Living with OCD can feel overwhelming, especially when the symptoms disrupt your daily life. Understanding OCD symptoms is crucial for recognizing its impact on you or someone you care about. From intrusive thoughts to compulsive behaviors, these signs often lead to significant distress and anxiety.
In this article, you’ll discover various examples of OCD symptoms that manifest in different ways. By identifying these symptoms early, you can take steps toward effective management and support. Whether it’s excessive handwashing or an obsession with orderliness, knowing what to look for can empower you to seek help. Are you ready to explore how these symptoms might affect your life? Let’s dive deeper into the world of OCD and uncover what it truly means.
Understanding OCD Symptoms
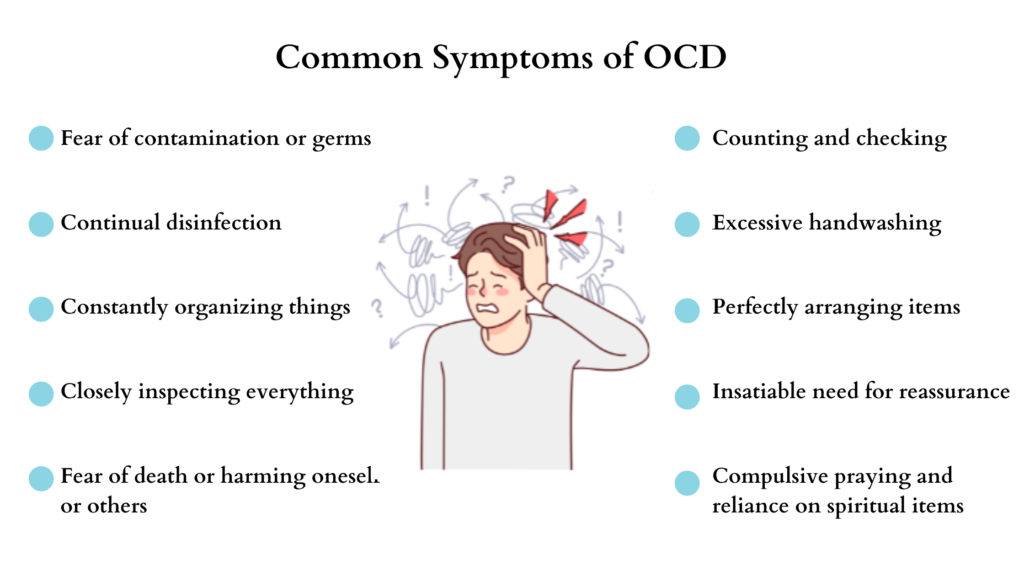
OCD symptoms can manifest in various ways, impacting daily life significantly. Here are some common examples you might encounter:
- Intrusive Thoughts: These are unwanted and distressing thoughts that pop into your mind repeatedly. They often involve fears of harming others or oneself, leading to significant anxiety.
- Compulsive Behaviors: You may feel compelled to perform certain actions to reduce anxiety caused by intrusive thoughts. For example, excessive handwashing or checking locks multiple times before leaving home.
- Ritualistic Actions: Engaging in specific routines is common. This could include counting objects or arranging items in a particular order, creating a false sense of control over anxiety.
- Avoidance: Some individuals avoid situations or places that trigger their obsessions. This behavior can limit activities and social interactions.
Recognizing these symptoms early on is vital for effective management and support. If you notice these patterns in yourself or someone else, reaching out for help can lead to better outcomes.
Common Types of OCD Symptoms
Understanding the common types of OCD symptoms can clarify how they manifest in daily life. These symptoms can vary significantly from person to person, but a few key categories often appear.
Compulsive Behaviors
Compulsive behaviors serve as responses to obsessive thoughts. These actions may provide temporary relief from anxiety but often interfere with everyday activities. Examples include:
- Excessive handwashing: Washing hands multiple times to avoid contamination.
- Checking locks or appliances: Repeatedly checking if doors are locked or appliances are turned off.
- Counting rituals: Counting objects or steps a specific number of times before feeling safe.
You might notice these compulsions taking up significant time and energy, disrupting your routine.
Obsessive Thoughts
Obsessive thoughts persistently intrude into your mind, causing distress and discomfort. They can create an overwhelming fear of harm or disaster. Common examples encompass:
- Fear of harming oneself or others: Constantly worrying about accidentally causing injury.
- Intrusive sexual thoughts: Unwanted thoughts regarding inappropriate situations.
- Contamination fears: Extreme concern over germs or dirt affecting health.
These obsessions can lead to intense anxiety and compel you to engage in compulsive behaviors for relief. Recognizing these patterns plays a crucial role in managing OCD effectively.
Impact of OCD Symptoms on Daily Life
OCD symptoms affect various aspects of your daily life. These symptoms can disrupt routines, hinder productivity, and strain relationships.
Compulsive behaviors often consume significant time. You might find yourself spending hours performing rituals like excessive handwashing or checking appliances multiple times. This not only delays daily tasks but also creates frustration.
Obsessive thoughts can lead to constant distraction. While you try to focus on work or social activities, intrusive thoughts about harming yourself or others may intrude. This mental struggle contributes to heightened anxiety and reduces your ability to concentrate.
Avoidance behaviors limit social interactions. If certain places trigger anxiety, you might avoid them altogether. Skipping social events due to fear of contamination or judgment isolates you from friends and family, leading to loneliness.
Emotional distress is a common consequence. Living with OCD causes feelings of shame and guilt over compulsions and obsessions. You may feel embarrassed discussing these struggles with others, which exacerbates isolation.
Overall, recognizing how OCD symptoms impact your daily life is crucial for seeking help and developing effective coping strategies. Addressing these challenges can improve your well-being significantly.
Treatment Options for OCD Symptoms
Effective treatment options exist for managing OCD symptoms, combining therapy and medication to enhance quality of life. Understanding these approaches can facilitate better outcomes.
Therapy Approaches
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) stands out as a primary treatment method for OCD. Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP) is a specific type of CBT that involves gradual exposure to feared situations while refraining from compulsive responses. This method helps reduce anxiety over time.
Another effective approach is Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), which encourages acceptance of thoughts without judgment. Rather than trying to eliminate intrusive thoughts, you learn to live with them in a healthier way.
Group therapy also offers support by connecting individuals facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences fosters understanding and reduces feelings of isolation.
Medication Options
Several medications effectively manage OCD symptoms. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly prescribed, including:
- Fluoxetine: Often known as Prozac.
- Sertraline: Frequently referred to as Zoloft.
- Escitalopram: Marketed under the name Lexapro.
These medications help increase serotonin levels in the brain, alleviating obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors.
In some cases, doctors may prescribe clomipramine, a tricyclic antidepressant with proven efficacy for OCD. Always consult with healthcare professionals before starting or adjusting any medication regimen.