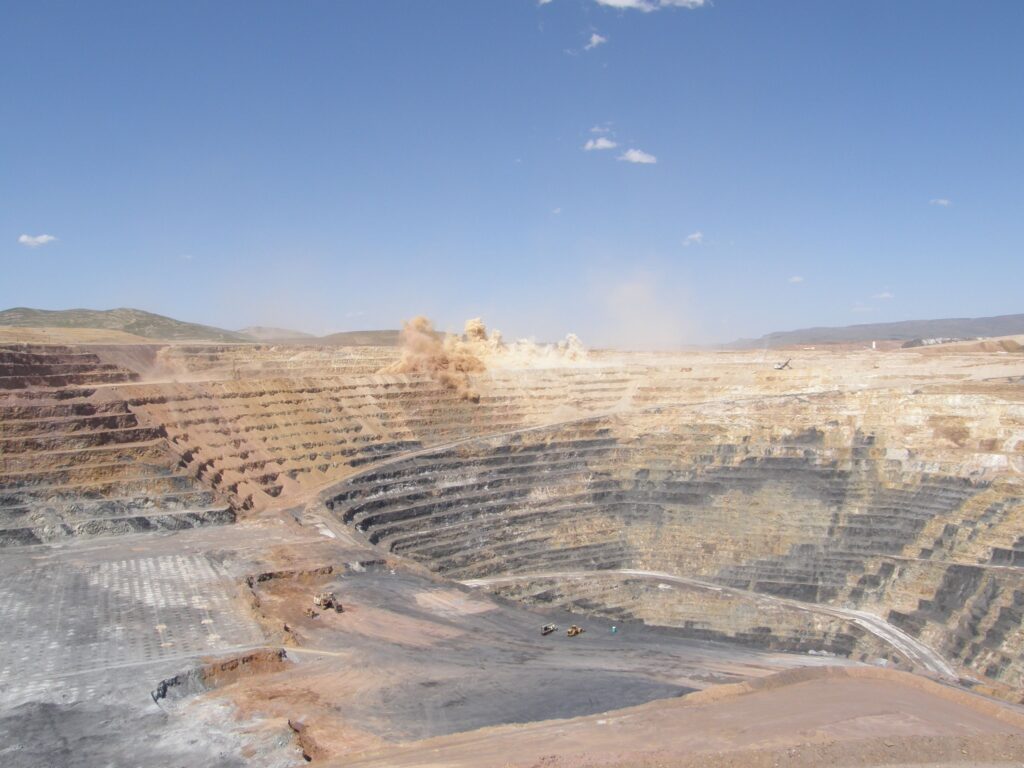
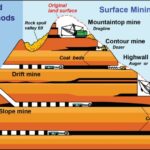
Imagine standing at the edge of a massive excavation, where the earth has been stripped away to reveal valuable minerals beneath. Open pit mining is one of the most efficient methods for extracting resources like gold, copper, and diamonds from the ground. This technique involves digging a large hole in the ground, allowing miners to access deposits that are too deep for traditional mining methods.
Overview of Open Pit Mining
Open pit mining is a prevalent method for extracting minerals from the earth. This technique allows access to valuable resources like gold, copper, and diamonds by creating large excavations.
Definition and Process
Open pit mining involves removing overburden to expose mineral deposits. The process begins with site preparation, including surveying and designing the pit layout. Then, machinery removes soil and rock layers, forming a stepped structure known as benches. These benches facilitate safe movement of equipment and personnel while optimizing resource extraction.
Historical Context
Open pit mining’s origins date back to the 19th century during the industrial revolution. It became popular due to its efficiency compared to underground methods. For example:
- Bingham Canyon Mine in Utah started operations in 1906 and remains one of the largest open-pit mines.
- Mirny Mine in Siberia opened in 1957, showcasing massive scale operations for diamond extraction.
These examples illustrate how open pit mining has evolved into a critical component of modern resource acquisition strategies.
Advantages of Open Pit Mining
Open pit mining offers several significant advantages that contribute to its widespread use in resource extraction. Its efficiency and accessibility make it a preferred method for many operations.
Cost-Effective Extraction
Open pit mining generally requires lower operational costs compared to underground mining. The large-scale removal of overburden allows for the easy access of minerals, which reduces labor costs and equipment expenses. Additionally, the ability to transport materials using trucks or conveyors directly from the pit enhances logistical efficiency. For instance:
- Bingham Canyon Mine: This mine in Utah is one of the largest open pits globally, showcasing how economies of scale can significantly lower production costs.
