Imagine navigating a world that often overlooks your struggles. Non-visible disabilities can be just as challenging as those that are immediately apparent, yet they frequently go unrecognized. Conditions like chronic pain, mental health disorders, and learning disabilities affect millions daily but remain hidden from view.
In this article, you’ll discover the various types of non-visible disabilities and their profound impact on individuals’ lives. You’ll learn how these conditions can influence everything from work performance to social interactions. Why is it crucial to raise awareness about these invisible challenges? Understanding them fosters empathy and creates a more inclusive society where everyone’s experiences are validated. Join us as we explore real-life examples that shed light on the complexities of living with non-visible disabilities and why they deserve our attention and understanding.
Understanding Non Visible Disabilities
Non-visible disabilities significantly impact individuals’ lives, yet they often remain misunderstood. By grasping their definitions and examples, you can foster greater empathy and awareness.
Definition and Examples
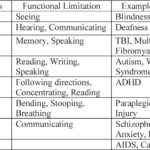
Non-visible disabilities refer to conditions that aren’t immediately apparent. These can include:
- Chronic Pain: Conditions like fibromyalgia lead to persistent pain without visible signs.
- Mental Health Disorders: Anxiety, depression, and bipolar disorder affect daily functioning but may not show physical symptoms.
- Learning Disabilities: Dyslexia or ADHD impact learning processes without any outward indications.
Understanding these examples highlights the complexities many individuals face daily.
Common Types of Non Visible Disabilities
Common non-visible disabilities encompass a wide range of conditions. Some prevalent types include:
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS): A debilitating condition causing extreme fatigue lasting six months or more.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): An autoimmune disease affecting the central nervous system with fluctuating symptoms.
- Sensory Processing Disorder (SPD): Difficulty in processing sensory information leads to overwhelming reactions to stimuli.
Recognizing these types fosters better support systems for those affected by them.
Challenges Faced by Individuals
Individuals with non-visible disabilities encounter numerous challenges that can significantly affect their daily lives. These challenges often go unrecognized, leading to a lack of understanding and support.
Social Stigma and Misunderstanding
Social stigma greatly impacts individuals with non-visible disabilities. Many people mistakenly believe these conditions are not real or serious. This misunderstanding leads to judgment and isolation. For example, someone with anxiety may face skepticism about their struggles, as others can’t see the internal battle they fight daily. Additionally, individuals with chronic pain might hear comments like “you don’t look sick,” reinforcing feelings of invalidation.
It’s crucial to address this stigma through education. By sharing accurate information about conditions such as fibromyalgia or ADHD, you foster empathy among peers and create a more inclusive environment.
Barriers to Access and Support
Barriers to access hinder those living with non-visible disabilities from receiving necessary support. In many cases, workplaces lack accommodations for mental health issues or learning disabilities. For instance:
- Job flexibility: Employees may struggle without remote work options.
- Awareness training: Employers often miss training sessions that highlight invisible conditions.
- Healthcare resources: Limited access to mental health services can exacerbate existing challenges.
Recognizing these barriers is essential for fostering supportive environments at work and in social settings. You can advocate for policy changes that prioritize inclusivity and accessibility for all individuals facing these obstacles.
Coping Strategies and Accommodations
Coping strategies and accommodations play a crucial role in managing non-visible disabilities. Individuals can adopt various approaches to enhance their quality of life, both emotionally and in the workplace.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Emotional support is vital for individuals with non-visible disabilities. You can benefit from several resources:
- Therapy: Professional counseling helps address mental health issues like anxiety or depression.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges fosters understanding and shared experiences.
- Mindfulness Practices: Techniques such as meditation or yoga can improve emotional resilience.
These strategies create a supportive environment where you feel understood and less isolated. Have you considered how these supports might help you navigate daily challenges?
Workplace Accommodations
Workplace accommodations significantly improve productivity for those with non-visible disabilities. Consider implementing these adjustments:
- Flexible Hours: Allowing varied start times can help manage energy levels throughout the day.
- Remote Work Options: Working from home often reduces stress associated with commuting.
- Quiet Spaces: Providing access to quiet areas can aid concentration for individuals who experience sensory overload.
These changes not only foster inclusivity but also enhance overall job satisfaction. What accommodations would make your work environment more manageable?
Raising Awareness and Advocacy
Raising awareness about non-visible disabilities is crucial for fostering understanding and support. Advocating for those with these conditions leads to a more inclusive society, where individuals feel valued and understood.
Importance of Educating Others
Educating others about non-visible disabilities dispels myths and reduces stigma. Many people may not recognize that conditions like anxiety or fibromyalgia affect daily life significantly. By sharing accurate information, you encourage empathy and support from friends, family, and coworkers. Consider organizing workshops or informational sessions to spread awareness within your community.
Organizations Supporting Non-Visible Disabilities
Numerous organizations focus on supporting individuals with non-visible disabilities through resources, advocacy, and education. Examples include:
These organizations play a vital role in creating supportive networks, offering guidance to both those affected by non-visible disabilities and their families. Engaging with such groups can amplify your advocacy efforts while connecting you to a broader community dedicated to raising awareness.