Imagine a world where the oceans are barren and forests stand silent. Overharvesting examples highlight the urgent consequences of unchecked resource extraction. From overfishing to deforestation, these practices threaten ecosystems and biodiversity globally.
In this article, you’ll explore real-world instances of overharvesting that have led to devastating impacts on wildlife and habitats. Have you ever wondered how the demand for certain products can lead to the extinction of species? By examining various case studies, you’ll gain insight into how human actions disrupt natural balances and what we can do to mitigate these effects. Join us as we uncover the stories behind overharvesting and its far-reaching implications for our planet’s future.
Overview of Overharvesting
Overharvesting occurs when resources are extracted at unsustainable rates, leading to severe ecological consequences. Some key examples include:
- Overfishing: Species like the Atlantic cod have faced drastic population declines due to excessive fishing. In fact, some estimates suggest that stocks fell by over 90% since the late 20th century.
- Deforestation for Timber: Forests in Brazil and Indonesia have experienced significant loss as timber companies harvest trees faster than they can regenerate. This practice not only destroys habitats but also contributes to climate change.
- Illegal Wildlife Trade: Elephants and rhinos face threats from poaching driven by demand for ivory and horn. Recent data shows that rhino populations decreased by approximately 90% in the last century.
- Harvesting of Medicinal Plants: Certain plants like ginseng are being collected faster than they can grow back, threatening their survival in the wild.
These instances illustrate how human actions directly impact biodiversity and ecosystem health. Understanding these examples helps highlight the urgent need for sustainable practices.
Impact on Ecosystems
Overharvesting significantly disrupts ecosystems, leading to biodiversity loss and habitat destruction. This section outlines key examples that illustrate the impact of unsustainable resource extraction practices.
Forest Overharvesting Examples
Deforestation in the Amazon rainforest contributes to climate change and species extinction. The logging industry often targets valuable hardwood trees, resulting in massive forest loss. For instance, between 2000 and 2018, Brazil lost approximately 1.3 million square kilometers of forest cover due to illegal logging and agricultural expansion.
In Indonesia, palm oil production drives significant deforestation. This practice not only destroys habitats for endangered species like orangutans but also releases vast amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Between 1990 and 2015, Indonesia lost about 6 million hectares of forest land primarily for palm oil plantations.
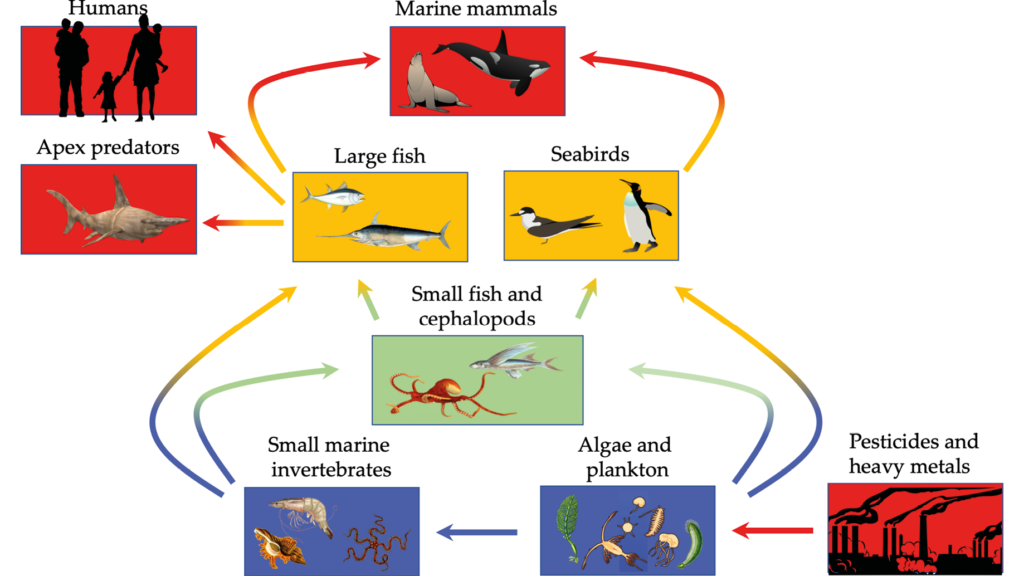
Marine Species Overharvesting Examples
Overfishing has led to drastic declines in fish populations worldwide. An example is the Atlantic cod, whose population plummeted by over 90% since the mid-20th century due to excessive fishing pressures. Such reductions disrupt marine food webs and threaten predator species.
The illegal trade of shark fins threatens global shark populations. Estimates suggest that as many as 100 million sharks are killed annually for their fins alone. This practice endangers various shark species, which are vital for maintaining healthy ocean ecosystems.
By understanding these examples of overharvesting’s impact on ecosystems, you can better appreciate the urgency behind adopting sustainable practices.
Economic Consequences
Overharvesting leads to significant economic repercussions across various sectors. As resources diminish, industries reliant on those resources face severe challenges.
Case Studies in Agriculture
Overharvesting has drastically affected agriculture in several regions. For instance, intensive farming methods have depleted soil nutrients in parts of the United States. This depletion results in lower crop yields and increased dependence on chemical fertilizers, which can further harm the environment.
Another example is the over-extraction of water for irrigation in regions like California. This practice threatens both agricultural productivity and local ecosystems. When water sources dry up, farmers struggle to maintain their crops, leading to increased food prices and potential shortages.
Effects on Fishing Industries
The fishing industry suffers immensely due to overfishing practices. The collapse of fish stocks, such as Atlantic cod off the coast of New England, illustrates this point well. Once abundant, these fish populations dwindled dramatically due to unsustainable fishing techniques.
Moreover, coastal communities relying on fisheries face economic decline as jobs disappear and local economies weaken. With fewer fish available, competition among fishermen increases. This competition drives down profit margins while pushing some smaller operators out of business entirely.
Overharvesting not only impacts biodiversity but also disrupts economic stability within agriculture and fishing industries.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts play a crucial role in addressing the impacts of overharvesting. Various initiatives aim to restore ecosystems, protect species, and promote sustainable practices.
Successful Restoration Projects
Many successful restoration projects demonstrate the potential for recovery from overharvesting. For example:
- The Atlantic cod fishery has seen gradual improvements due to strict fishing quotas.
- The reforestation initiative in Brazil aims to restore millions of trees lost to deforestation.
- California’s kelp forests are recovering through marine protected areas that limit harvesting activities.
These examples illustrate that with proper management, ecosystems can rebound from significant damage.
Legislative Measures
Legislation plays an essential role in curbing overharvesting. Key measures include:
- The Endangered Species Act (ESA) protects threatened and endangered wildlife by prohibiting harmful practices.
- Fisheries Management Plans (FMPs) help regulate fishing quotas and protect fish stocks from depletion.
- Sustainable Forestry Laws ensure timber harvesting meets specific environmental standards.
These laws create frameworks for responsible resource management, helping prevent further degradation of ecosystems affected by overharvesting.