- Mirny Mine: Located in Siberia, this diamond mine highlights cost effectiveness through its massive operation that minimizes per-unit extraction costs.
Safety Considerations
Safety remains a top priority in open pit mining operations. With fewer personnel working underground, risks associated with cave-ins and ventilation issues decrease. Moreover, modern technology enhances safety measures during extraction processes. Key considerations include:
- Stability Monitoring: Continuous monitoring systems assess slope stability to prevent collapses.
- Emergency Protocols: Established emergency plans ensure quick responses to incidents.
These factors contribute to an overall safer working environment while maximizing productivity.
Environmental Impact of Open Pit Mining
Open pit mining significantly affects the environment. This section outlines two major impacts: land degradation and water resource depletion.
Land Degradation
Open pit mining leads to extensive Land Degradation. The removal of soil and rock layers disrupts ecosystems. For instance, at the Bingham Canyon Mine in Utah, over 1,900 acres of land have been altered due to mining activities. Such alterations result in habitat loss for wildlife and contribute to increased erosion rates. Moreover, tailings and waste materials can contaminate surrounding areas, affecting both flora and fauna.
Water Resources
Water resources face considerable strain from open pit mining operations. Water consumption is substantial during mineral extraction processes. For example, the Mirny Mine in Siberia uses millions of gallons daily for dust suppression and equipment cooling. Additionally, contaminated water runoff poses risks to local aquifers and rivers. Pollutants from mine sites can seep into groundwater or flow into nearby bodies of water, impacting aquatic life and human health.
By understanding these environmental impacts, you grasp the broader implications of open pit mining on ecosystems and communities.
Modern Techniques and Technologies
Modern open pit mining utilizes advanced techniques and technologies to enhance efficiency and safety. These innovations streamline operations while addressing environmental concerns associated with the process.
Equipment Used in Open Pit Mining
Open pit mining employs various specialized equipment designed for large-scale mineral extraction. Key examples include:
- Excavators: These machines remove overburden and dig deep into the earth to access valuable minerals.
- Haul Trucks: Designed for transporting mined materials, these trucks can carry loads exceeding 400 tons.
- Drills: Used for blasting operations, drills create holes that facilitate controlled explosions to break rock.
- Bulldozers: They assist in site preparation by clearing land and pushing material around the site efficiently.
Each piece of equipment plays a crucial role in optimizing resource extraction while maintaining operational safety.
Innovations in Safety and Efficiency
Innovations significantly enhance safety measures and overall efficiency in open pit mining. Some notable advancements include:
- Automated Systems: Remote-controlled machinery reduces personnel exposure to hazardous conditions.
- Real-Time Monitoring Tools: Technologies like slope stability sensors provide continuous data, improving decision-making processes on-site.
- Drones: Drones perform aerial surveys, allowing for precise mapping of excavation sites without putting workers at risk.
These innovations not only improve productivity but also promote a safer working environment. Have you ever wondered how technology continues to transform industries? In open pit mining, it’s clear that embracing new tools is essential for progress.
Case Studies
Open pit mining has transformed the landscape of mineral extraction, with notable examples showcasing its effectiveness. These case studies illustrate the successes and challenges faced in this industry.
Successful Open Pit Mining Operations
Bingham Canyon Mine in Utah is one of the largest open pit mines globally. It has produced over 19 million tons of copper since its inception in 1906. The mine employs advanced technology for efficient resource extraction, contributing to significant economic benefits for the region.
Mirny Mine in Siberia stands out as one of the deepest open pit diamond mines. Its depth exceeds 1,700 feet, demonstrating innovative techniques to manage challenging geological conditions. This operation showcases how effective planning can lead to substantial yields while addressing safety concerns.
Lessons Learned from Failures
Not every open pit mining project succeeds. For instance, the Ok Tedi Mine in Papua New Guinea faced severe environmental repercussions due to inadequate waste management practices. Contaminated river systems resulted from tailings disposal, affecting local communities and ecosystems.
Another example is the Sierra Leone Diamond Mines, which experienced significant operational inefficiencies and legal issues related to land use rights. The situation highlighted how crucial stakeholder engagement is for sustainable mining operations.
These case studies underline both best practices and pitfalls within open pit mining, emphasizing a balanced approach that integrates technological advancements with environmental stewardship and community involvement.