threats.
Understanding Password Management
Password management involves several critical practices aimed at enhancing security. These include password complexity, password history, and password reuse.
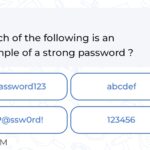
Password complexity refers to the requirement for passwords to contain a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. For example, a password like “P@ssw0rd123!” is more secure than “password.” Creating complex passwords helps protect accounts from being easily compromised.
Password history ensures that users cannot reuse previous passwords within a specified number of changes. Organizations often enforce rules such as not allowing the last five passwords to be reused. This approach decreases the likelihood of unauthorized access due to old credentials still being valid.
Password reuse occurs when individuals use the same password across multiple accounts. This practice can be risky; if one account gets breached, all other accounts using that same password are vulnerable too. To mitigate this risk, varying your passwords for different sites is essential.
By applying these strategies consistently, you improve your online security posture significantly.
The Importance of Password Complexity
Password complexity plays a crucial role in securing your online accounts. Strong passwords act as the first line of defense against cyber threats. By creating complex passwords, you significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to your sensitive information.
Definition and Benefits
Password complexity refers to the requirement for passwords to include various character types, enhancing their strength. A strong password typically contains a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, making it harder for attackers to guess or crack.
The benefits are clear:
- Increased security: Complex passwords thwart brute force attacks.
- Protection against credential stuffing: Unique combinations prevent attackers from easily accessing multiple accounts.
- Enhanced trust: Using strong passwords fosters user confidence in your security measures.
Common Complexity Rules
Implementing common rules can improve password strength significantly. Consider these guidelines when setting up or updating your passwords:
Following these complexity rules helps create robust defenses against potential breaches.
The Role of Password History
Password history plays a crucial role in maintaining security for online accounts. It helps prevent users from reusing previous passwords, making it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Why Password History Matters
Password history prevents easy exploitation by ensuring you can’t reuse your last several passwords. When you change your password, systems often require you to select one that hasn’t appeared in the recent past. This measure mitigates risks associated with stolen credentials. For instance, if an attacker acquires a password from another breach, they’ll find it difficult to use if you’ve implemented strict password history rules.
Best Practices for Implementation
Implementing effective password history policies involves several best practices:
By following these strategies, you enhance account protection while promoting better security habits among users.
Risks of Password Reuse
Password reuse poses significant risks to your online security. When you use the same password across multiple accounts, a breach in one can compromise all associated accounts. It’s crucial to understand these dangers and take proactive measures.
Consequences of Reusing Passwords
Reusing passwords leads to various negative outcomes:
- Account Takeover: An attacker gaining access to one account can use that same password on other platforms.
- Data Breaches: If a site suffers a data breach, stolen credentials may allow hackers to infiltrate additional services.
- Identity Theft: Personal information might get exposed, leading to unauthorized transactions or fraudulent activities.
By recognizing these consequences, you can appreciate the importance of unique passwords for different accounts.
Strategies to Prevent Reuse
Implementing effective strategies helps prevent password reuse:
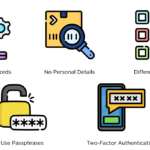
- Use a Password Manager: These tools store and generate unique passwords for each account securely.
- Create Complex Passwords: Ensure each password contains uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): This adds an extra layer of security by requiring another verification method beyond just the password.
By adopting these practices, you significantly reduce the risks associated with password reuse and enhance your overall online security.