Living with chronic conditions can be overwhelming, especially when they impact your daily life. Osteoarthritis and diabetes are examples of two prevalent health issues that not only affect millions but also share common risk factors. Have you ever wondered how these conditions intertwine, influencing each other in ways that complicate treatment?
Osteoarthritis and Diabetes Are Examples Of Chronic Conditions
Osteoarthritis and diabetes represent significant chronic conditions that impact daily life. Both conditions affect millions of individuals worldwide. Understanding their characteristics helps in managing symptoms effectively.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis primarily affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling. This condition results from wear and tear on cartilage over time. Common symptoms include:
- Joint pain during movement
- Swelling around affected joints
- Stiffness after resting
- Reduced range of motion
Diabetes
Diabetes involves issues with insulin production or use in the body. This leads to elevated blood sugar levels that can cause serious health complications. Symptoms often include:
- Increased thirst and hunger
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
Interconnectedness of Osteoarthritis and Diabetes
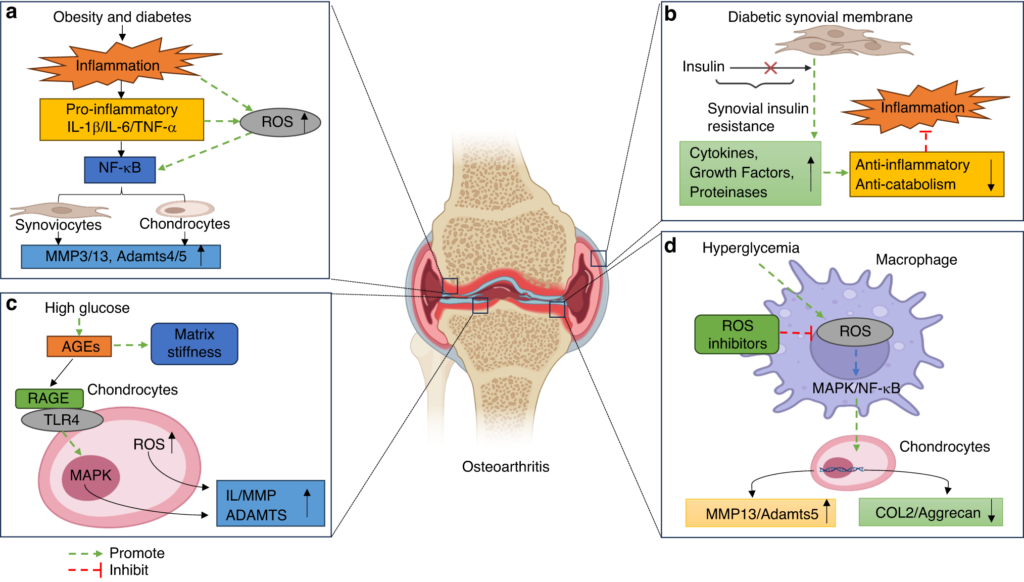
Osteoarthritis and diabetes can influence each other. For instance, obesity often contributes to both conditions. Losing weight may alleviate stress on joints while improving blood sugar levels. Furthermore, inflammation plays a role in both diseases, making management strategies crucial.
Understanding these chronic conditions is vital for effective treatment plans. You’ll find that addressing lifestyle factors like diet and exercise significantly impacts your overall health while managing osteoarthritis and diabetes.
Impact on Quality of Life
Osteoarthritis and diabetes significantly impact daily life. These chronic conditions lead to various challenges that affect physical health, emotional well-being, and social interactions.
Pain Management Strategies
Managing pain effectively is crucial for improving your quality of life. You might consider several approaches:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help reduce inflammation and alleviate discomfort.
- Therapies: Physical therapy focuses on strengthening muscles around affected joints, enhancing mobility.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections provide temporary relief from severe joint pain.
- Alternative therapies: Acupuncture or massage may offer additional benefits by reducing stress and promoting relaxation.
These strategies work best when tailored to individual needs.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making specific lifestyle changes can enhance overall health while managing both osteoarthritis and diabetes. Here are some effective modifications:
- Healthy diet: Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your meals.
- Regular exercise: Engage in low-impact activities like swimming or walking to maintain joint flexibility and manage blood sugar levels.
- Weight management: Achieving a healthy weight reduces stress on joints while improving insulin sensitivity.
- Stress reduction techniques: Practice mindfulness or yoga to lower stress levels, which can negatively influence both conditions.
By adopting these modifications, you can improve your quality of life while effectively managing osteoarthritis and diabetes.
Relationship Between Osteoarthritis and Diabetes
Osteoarthritis and diabetes often coexist, impacting each other significantly. Understanding their relationship helps manage both conditions effectively.
Inflammation and Joint Health
Inflammation plays a critical role in both osteoarthritis and diabetes. Elevated levels of inflammatory markers can worsen joint damage in osteoarthritis. This inflammation also contributes to insulin resistance, complicating diabetes management. Research indicates that managing inflammation can improve joint health while stabilizing blood sugar levels.
Common Risk Factors
Several risk factors connect osteoarthritis and diabetes:
- Obesity: Excess weight increases stress on joints and disrupts insulin sensitivity.
- Age: Aging raises the likelihood of developing both conditions.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity leads to muscle weakness, further straining joints while promoting weight gain.
- Genetics: Family history influences susceptibility to both health issues.
Recognizing these commonalities empowers you to adopt preventive measures for better overall health.
Treatment Approaches
Managing osteoarthritis and diabetes requires a multi-faceted approach. Effective treatment strategies focus on reducing symptoms, improving mobility, and controlling blood sugar levels.
Medication Options
Several medications target both conditions effectively. For osteoarthritis, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen reduce pain and inflammation. In contrast, oral hypoglycemics, such as metformin, help manage blood sugar levels in diabetes. Additionally, some individuals benefit from corticosteroid injections for joint pain relief or antidepressants that can alleviate chronic pain while also addressing mental health.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Engaging in physical therapy enhances mobility and strength while alleviating discomfort in osteoarthritis sufferers. A tailored exercise program improves flexibility and reduces stiffness. Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling are particularly effective for both osteoarthritis management and diabetes control. Regular physical activity not only promotes weight loss but also increases insulin sensitivity—making it a vital component of your treatment plan.
By combining medication with lifestyle changes such as diet modification and regular exercise, you can significantly improve your quality of life while managing these chronic conditions effectively.