In the world of business, understanding overhead costs can be a game changer. Have you ever wondered why some companies thrive while others struggle? It often boils down to how well they manage these hidden expenses that don’t directly tie to production but impact profitability significantly.
Understanding Overhead Costs
Overhead costs represent essential expenses that aren’t directly tied to production. Understanding these costs helps you manage your budget effectively and improve profitability.
Definition and Importance
Overhead costs are ongoing expenses related to operating a business. These include utilities, rent, salaries of non-production staff, and more. Recognizing their significance can transform your financial management approach. When you control overhead costs efficiently, it enhances your overall profit margins.
Types of Overhead Costs
Several types of overhead costs exist, each impacting your bottom line differently:
- Fixed Costs:These remain constant regardless of production levels. Examples include lease payments for office space or insurance premiums.
- Variable Costs:These fluctuate based on activity levels. For instance, utility bills may rise with increased usage during peak seasons.
- Semi-variable Costs:This type combines fixed and variable elements. A common example is a phone bill that has a base charge plus additional fees based on usage.
Understanding the various categories helps in identifying areas for potential savings. By evaluating these overhead costs regularly, you position yourself better for financial success.
Factors Influencing Overhead Costs
Overhead costs can vary significantly based on several factors. Understanding these influences helps manage expenses effectively.
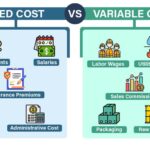
Fixed vs. Variable Overhead Costs
Fixed overhead costs remain constant regardless of production levels. Examples include rent, salaries for management staff, and insurance premiums. These expenses don’t change with the volume of goods produced.
Variable overhead costs fluctuate based on production activities. For instance, utility bills may rise during peak production periods due to increased machine use. Other examples are raw materials and direct labor associated with manufacturing.
Industry-Specific Considerations
Different industries encounter unique overhead cost structures.
- Manufacturing: Often faces higher fixed costs due to machinery maintenance and factory space.
- Retail: Typically experiences variable overhead through inventory storage and staffing needs that change seasonally.
- Technology: May incur significant investment in software licenses or data storage solutions as part of their operational overhead.
Recognizing these specific factors allows you to tailor your approach to managing overhead costs efficiently.
Methods for Managing Overhead Costs
Managing overhead costs effectively can enhance your business’s profitability. Several methods exist to streamline these expenses while maintaining operational efficiency.
Budgeting and Forecasting
Budgeting allows you to plan your financial resources strategically. By establishing a clear budget, you can allocate funds appropriately across various departments. Regularly reviewing this budget helps identify areas where expenses exceed expectations. Incorporating forecasting techniques enables you to predict future costs based on historical data, allowing for more informed decision-making. For example, if past utility bills indicate seasonal spikes, adjusting the budget accordingly prepares you for fluctuations.
Cost-Reduction Strategies
Implementing cost-reduction strategies directly impacts overhead costs. Evaluate fixed contracts like rent or service agreements; negotiating better terms may yield savings. Consider adopting technology solutions that automate routine tasks, reducing labor costs associated with administrative functions. Additionally, exploring remote work options can decrease office-related expenses significantly. Look at vendor relationships as well; consolidating purchases from fewer suppliers often leads to bulk discounts and lower per-unit costs.
Impact of Overhead Costs on Business
Overhead costs significantly influence a business’s financial landscape. Understanding their impact can enhance decision-making and improve profitability.
Profit Margins and Pricing Strategies
Overhead costs directly affect your profit margins. For instance, if overhead expenses increase without a corresponding rise in sales, profits decrease. You might consider adjusting pricing strategies to maintain margins. Examples include:
- Cost-plus pricing: Setting prices based on production costs plus a markup.
- Value-based pricing: Adjusting prices according to perceived value rather than just costs.
- Dynamic pricing: Modifying prices based on market demand or seasonal factors.
By implementing these strategies, you can manage the effects of overhead costs more effectively.
Decision-Making and Financial Health
Overhead costs play a crucial role in decision-making processes within your business. They provide insights into operational efficiency and resource allocation. Evaluating these expenses influences key decisions such as:
- Budgeting for projects
- Hiring additional staff
- Expanding product lines
You should regularly analyze your overhead to ensure financial health. Knowing where money goes helps identify areas for improvement, ultimately leading to better overall performance.